Eric Sauser
X-MIC: Cross-Modal Instance Conditioning for Egocentric Action Generalization
Mar 28, 2024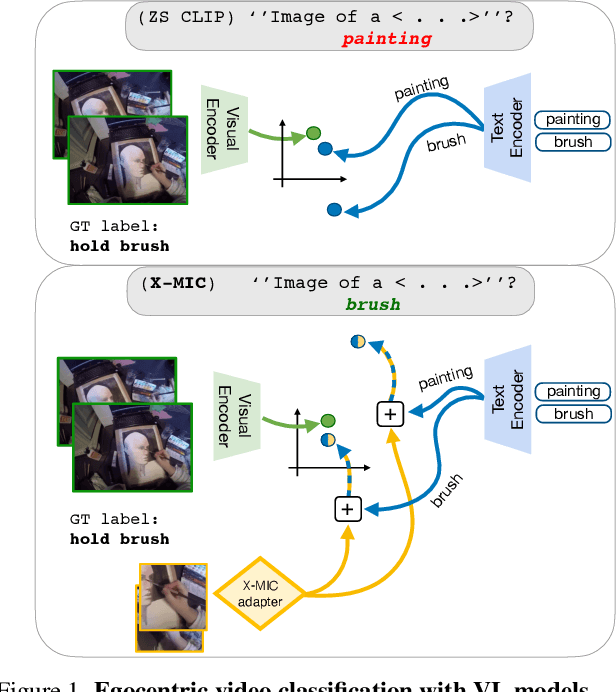
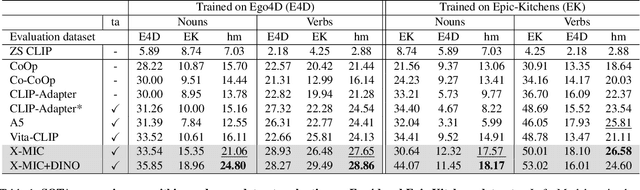
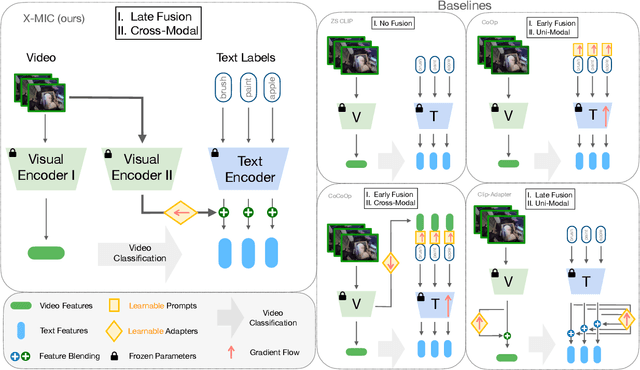
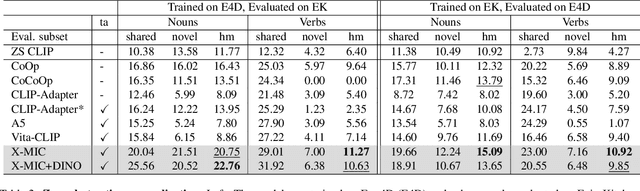
Abstract:Lately, there has been growing interest in adapting vision-language models (VLMs) to image and third-person video classification due to their success in zero-shot recognition. However, the adaptation of these models to egocentric videos has been largely unexplored. To address this gap, we propose a simple yet effective cross-modal adaptation framework, which we call X-MIC. Using a video adapter, our pipeline learns to align frozen text embeddings to each egocentric video directly in the shared embedding space. Our novel adapter architecture retains and improves generalization of the pre-trained VLMs by disentangling learnable temporal modeling and frozen visual encoder. This results in an enhanced alignment of text embeddings to each egocentric video, leading to a significant improvement in cross-dataset generalization. We evaluate our approach on the Epic-Kitchens, Ego4D, and EGTEA datasets for fine-grained cross-dataset action generalization, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method. Code is available at https://github.com/annusha/xmic
DiffH2O: Diffusion-Based Synthesis of Hand-Object Interactions from Textual Descriptions
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:Generating natural hand-object interactions in 3D is challenging as the resulting hand and object motions are expected to be physically plausible and semantically meaningful. Furthermore, generalization to unseen objects is hindered by the limited scale of available hand-object interaction datasets. We propose DiffH2O, a novel method to synthesize realistic, one or two-handed object interactions from provided text prompts and geometry of the object. The method introduces three techniques that enable effective learning from limited data. First, we decompose the task into a grasping stage and a text-based interaction stage and use separate diffusion models for each. In the grasping stage, the model only generates hand motions, whereas in the interaction phase both hand and object poses are synthesized. Second, we propose a compact representation that tightly couples hand and object poses. Third, we propose two different guidance schemes to allow more control of the generated motions: grasp guidance and detailed textual guidance. Grasp guidance takes a single target grasping pose and guides the diffusion model to reach this grasp at the end of the grasping stage, which provides control over the grasping pose. Given a grasping motion from this stage, multiple different actions can be prompted in the interaction phase. For textual guidance, we contribute comprehensive text descriptions to the GRAB dataset and show that they enable our method to have more fine-grained control over hand-object interactions. Our quantitative and qualitative evaluation demonstrates that the proposed method outperforms baseline methods and leads to natural hand-object motions. Moreover, we demonstrate the practicality of our framework by utilizing a hand pose estimate from an off-the-shelf pose estimator for guidance, and then sampling multiple different actions in the interaction stage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge