Fazel Arasteh
Network-Constrained Policy Optimization for Adaptive Multi-agent Vehicle Routing
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Traffic congestion in urban road networks leads to longer trip times and higher emissions, especially during peak periods. While the Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm is optimal for a single vehicle in a static network, it performs poorly in dynamic, multi-vehicle settings, often worsening congestion by routing all vehicles along identical paths. We address dynamic vehicle routing through a multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) framework for coordinated, network-aware fleet navigation. We first propose Adaptive Navigation (AN), a decentralized MARL model where each intersection agent provides routing guidance based on (i) local traffic and (ii) neighborhood state modeled using Graph Attention Networks (GAT). To improve scalability in large networks, we further propose Hierarchical Hub-based Adaptive Navigation (HHAN), an extension of AN that assigns agents only to key intersections (hubs). Vehicles are routed hub-to-hub under agent control, while SPF handles micro-routing within each hub region. For hub coordination, HHAN adopts centralized training with decentralized execution (CTDE) under the Attentive Q-Mixing (A-QMIX) framework, which aggregates asynchronous vehicle decisions via attention. Hub agents use flow-aware state features that combine local congestion and predictive dynamics for proactive routing. Experiments on synthetic grids and real urban maps (Toronto, Manhattan) show that AN reduces average travel time versus SPF and learning baselines, maintaining 100% routing success. HHAN scales to networks with hundreds of intersections, achieving up to 15.9% improvement under heavy traffic. These findings highlight the potential of network-constrained MARL for scalable, coordinated, and congestion-aware routing in intelligent transportation systems.
CAPS: Context-Aware Priority Sampling for Enhanced Imitation Learning in Autonomous Driving
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we introduce CAPS (Context-Aware Priority Sampling), a novel method designed to enhance data efficiency in learning-based autonomous driving systems. CAPS addresses the challenge of imbalanced training datasets in imitation learning by leveraging Vector Quantized Variational Autoencoders (VQ-VAEs). The use of VQ-VAE provides a structured and interpretable data representation, which helps reveal meaningful patterns in the data. These patterns are used to group the data into clusters, with each sample being assigned a cluster ID. The cluster IDs are then used to re-balance the dataset, ensuring that rare yet valuable samples receive higher priority during training. By ensuring a more diverse and informative training set, CAPS improves the generalization of the trained planner across a wide range of driving scenarios. We evaluate our method through closed-loop simulations in the CARLA environment. The results on Bench2Drive scenarios demonstrate that our framework outperforms state-of-the-art methods, leading to notable improvements in model performance.
Learning Soft Driving Constraints from Vectorized Scene Embeddings while Imitating Expert Trajectories
Dec 07, 2024Abstract:The primary goal of motion planning is to generate safe and efficient trajectories for vehicles. Traditionally, motion planning models are trained using imitation learning to mimic the behavior of human experts. However, these models often lack interpretability and fail to provide clear justifications for their decisions. We propose a method that integrates constraint learning into imitation learning by extracting driving constraints from expert trajectories. Our approach utilizes vectorized scene embeddings that capture critical spatial and temporal features, enabling the model to identify and generalize constraints across various driving scenarios. We formulate the constraint learning problem using a maximum entropy model, which scores the motion planner's trajectories based on their similarity to the expert trajectory. By separating the scoring process into distinct reward and constraint streams, we improve both the interpretability of the planner's behavior and its attention to relevant scene components. Unlike existing constraint learning methods that rely on simulators and are typically embedded in reinforcement learning (RL) or inverse reinforcement learning (IRL) frameworks, our method operates without simulators, making it applicable to a wider range of datasets and real-world scenarios. Experimental results on the InD and TrafficJams datasets demonstrate that incorporating driving constraints enhances model interpretability and improves closed-loop performance.
Learning from Mistakes: a Weakly-supervised Method for Mitigating the Distribution Shift in Autonomous Vehicle Planning
Jun 03, 2024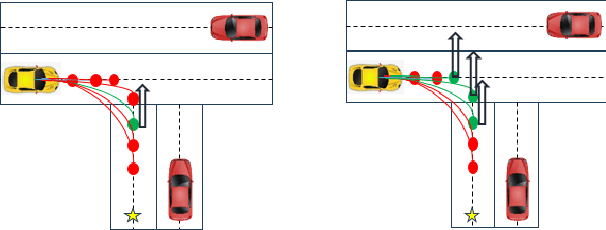



Abstract:The planning problem constitutes a fundamental aspect of the autonomous driving framework. Recent strides in representation learning have empowered vehicles to comprehend their surrounding environments, thereby facilitating the integration of learning-based planning strategies. Among these approaches, Imitation Learning stands out due to its notable training efficiency. However, traditional Imitation Learning methodologies encounter challenges associated with the co-variate shift phenomenon. We propose Learn from Mistakes (LfM) as a remedy to address this issue. The essence of LfM lies in deploying a pre-trained planner across diverse scenarios. Instances where the planner deviates from its immediate objectives, such as maintaining a safe distance from obstacles or adhering to traffic rules, are flagged as mistakes. The environments corresponding to these mistakes are categorized as out-of-distribution states and compiled into a new dataset termed closed-loop mistakes dataset. Notably, the absence of expert annotations for the closed-loop data precludes the applicability of standard imitation learning approaches. To facilitate learning from the closed-loop mistakes, we introduce Validity Learning, a weakly supervised method, which aims to discern valid trajectories within the current environmental context. Experimental evaluations conducted on the InD and Nuplan datasets reveal substantial enhancements in closed-loop metrics such as Progress and Collision Rate, underscoring the effectiveness of the proposed methodology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge