Eduardo Benitez Sandoval
Attention-Enhanced Lightweight Hourglass Network for Human Pose Estimation
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:Pose estimation is a critical task in computer vision with a wide range of applications from activity monitoring to human-robot interaction. However,most of the existing methods are computationally expensive or have complex architecture. Here we propose a lightweight attention based pose estimation network that utilizes depthwise separable convolution and Convolutional Block Attention Module on an hourglass backbone. The network significantly reduces the computational complexity (floating point operations) and the model size (number of parameters) containing only about 10% of parameters of original eight stack Hourglass network.Experiments were conducted on COCO and MPII datasets using a two stack hourglass backbone. The results showed that our model performs well in comparison to six other lightweight pose estimation models with an average precision of 72.07. The model achieves this performance with only 2.3M parameters and 3.7G FLOPs.
PERCY: A Multimodal Dataset and Conversational System for Personalized and Emotionally Aware Human-Robot Interaction
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:The integration of conversational agents into our daily lives has become increasingly common, yet many of these agents cannot engage in deep interactions with humans. Despite this, there is a noticeable shortage of datasets that capture multimodal information from human-robot interaction dialogues. To address this gap, we have developed a Personal Emotional Robotic Conversational sYstem (PERCY) and recorded a novel multimodal dataset that encompasses rich embodied interaction data. The process involved asking participants to complete a questionnaire and gathering their profiles on ten topics, such as hobbies and favourite music. Subsequently, we initiated conversations between the robot and the participants, leveraging GPT-4 to generate contextually appropriate responses based on the participant's profile and emotional state, as determined by facial expression recognition and sentiment analysis. Automatic and user evaluations were conducted to assess the overall quality of the collected data. The results of both evaluations indicated a high level of naturalness, engagement, fluency, consistency, and relevance in the conversation, as well as the robot's ability to provide empathetic responses. It is worth noting that the dataset is derived from genuine interactions with the robot, involving participants who provided personal information and conveyed actual emotions.
Self context-aware emotion perception on human-robot interaction
Jan 18, 2024Abstract:Emotion recognition plays a crucial role in various domains of human-robot interaction. In long-term interactions with humans, robots need to respond continuously and accurately, however, the mainstream emotion recognition methods mostly focus on short-term emotion recognition, disregarding the context in which emotions are perceived. Humans consider that contextual information and different contexts can lead to completely different emotional expressions. In this paper, we introduce self context-aware model (SCAM) that employs a two-dimensional emotion coordinate system for anchoring and re-labeling distinct emotions. Simultaneously, it incorporates its distinctive information retention structure and contextual loss. This approach has yielded significant improvements across audio, video, and multimodal. In the auditory modality, there has been a notable enhancement in accuracy, rising from 63.10% to 72.46%. Similarly, the visual modality has demonstrated improved accuracy, increasing from 77.03% to 80.82%. In the multimodal, accuracy has experienced an elevation from 77.48% to 78.93%. In the future, we will validate the reliability and usability of SCAM on robots through psychology experiments.
Asch Meets HRI: Human Conformity to Robot Groups
Aug 25, 2023
Abstract:We present a research outline that aims at investigating group dynamics and peer pressure in the context of industrial robots. Our research plan was motivated by the fact that industrial robots became already an integral part of human-robot co-working. However, industrial robots have been sparsely integrated into research on robot credibility, group dynamics, and potential users' tendency to follow a robot's indication. Therefore, we aim to transfer the classic Asch experiment (see \cite{Asch_51}) into HRI with industrial robots. More precisely, we will test to what extent participants follow a robot's response when confronted with a group (vs. individual) industrial robot arms (vs. human) peers who give a false response. We are interested in highlighting the effects of group size, perceived robot credibility, psychological stress, and peer pressure in the context of industrial robots. With the results of this research, we hope to highlight group dynamics that might underlie HRI in industrial settings in which numerous robots already work closely together with humans in shared environments.
Human-Robot Creative Interactions (HRCI): Exploring Creativity in Artificial Agents Using a Story-Telling Game
Feb 08, 2022
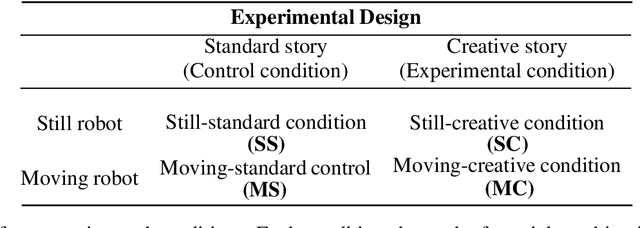
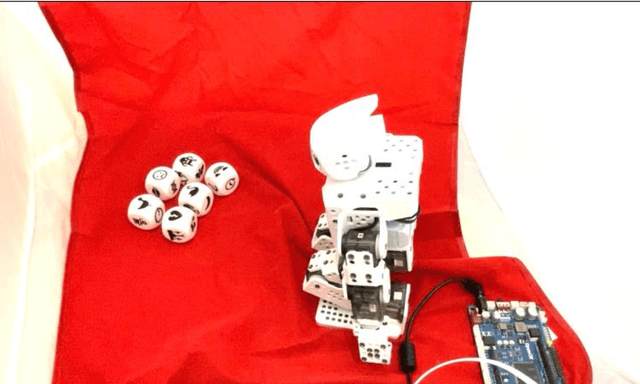

Abstract:Creativity in social robots requires further attention in the interdisciplinary field of Human-Robot Interaction (HRI). This paper investigates the hypothesised connection between the perceived creative agency and the animacy of social robots. The goal of this work is to assess the relevance of robot movements in the attribution of creativity to robots. The results of this work inform the design of future Human-Robot Creative Interactions (HRCI). The study uses a storytelling game based on visual imagery inspired by the game 'Story Cubes' to explore the perceived creative agency of social robots. This game is used to tell a classic story for children with an alternative ending. A 2x2 experiment was designed to compare two conditions: the robot telling the original version of the story and the robot plot-twisting the end of the story. A Robotis Mini humanoid robot was used for the experiment. As a novel contribution, we propose an adaptation of the Short Scale Creative Self scale (SSCS) to measure perceived creative agency in robots. We also use the Godspeed scale to explore different attributes of social robots in this setting. We did not obtain significant main effects of the robot movements or the story in the participants' scores. However, we identified significant main effects of the robot movements in features of animacy, likeability, and perceived safety. This initial work encourages further studies experimenting with different robot embodiment and movements to evaluate the perceived creative agency in robots and inform the design of future robots that participate in creative interactions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge