Elisa Ferracane
Analyzing LLM Behavior in Dialogue Summarization: Unveiling Circumstantial Hallucination Trends
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have considerably advanced the capabilities of summarization systems. However, they continue to face concerns about hallucinations. While prior work has evaluated LLMs extensively in news domains, most evaluation of dialogue summarization has focused on BART-based models, leaving a gap in our understanding of their faithfulness. Our work benchmarks the faithfulness of LLMs for dialogue summarization, using human annotations and focusing on identifying and categorizing span-level inconsistencies. Specifically, we focus on two prominent LLMs: GPT-4 and Alpaca-13B. Our evaluation reveals subtleties as to what constitutes a hallucination: LLMs often generate plausible inferences, supported by circumstantial evidence in the conversation, that lack direct evidence, a pattern that is less prevalent in older models. We propose a refined taxonomy of errors, coining the category of "Circumstantial Inference" to bucket these LLM behaviors and release the dataset. Using our taxonomy, we compare the behavioral differences between LLMs and older fine-tuned models. Additionally, we systematically assess the efficacy of automatic error detection methods on LLM summaries and find that they struggle to detect these nuanced errors. To address this, we introduce two prompt-based approaches for fine-grained error detection that outperform existing metrics, particularly for identifying "Circumstantial Inference."
Clickbait Classification and Spoiling Using Natural Language Processing
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:Clickbait is the practice of engineering titles to incentivize readers to click through to articles. Such titles with sensationalized language reveal as little information as possible. Occasionally, clickbait will be intentionally misleading, so natural language processing (NLP) can scan the article and answer the question posed by the clickbait title, or spoil it. We tackle two tasks: classifying the clickbait into one of 3 types (Task 1), and spoiling the clickbait (Task 2). For Task 1, we propose two binary classifiers to determine the final spoiler type. For Task 2, we experiment with two approaches: using a question-answering model to identify the span of text of the spoiler, and using a large language model (LLM) to generate the spoiler. Because the spoiler is contained in the article, we frame the second task as a question-answering approach for identifying the starting and ending positions of the spoiler. We created models for Task 1 that were better than the baselines proposed by the dataset authors and engineered prompts for Task 2 that did not perform as well as the baselines proposed by the dataset authors due to the evaluation metric performing worse when the output text is from a generative model as opposed to an extractive model.
Extractive Question Answering on Queries in Hindi and Tamil
Sep 27, 2022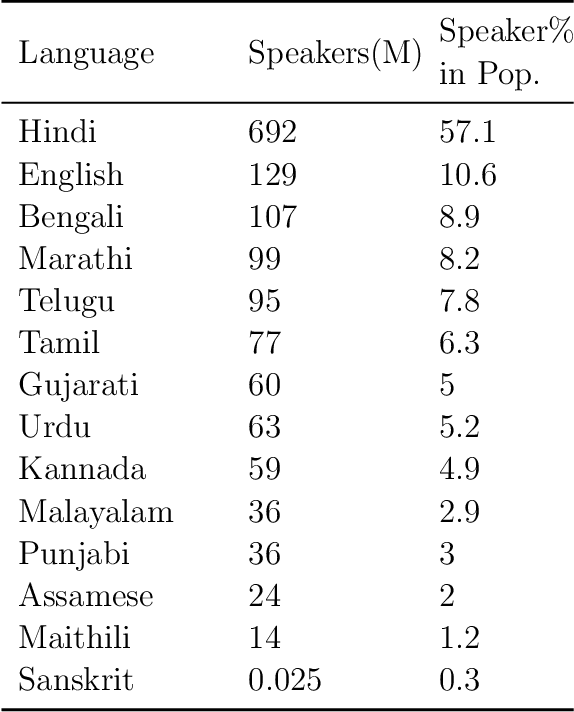

Abstract:Indic languages like Hindi and Tamil are underrepresented in the natural language processing (NLP) field compared to languages like English. Due to this underrepresentation, performance on NLP tasks (such as search algorithms) in Indic languages are inferior to their English counterparts. This difference disproportionately affects those who come from lower socioeconomic statuses because they consume the most Internet content in local languages. The goal of this project is to build an NLP model that performs better than pre-existing models for the task of extractive question-answering (QA) on a public dataset in Hindi and Tamil. Extractive QA is an NLP task where answers to questions are extracted from a corresponding body of text. To build the best solution, we used three different models. The first model is an unmodified cross-lingual version of the NLP model RoBERTa, known as XLM-RoBERTa, that is pretrained on 100 languages. The second model is based on the pretrained RoBERTa model with an extra classification head for the question answering, but we used a custom Indic tokenizer, then optimized hyperparameters and fine tuned on the Indic dataset. The third model is based on XLM-RoBERTa, but with extra finetuning and training on the Indic dataset. We hypothesize the third model will perform best because of the variety of languages the XLM-RoBERTa model has been pretrained on and the additional finetuning on the Indic dataset. This hypothesis was proven wrong because the paired RoBERTa models performed the best as the training data used was most specific to the task performed as opposed to the XLM-RoBERTa models which had much data that was not in either Hindi or Tamil.
Did they answer? Subjective acts and intents in conversational discourse
Apr 09, 2021



Abstract:Discourse signals are often implicit, leaving it up to the interpreter to draw the required inferences. At the same time, discourse is embedded in a social context, meaning that interpreters apply their own assumptions and beliefs when resolving these inferences, leading to multiple, valid interpretations. However, current discourse data and frameworks ignore the social aspect, expecting only a single ground truth. We present the first discourse dataset with multiple and subjective interpretations of English conversation in the form of perceived conversation acts and intents. We carefully analyze our dataset and create computational models to (1) confirm our hypothesis that taking into account the bias of the interpreters leads to better predictions of the interpretations, (2) and show disagreements are nuanced and require a deeper understanding of the different contextual factors. We share our dataset and code at http://github.com/elisaF/subjective_discourse.
Towards Fairness in Classifying Medical Conversations into SOAP Sections
Dec 02, 2020



Abstract:As machine learning algorithms are more widely deployed in healthcare, the question of algorithmic fairness becomes more critical to examine. Our work seeks to identify and understand disparities in a deployed model that classifies doctor-patient conversations into sections of a medical SOAP note. We employ several metrics to measure disparities in the classifier performance, and find small differences in a portion of the disadvantaged groups. A deeper analysis of the language in these conversations and further stratifying the groups suggests these differences are related to and often attributable to the type of medical appointment (e.g., psychiatric vs. internist). Our findings stress the importance of understanding the disparities that may exist in the data itself and how that affects a model's ability to equally distribute benefits.
Evaluating Discourse in Structured Text Representations
Jun 10, 2019



Abstract:Discourse structure is integral to understanding a text and is helpful in many NLP tasks. Learning latent representations of discourse is an attractive alternative to acquiring expensive labeled discourse data. Liu and Lapata (2018) propose a structured attention mechanism for text classification that derives a tree over a text, akin to an RST discourse tree. We examine this model in detail, and evaluate on additional discourse-relevant tasks and datasets, in order to assess whether the structured attention improves performance on the end task and whether it captures a text's discourse structure. We find the learned latent trees have little to no structure and instead focus on lexical cues; even after obtaining more structured trees with proposed model modifications, the trees are still far from capturing discourse structure when compared to discourse dependency trees from an existing discourse parser. Finally, ablation studies show the structured attention provides little benefit, sometimes even hurting performance.
From News to Medical: Cross-domain Discourse Segmentation
Apr 14, 2019



Abstract:The first step in discourse analysis involves dividing a text into segments. We annotate the first high-quality small-scale medical corpus in English with discourse segments and analyze how well news-trained segmenters perform on this domain. While we expectedly find a drop in performance, the nature of the segmentation errors suggests some problems can be addressed earlier in the pipeline, while others would require expanding the corpus to a trainable size to learn the nuances of the medical domain.
Leveraging Discourse Information Effectively for Authorship Attribution
Sep 07, 2017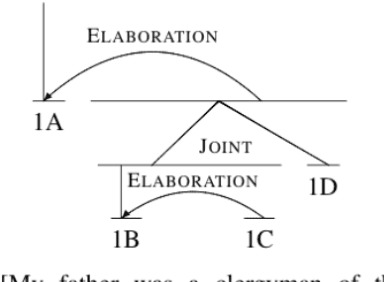

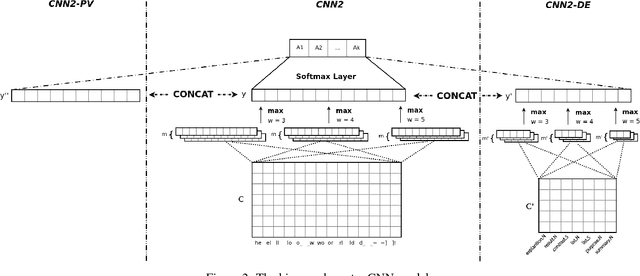
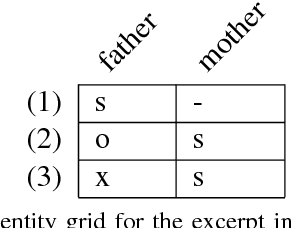
Abstract:We explore techniques to maximize the effectiveness of discourse information in the task of authorship attribution. We present a novel method to embed discourse features in a Convolutional Neural Network text classifier, which achieves a state-of-the-art result by a substantial margin. We empirically investigate several featurization methods to understand the conditions under which discourse features contribute non-trivial performance gains, and analyze discourse embeddings.
* Accepted at IJCNLP 2017 as a conference paper
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge