Eric M. Moult
Retinal blood flow speed quantification at the capillary level using temporal autocorrelation fitting OCTA
Feb 22, 2023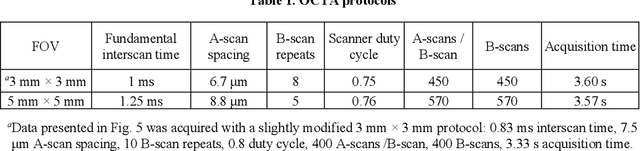
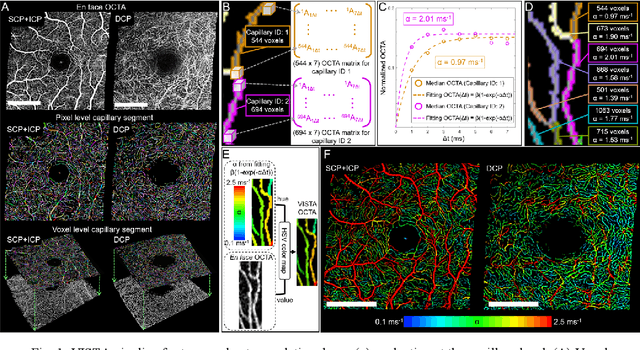
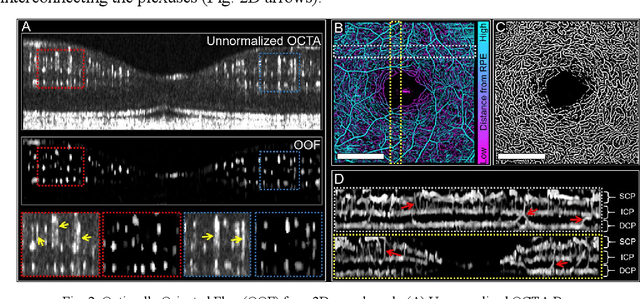
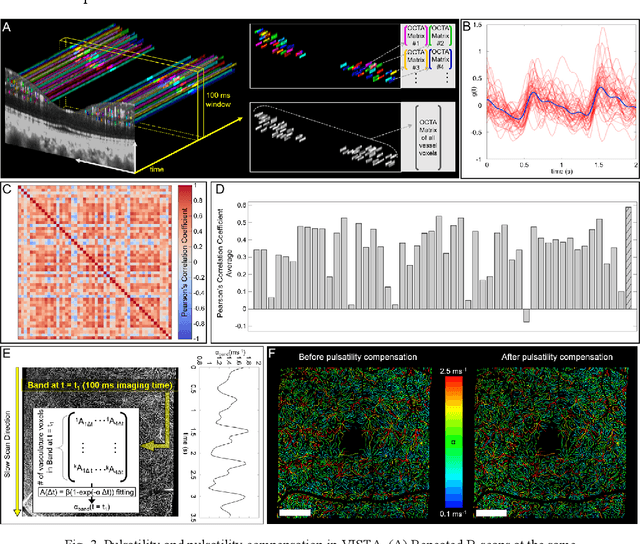
Abstract:Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) can visualize vasculature structures, but provides limited information about the blood flow speeds. Here, we present a second generation variable interscan time analysis (VISTA) OCTA, which evaluates a quantitative surrogate marker for blood flow speed in vasculature. At the capillary level, spatially compiled OCTA and a simple temporal autocorrelation model, {\rho}({\tau}) = exp(-{\alpha}{\tau}), were used to evaluate a temporal autocorrelation decay constant, {\alpha}, as the blood flow speed marker. A 600 kHz A-scan rate swept-source provides short interscan time OCTA and fine A-scan spacing acquisition, while maintaining multi mm2 field of views for human retinal imaging. We demonstrate the cardiac pulsatility and repeatability of {\alpha} measured with VISTA. We show different {\alpha} for different retinal capillary plexuses in healthy eyes and present representative VISTA OCTA of eyes with diabetic retinopathy.
Efficient and high accuracy 3-D OCT angiography motion correction in pathology
Oct 14, 2020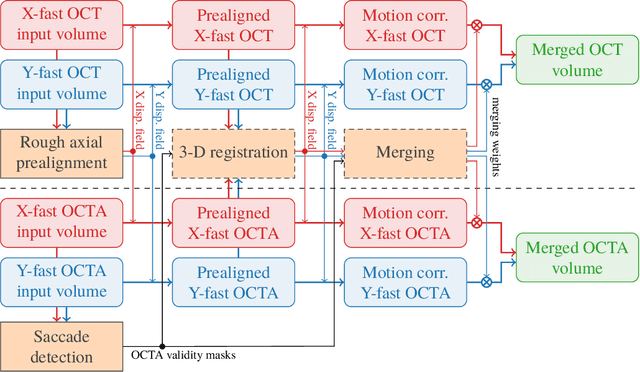
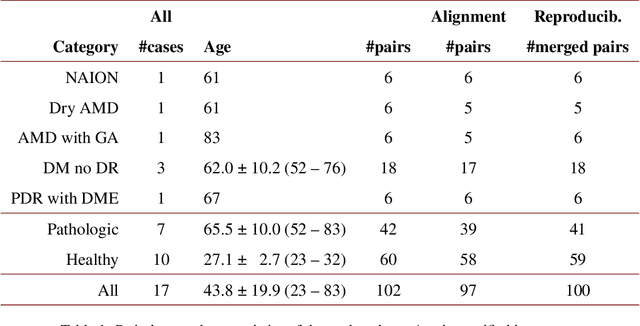
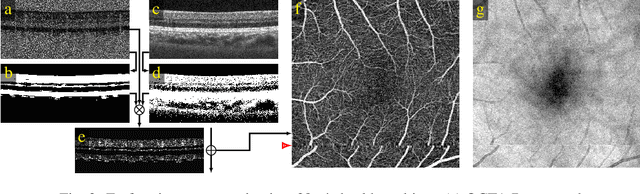
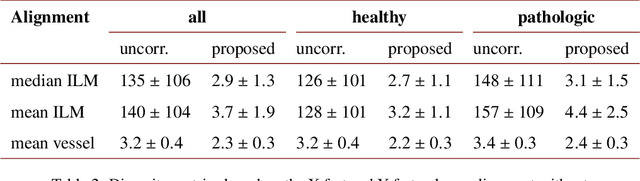
Abstract:We propose a novel method for non-rigid 3-D motion correction of orthogonally raster-scanned optical coherence tomography angiography volumes. This is the first approach that aligns predominantly axial structural features like retinal layers and transverse angiographic vascular features in a joint optimization. Combined with the use of orthogonal scans and favorization of kinematically more plausible displacements, the approach allows subpixel alignment and micrometer-scale distortion correction in all 3 dimensions. As no specific structures or layers are segmented, the approach is by design robust to pathologic changes. It is furthermore designed for highly parallel implementation and brief runtime, allowing its integration in clinical routine even for high density or wide-field scans. We evaluated the algorithm with metrics related to clinically relevant features in a large-scale quantitative evaluation based on 204 volumetric scans of 17 subjects including both a wide range of pathologies and healthy controls. Using this method, we achieve state-of-the-art axial performance and show significant advances in both transverse co-alignment and distortion correction, especially in the pathologic subgroup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge