Fangwen Tu
Fast and Accurate Single-Image Depth Estimation on Mobile Devices, Mobile AI 2021 Challenge: Report
May 17, 2021
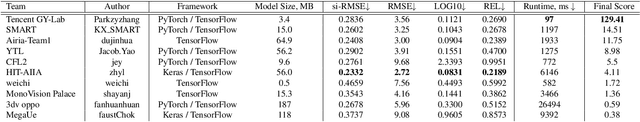
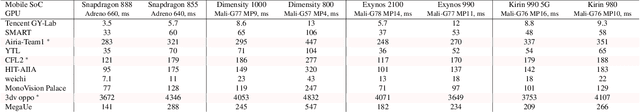
Abstract:Depth estimation is an important computer vision problem with many practical applications to mobile devices. While many solutions have been proposed for this task, they are usually very computationally expensive and thus are not applicable for on-device inference. To address this problem, we introduce the first Mobile AI challenge, where the target is to develop an end-to-end deep learning-based depth estimation solutions that can demonstrate a nearly real-time performance on smartphones and IoT platforms. For this, the participants were provided with a new large-scale dataset containing RGB-depth image pairs obtained with a dedicated stereo ZED camera producing high-resolution depth maps for objects located at up to 50 meters. The runtime of all models was evaluated on the popular Raspberry Pi 4 platform with a mobile ARM-based Broadcom chipset. The proposed solutions can generate VGA resolution depth maps at up to 10 FPS on the Raspberry Pi 4 while achieving high fidelity results, and are compatible with any Android or Linux-based mobile devices. A detailed description of all models developed in the challenge is provided in this paper.
Adaptive Control for Marine Vessels Against Harsh Environmental Variation
Sep 29, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, robust control with sea state observer and dynamic thrust allocation is proposed for the Dynamic Positioning (DP) of an accommodation vessel in the presence of unknown hydrodynamic force variation and the input time delay. In order to overcome the huge force variation due to the adjoining Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO) and accommodation vessel, a novel sea state observer is designed. The sea observer can effectively monitor the variation of the drift wave-induced force on the vessel and activate Neural Network (NN) compensator in the controller when large wave force is identified. Moreover, the wind drag coefficients can be adaptively approximated in the sea observer so that a feedforward control can be achieved. Based on this, a robust constrained control is developed to guarantee a safe operation. The time delay inside the control input is also considered. Dynamic thrust allocation module is presented to distribute the generalized control input among azimuth thrusters. Under the proposed sea observer and control, the boundedness of all the closed-loop signals are demonstrated via rigorous Lyapunov analysis. A set of simulation studies are conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed control scheme.
Saliency Guided Hierarchical Robust Visual Tracking
Dec 21, 2018



Abstract:A saliency guided hierarchical visual tracking (SHT) algorithm containing global and local search phases is proposed in this paper. In global search, a top-down saliency model is novelly developed to handle abrupt motion and appearance variation problems. Nineteen feature maps are extracted first and combined with online learnt weights to produce the final saliency map and estimated target locations. After the evaluation of integration mechanism, the optimum candidate patch is passed to the local search. In local search, a superpixel based HSV histogram matching is performed jointly with an L2-RLS tracker to take both color distribution and holistic appearance feature of the object into consideration. Furthermore, a linear refinement search process with fast iterative solver is implemented to attenuate the possible negative influence of dominant particles. Both qualitative and quantitative experiments are conducted on a series of challenging image sequences. The superior performance of the proposed method over other state-of-the-art algorithms is demonstrated by comparative study.
Shallow Cue Guided Deep Visual Tracking via Mixed Models
Dec 19, 2018



Abstract:In this paper, a robust visual tracking approach via mixed model based convolutional neural networks (SDT) is developed. In order to handle abrupt or fast motion, a prior map is generated to facilitate the localization of region of interest (ROI) before the deep tracker is performed. A top-down saliency model with nineteen shallow cues are employed to construct the prior map with online learnt combination weights. Moreover, apart from a holistic deep learner, four local networks are also trained to learn different components of the target. The generated four local heat maps will facilitate to rectify the holistic map by eliminating the distracters to avoid drifting. Furthermore, to guarantee the instance for online update of high quality, a prioritised update strategy is implemented by casting the problem into a label noise problem. The selection probability is designed by considering both confidence values and bio-inspired memory for temporal information integration. Experiments are conducted qualitatively and quantitatively on a set of challenging image sequences. Comparative study demonstrates that the proposed algorithm outperforms other state-of-the-art methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge