Eric M. Yeatman
An LLM-enabled Multi-Agent Autonomous Mechatronics Design Framework
Apr 20, 2025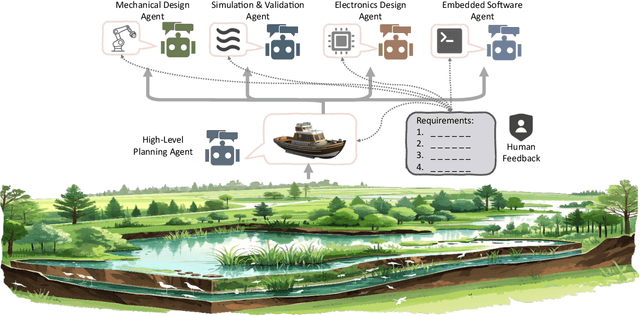
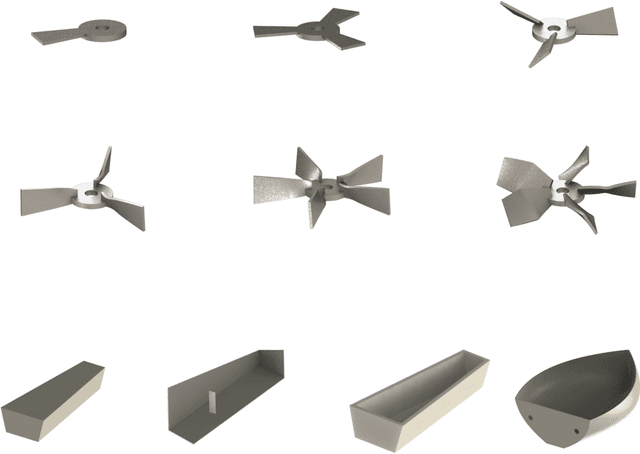
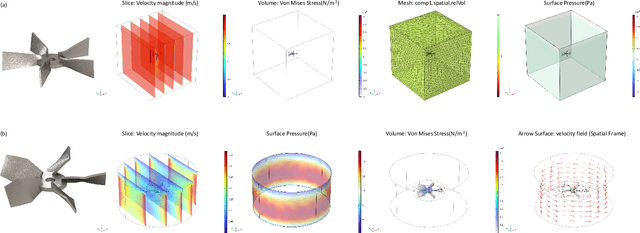
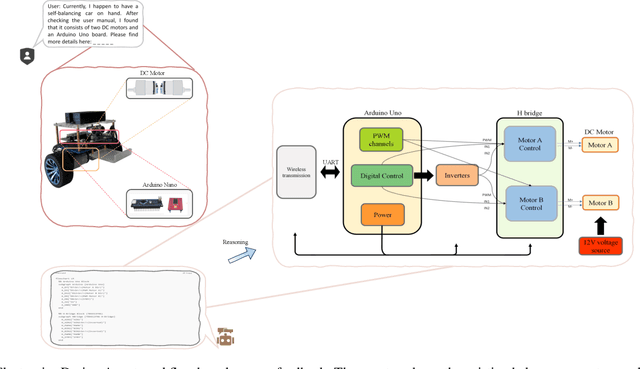
Abstract:Existing LLM-enabled multi-agent frameworks are predominantly limited to digital or simulated environments and confined to narrowly focused knowledge domain, constraining their applicability to complex engineering tasks that require the design of physical embodiment, cross-disciplinary integration, and constraint-aware reasoning. This work proposes a multi-agent autonomous mechatronics design framework, integrating expertise across mechanical design, optimization, electronics, and software engineering to autonomously generate functional prototypes with minimal direct human design input. Operating primarily through a language-driven workflow, the framework incorporates structured human feedback to ensure robust performance under real-world constraints. To validate its capabilities, the framework is applied to a real-world challenge involving autonomous water-quality monitoring and sampling, where traditional methods are labor-intensive and ecologically disruptive. Leveraging the proposed system, a fully functional autonomous vessel was developed with optimized propulsion, cost-effective electronics, and advanced control. The design process was carried out by specialized agents, including a high-level planning agent responsible for problem abstraction and dedicated agents for structural, electronics, control, and software development. This approach demonstrates the potential of LLM-based multi-agent systems to automate real-world engineering workflows and reduce reliance on extensive domain expertise.
High-Sensitivity Vision-Based Tactile Sensing Enhanced by Microstructures and Lightweight CNN
Dec 30, 2024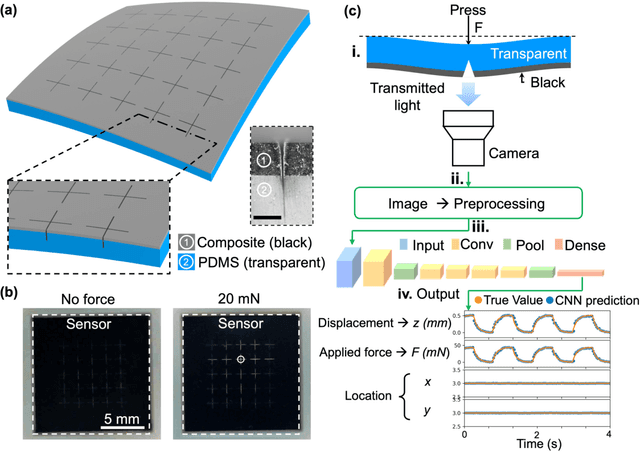
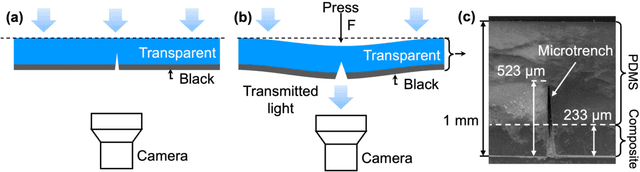
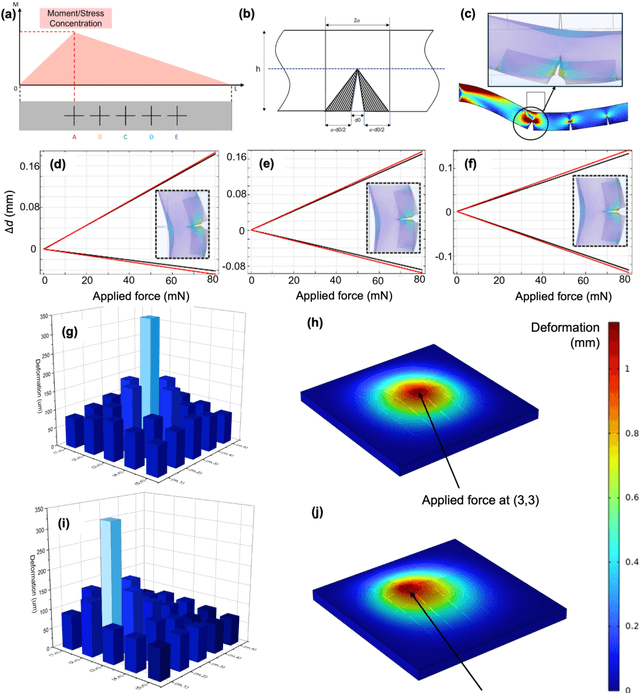
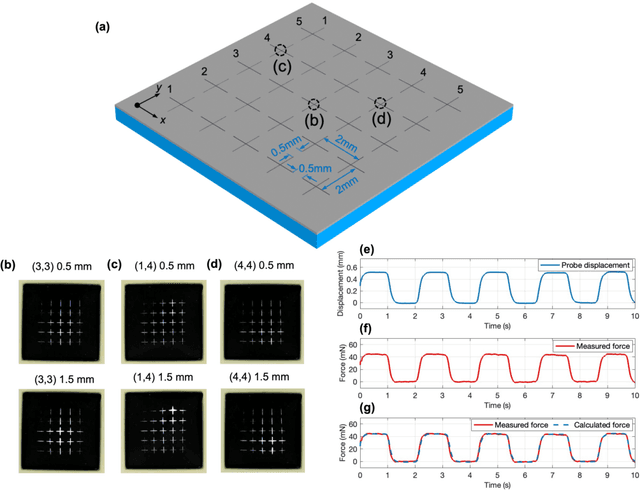
Abstract:Tactile sensing is critical in advanced interactive systems by emulating the human sense of touch to detect stimuli. Vision-based tactile sensors (VBTSs) are promising for their ability to provide rich information, robustness, adaptability, low cost, and multimodal capabilities. However, current technologies still have limitations in sensitivity, spatial resolution, and the high computational demands of deep learning-based image processing. This paper presents a comprehensive approach combining a novel sensor structure with micromachined structures and an efficient image processing method, and demonstrates that carefully engineered microstructures within the sensor hardware can significantly enhance sensitivity while reducing computational load. Unlike traditional designs with tracking markers, our sensor incorporates an interface surface with micromachined trenches, as an example of microstructures, which modulate light transmission and amplify the variation in response to applied force. By capturing variations in brightness, wire width, and cross pattern locations with a camera, the sensor accurately infers the contact location, the magnitude of displacement and applied force with a lightweight convolutional neural network (CNN). Theoretical and experimental results demonstrated that the microstructures significantly enhance sensitivity by amplifying the visual effects of shape distortion. The sensor system effectively detected forces below 10 mN, and achieved a millimetre-level single-point spatial resolution. Using a model with only one convolutional layer, a mean absolute error (MAE) below 0.05 mm have been achieved. Its soft sensor body ensures compatibility with soft robots and wearable electronics, while its immunity to electrical crosstalk and interference guarantees reliability in complex human-machine environments.
Multiple-Pilot Collaboration for Advanced Remote Intervention using Reinforcement Learning
Sep 27, 2021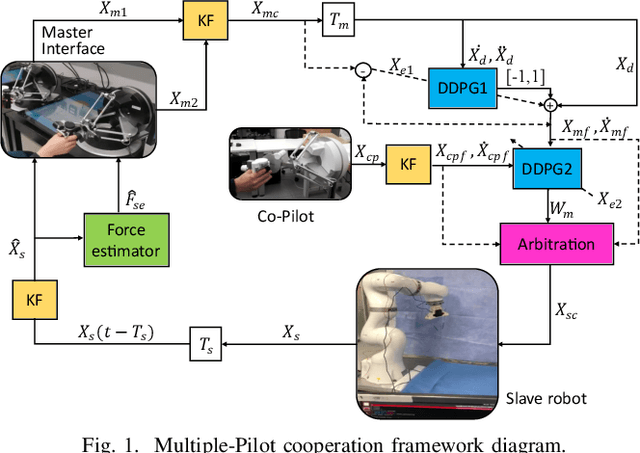
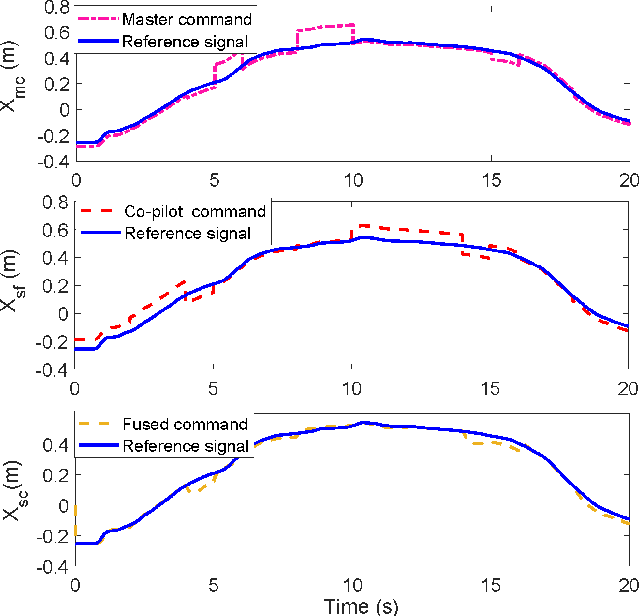
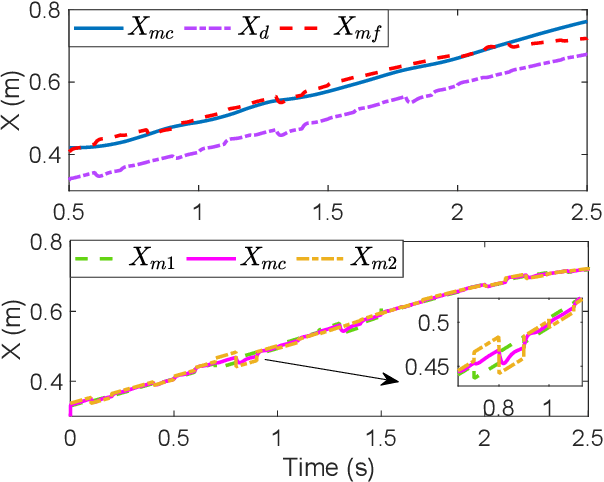
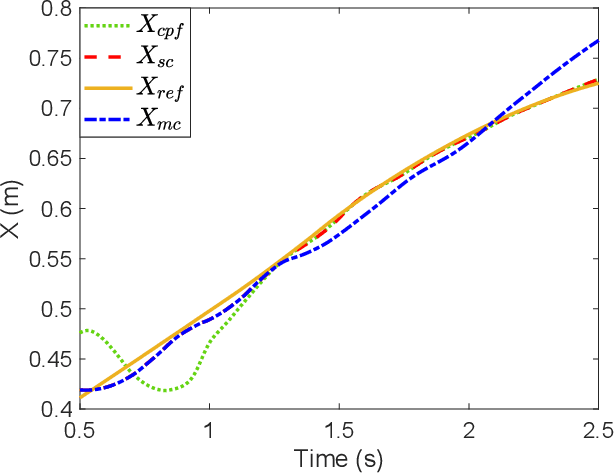
Abstract:The traditional master-slave teleoperation relies on human expertise without correction mechanisms, resulting in excessive physical and mental workloads. To address these issues, a co-pilot-in-the-loop control framework is investigated for cooperative teleoperation. A deep deterministic policy gradient(DDPG) based agent is realised to effectively restore the master operators' intents without prior knowledge on time delay. The proposed framework allows for introducing an operator (i.e., co-pilot) to generate commands at the slave side, whose weights are optimally assigned online through DDPG-based arbitration, thereby enhancing the command robustness in the case of possible human operational errors. With the help of interval type-2(IT2) Takagi-Sugeno (T-S) fuzzy identification, force feedback can be reconstructed at the master side without a sense of delay, thus ensuring the telepresence performance in the force-sensor-free scenarios. Two experimental applications validate the effectiveness of the proposed framework.
Kinematic Parameter Optimization of a Miniaturized Surgical Instrument Based on Dexterous Workspace Determination
Jul 08, 2021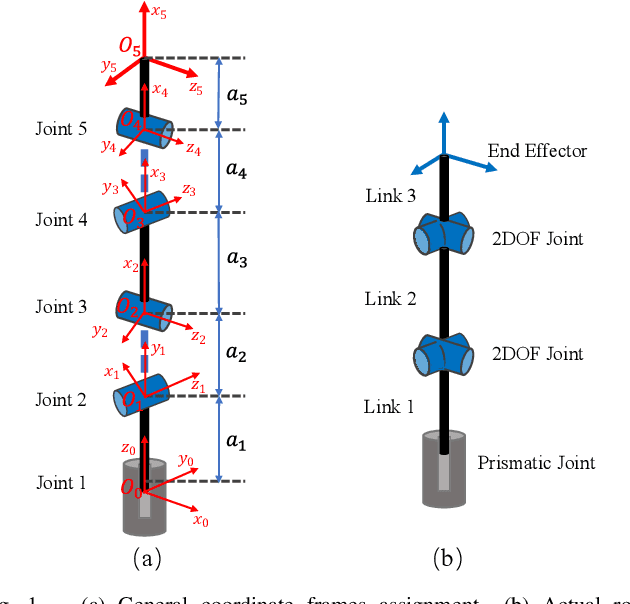
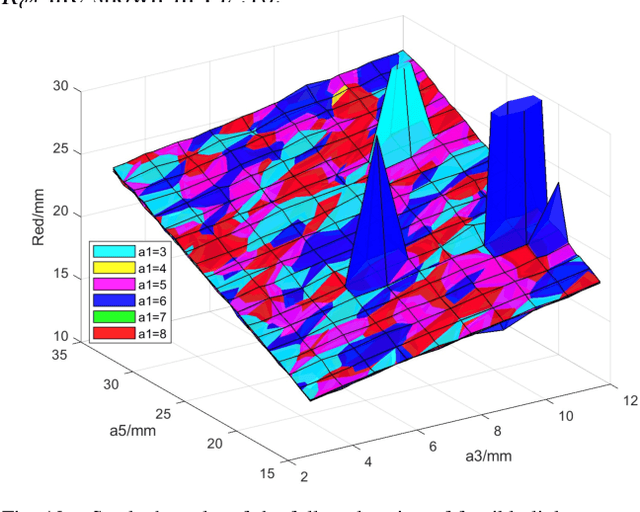
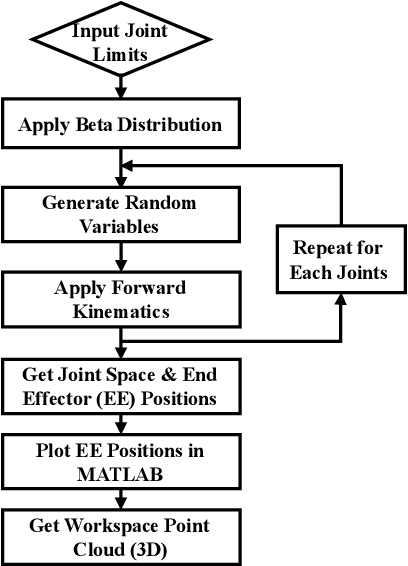
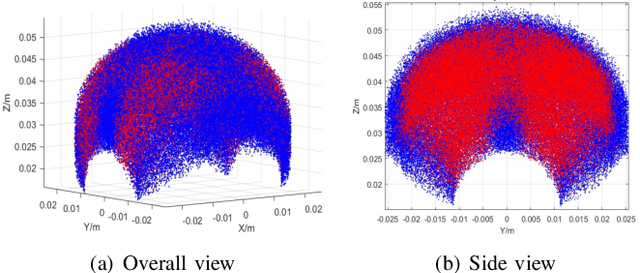
Abstract:Miniaturized instruments are highly needed for robot assisted medical healthcare and treatment, especially for less invasive surgery as it empowers more flexible access to restricted anatomic intervention. But the robotic design is more challenging due to the contradictory needs of miniaturization and the capability of manipulating with a large dexterous workspace. Thus, kinematic parameter optimization is of great significance in this case. To this end, this paper proposes an approach based on dexterous workspace determination for designing a miniaturized tendon-driven surgical instrument under necessary restraints. The workspace determination is achieved by boundary determination and volume estimation with partition and least-squares polynomial fitting methods. The final robotic configuration with optimized kinematic parameters is proved to be eligible with a large enough dexterous workspace and targeted miniature size.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge