Emrul Hasan
ViLBias: A Framework for Bias Detection using Linguistic and Visual Cues
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) and Vision-Language Models (VLMs) opens new avenues for addressing complex challenges in multimodal content analysis, particularly in biased news detection. This study introduces ViLBias, a framework that leverages state of the art LLMs and VLMs to detect linguistic and visual biases in news content, addressing the limitations of traditional text-only approaches. Our contributions include a novel dataset pairing textual content with accompanying visuals from diverse news sources and a hybrid annotation framework, combining LLM-based annotations with human review to enhance quality while reducing costs and improving scalability. We evaluate the efficacy of LLMs and VLMs in identifying biases, revealing their strengths in detecting subtle framing and text-visual inconsistencies. Empirical analysis demonstrates that incorporating visual cues alongside text enhances bias detection accuracy by 3 to 5 %, showcasing the complementary strengths of LLMs in generative reasoning and Small Language Models (SLMs) in classification. This study offers a comprehensive exploration of LLMs and VLMs as tools for detecting multimodal biases in news content, highlighting both their potential and limitations. Our research paves the way for more robust, scalable, and nuanced approaches to media bias detection, contributing to the broader field of natural language processing and multimodal analysis. (The data and code will be made available for research purposes).
Review-based Recommender Systems: A Survey of Approaches, Challenges and Future Perspectives
May 09, 2024



Abstract:Recommender systems play a pivotal role in helping users navigate an overwhelming selection of products and services. On online platforms, users have the opportunity to share feedback in various modes, including numerical ratings, textual reviews, and likes/dislikes. Traditional recommendation systems rely on users explicit ratings or implicit interactions (e.g. likes, clicks, shares, saves) to learn user preferences and item characteristics. Beyond these numerical ratings, textual reviews provide insights into users fine-grained preferences and item features. Analyzing these reviews is crucial for enhancing the performance and interpretability of personalized recommendation results. In recent years, review-based recommender systems have emerged as a significant sub-field in this domain. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive overview of the developments in review-based recommender systems over recent years, highlighting the importance of reviews in recommender systems, as well as the challenges associated with extracting features from reviews and integrating them into ratings. Specifically, we present a categorization of these systems and summarize the state-of-the-art methods, analyzing their unique features, effectiveness, and limitations. Finally, we propose potential directions for future research, including the integration of multi-modal data, multi-criteria rating information, and ethical considerations.
TMU at TREC Clinical Trials Track 2023
Mar 12, 2024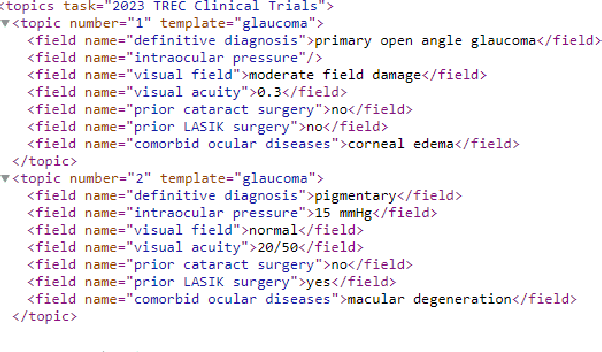
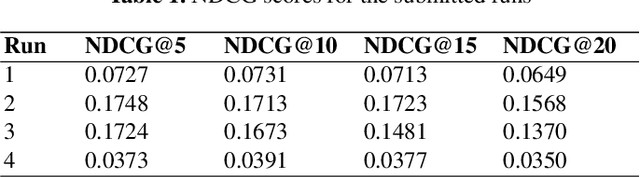
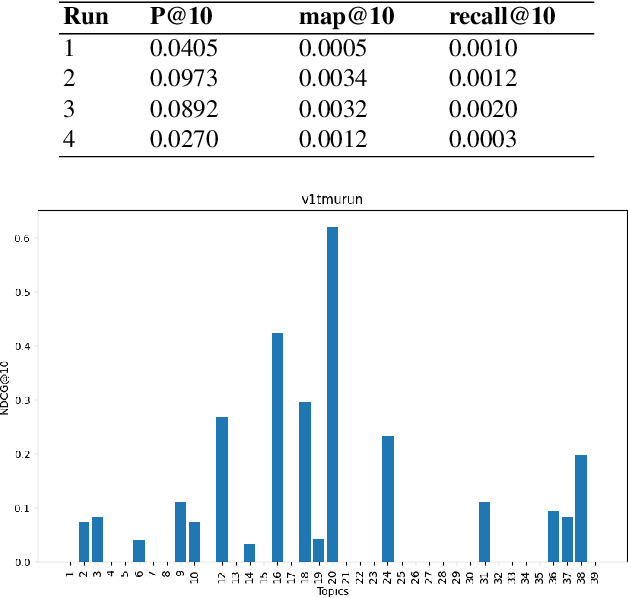
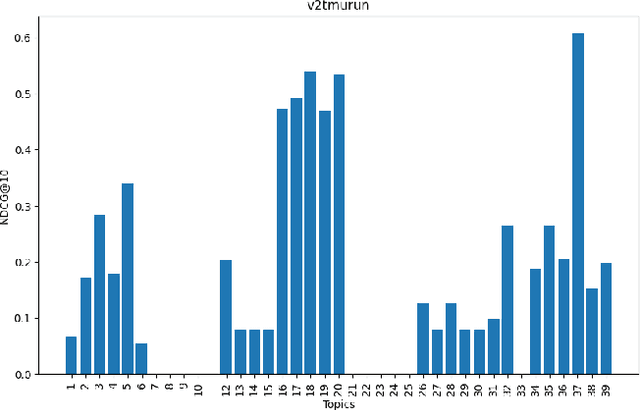
Abstract:This paper describes Toronto Metropolitan University's participation in the TREC Clinical Trials Track for 2023. As part of the tasks, we utilize advanced natural language processing techniques and neural language models in our experiments to retrieve the most relevant clinical trials. We illustrate the overall methodology, experimental settings, and results of our implementation for the run submission as part of Team - V-TorontoMU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge