Feng Ren
Quantum Computing-Enhanced Algorithm Unveils Novel Inhibitors for KRAS
Feb 13, 2024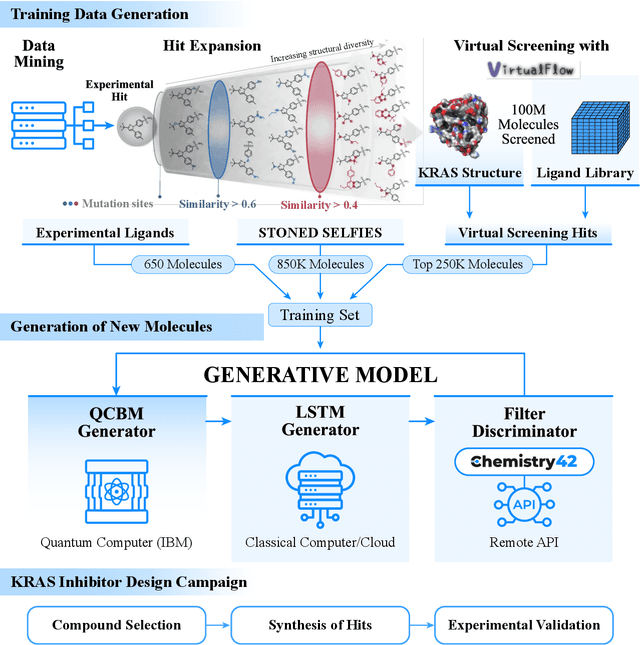
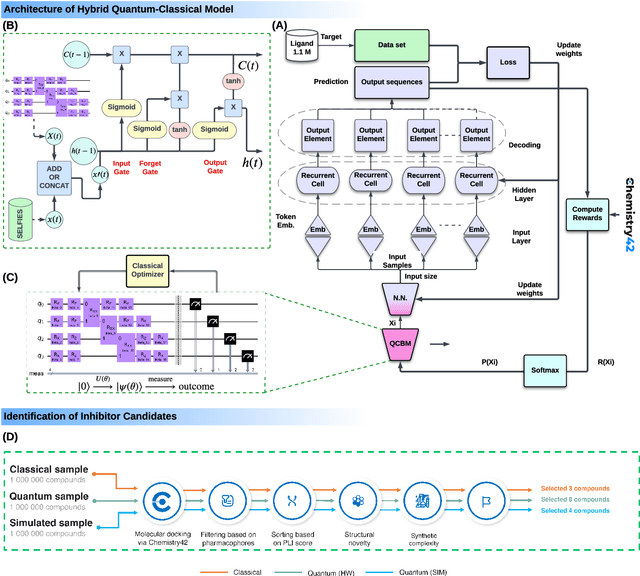
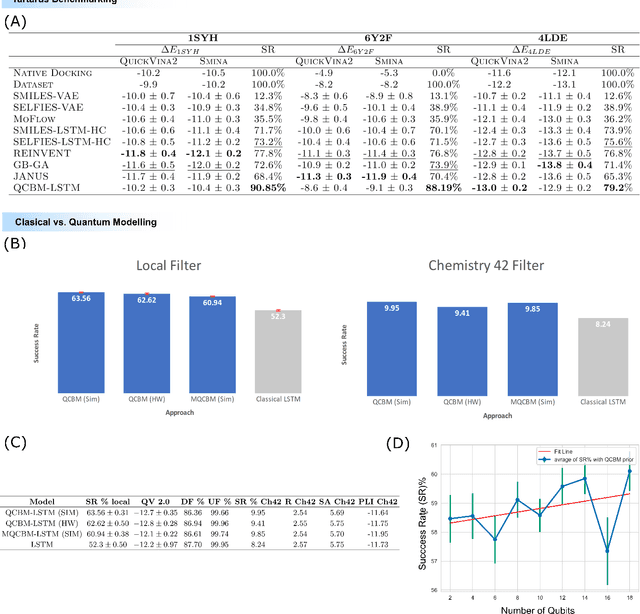
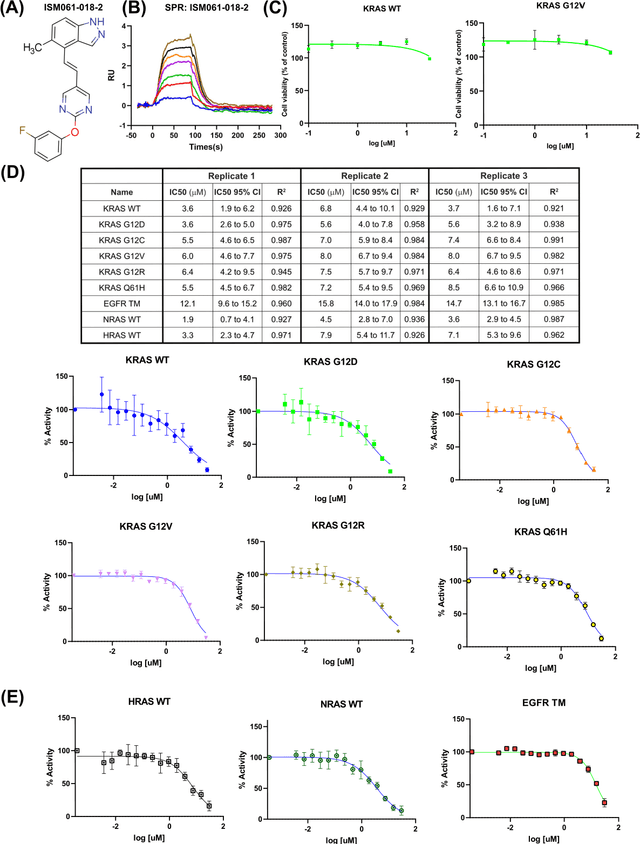
Abstract:The discovery of small molecules with therapeutic potential is a long-standing challenge in chemistry and biology. Researchers have increasingly leveraged novel computational techniques to streamline the drug development process to increase hit rates and reduce the costs associated with bringing a drug to market. To this end, we introduce a quantum-classical generative model that seamlessly integrates the computational power of quantum algorithms trained on a 16-qubit IBM quantum computer with the established reliability of classical methods for designing small molecules. Our hybrid generative model was applied to designing new KRAS inhibitors, a crucial target in cancer therapy. We synthesized 15 promising molecules during our investigation and subjected them to experimental testing to assess their ability to engage with the target. Notably, among these candidates, two molecules, ISM061-018-2 and ISM061-22, each featuring unique scaffolds, stood out by demonstrating effective engagement with KRAS. ISM061-018-2 was identified as a broad-spectrum KRAS inhibitor, exhibiting a binding affinity to KRAS-G12D at $1.4 \mu M$. Concurrently, ISM061-22 exhibited specific mutant selectivity, displaying heightened activity against KRAS G12R and Q61H mutants. To our knowledge, this work shows for the first time the use of a quantum-generative model to yield experimentally confirmed biological hits, showcasing the practical potential of quantum-assisted drug discovery to produce viable therapeutics. Moreover, our findings reveal that the efficacy of distribution learning correlates with the number of qubits utilized, underlining the scalability potential of quantum computing resources. Overall, we anticipate our results to be a stepping stone towards developing more advanced quantum generative models in drug discovery.
AlphaFold Accelerates Artificial Intelligence Powered Drug Discovery: Efficient Discovery of a Novel Cyclin-dependent Kinase 20 (CDK20) Small Molecule Inhibitor
Jan 21, 2022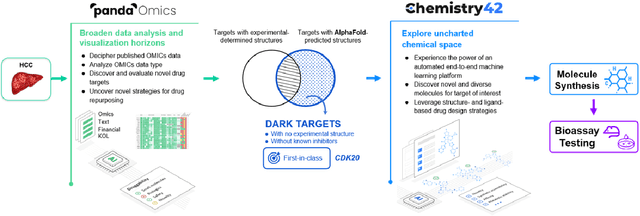
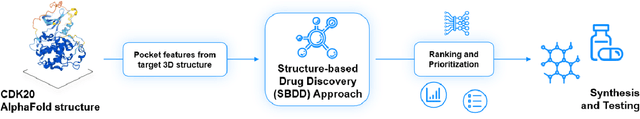
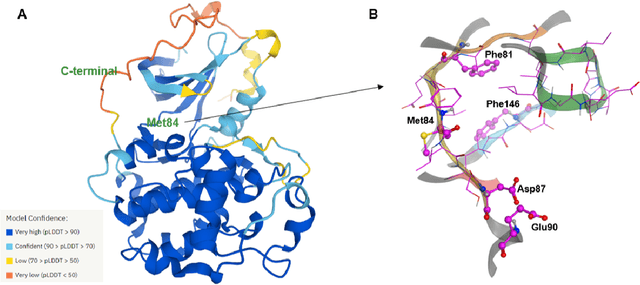
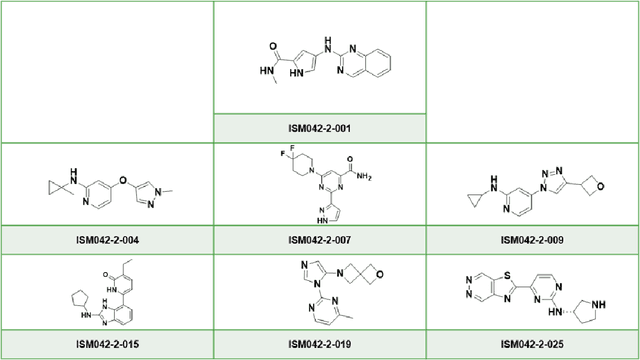
Abstract:The AlphaFold computer program predicted protein structures for the whole human genome, which has been considered as a remarkable breakthrough both in artificial intelligence (AI) application and structural biology. Despite the varying confidence level, these predicted structures still could significantly contribute to the structure-based drug design of novel targets, especially the ones with no or limited structural information. In this work, we successfully applied AlphaFold in our end-to-end AI-powered drug discovery engines constituted of a biocomputational platform PandaOmics and a generative chemistry platform Chemistry42, to identify a first-in-class hit molecule of a novel target without an experimental structure starting from target selection towards hit identification in a cost- and time-efficient manner. PandaOmics provided the targets of interest and Chemistry42 generated the molecules based on the AlphaFold predicted structure, and the selected molecules were synthesized and tested in biological assays. Through this approach, we identified a small molecule hit compound for CDK20 with a Kd value of 8.9 +/- 1.6 uM (n = 4) within 30 days from target selection and after only synthesizing 7 compounds. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported small molecule targeting CDK20 and more importantly, this work is the first demonstration of AlphaFold application in the hit identification process in early drug discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge