Aritra Kumar Lahiri
DragonVerseQA: Open-Domain Long-Form Context-Aware Question-Answering
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes a novel approach to develop an open-domain and long-form Over-The-Top (OTT) Question-Answering (QA) dataset, DragonVerseQA, specifically oriented to the fantasy universe of "House of the Dragon" and "Game Of Thrones" TV series. Most existing QA datasets focus on short, fact-based answers sourced almost solely from Wikipedia articles, devoid of depth and contextual richness for sophisticated narrative understanding. We curate a dataset that combines full episode summaries sourced from HBO and fandom wiki websites, user reviews from sources like IMDb and Rotten Tomatoes, and high-quality, open-domain, legally admissible sources, and structured data from repositories like WikiData into one dataset. The dataset provides a multi-dimensional context, reflecting complex character dynamics and plot developments from these varied sources. That means, on equal footing, only after heavy data preprocessing and filtering methods will meaningful, non-spam unbiased reviews be available in this enriched dataset. The comprehensive insights are given through the long-form answers generated from this enriched context. This is what makes this valuable dataset for improving conversational AI, narrative analysis, sentiment analysis, summarization techniques, and relation extraction. A comparative analysis with state-of-the-art QA datasets such as SQuAD 2.0, TriviaQA, and Natural Questions brings to light the unique advantages of our dataset in terms of contextual complexity and answer length. Detailed reviews add layers to audience sentiment and narrative interpretation, raising the bar for domain-specific QA with a new quality benchmark. Our work also allows a deeper understanding of entertainment-industry content and opens the door to more knowledgeable and creative AI-driven interactions within digital media environments.
AlzheimerRAG: Multimodal Retrieval Augmented Generation for PubMed articles
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in generative AI have flourished the development of highly adept Large Language Models (LLMs) that integrate diverse data types to empower decision-making. Among these, Multimodal Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) applications are promising for their capability to combine the strengths of information retrieval and generative models, enhancing their utility across various domains, including biomedical research. This paper introduces AlzheimerRAG, a Multimodal RAG pipeline tool for biomedical research use cases, primarily focusing on Alzheimer's disease from PubMed articles. Our pipeline incorporates multimodal fusion techniques to integrate textual and visual data processing by efficiently indexing and accessing vast amounts of biomedical literature. Preliminary experimental results against benchmarks, such as BioASQ and PubMedQA, have returned improved results in information retrieval and synthesis of domain-specific information. We also demonstrate a case study with our RAG pipeline across different Alzheimer's clinical scenarios. We infer that AlzheimerRAG can generate responses with accuracy non-inferior to humans and with low rates of hallucination. Overall, a reduction in cognitive task load is observed, which allows researchers to gain multimodal insights, improving understanding and treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
TMU at TREC Clinical Trials Track 2023
Mar 12, 2024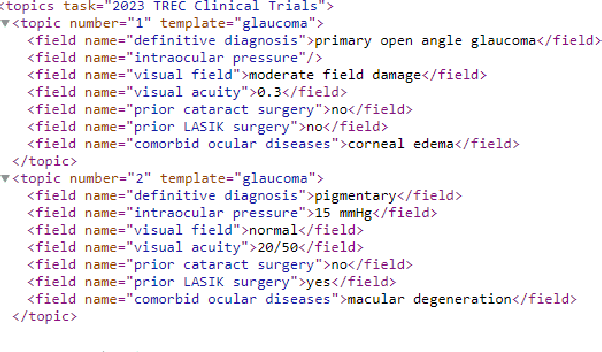
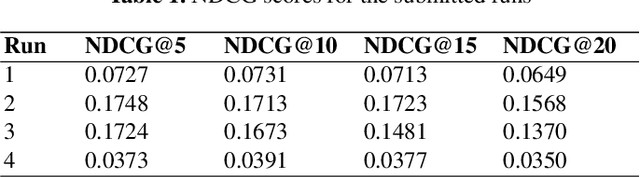
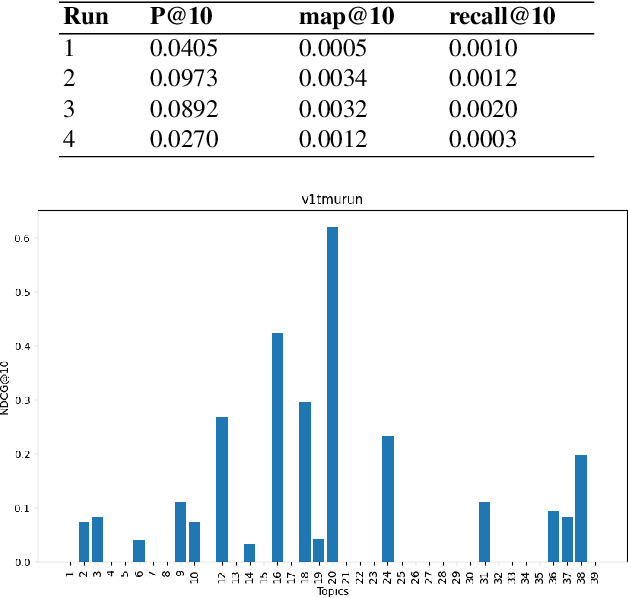
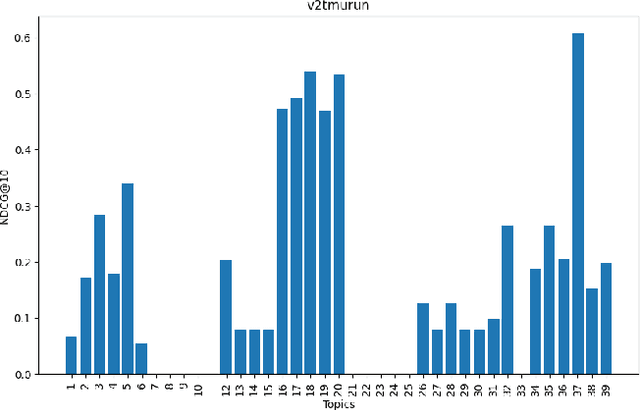
Abstract:This paper describes Toronto Metropolitan University's participation in the TREC Clinical Trials Track for 2023. As part of the tasks, we utilize advanced natural language processing techniques and neural language models in our experiments to retrieve the most relevant clinical trials. We illustrate the overall methodology, experimental settings, and results of our implementation for the run submission as part of Team - V-TorontoMU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge