Doratossadat Dastgheib
MEENA (PersianMMMU): Multimodal-Multilingual Educational Exams for N-level Assessment
Aug 24, 2025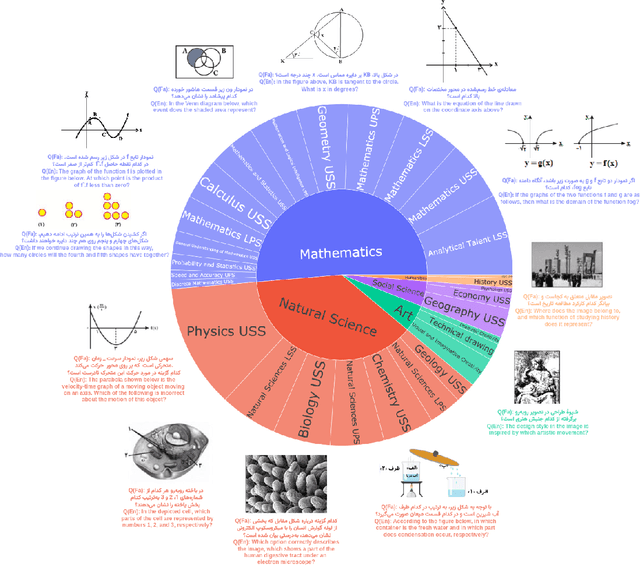
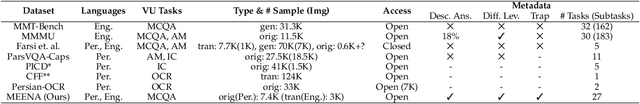
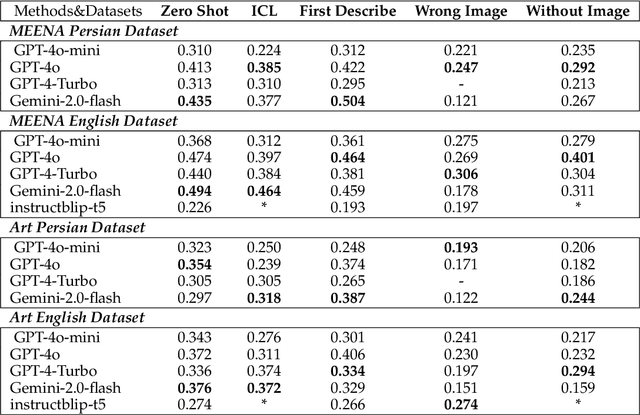
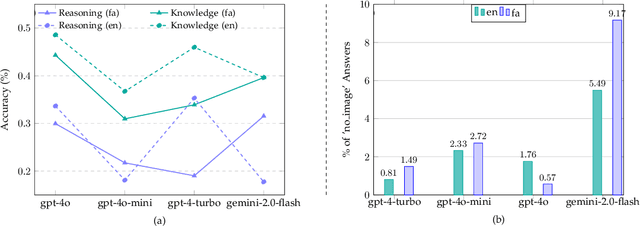
Abstract:Recent advancements in large vision-language models (VLMs) have primarily focused on English, with limited attention given to other languages. To address this gap, we introduce MEENA (also known as PersianMMMU), the first dataset designed to evaluate Persian VLMs across scientific, reasoning, and human-level understanding tasks. Our dataset comprises approximately 7,500 Persian and 3,000 English questions, covering a wide range of topics such as reasoning, mathematics, physics, diagrams, charts, and Persian art and literature. Key features of MEENA include: (1) diverse subject coverage spanning various educational levels, from primary to upper secondary school, (2) rich metadata, including difficulty levels and descriptive answers, (3) original Persian data that preserves cultural nuances, (4) a bilingual structure to assess cross-linguistic performance, and (5) a series of diverse experiments assessing various capabilities, including overall performance, the model's ability to attend to images, and its tendency to generate hallucinations. We hope this benchmark contributes to enhancing VLM capabilities beyond English.
Khayyam Challenge : Is Your LLM Truly Wise to The Persian Language?
Apr 09, 2024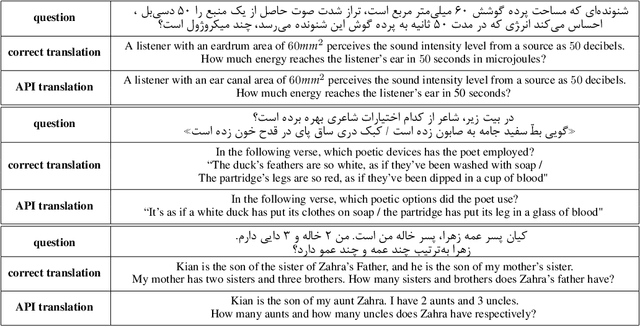
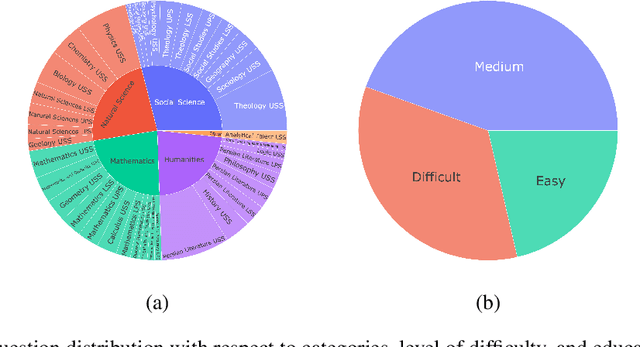
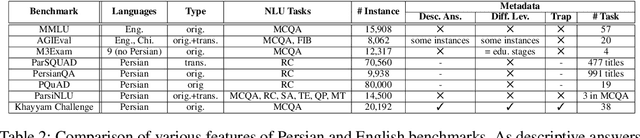
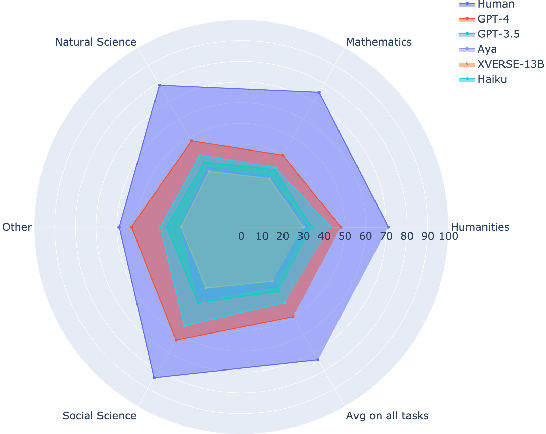
Abstract:Evaluating Large Language Models (LLMs) is challenging due to their generative nature, necessitating precise evaluation methodologies. Additionally, non-English LLM evaluation lags behind English, resulting in the absence or weakness of LLMs for many languages. In response to this necessity, we introduce Khayyam Challenge (also known as PersianMMLU), a meticulously curated collection comprising 20,192 four-choice questions sourced from 38 diverse tasks extracted from Persian examinations, spanning a wide spectrum of subjects, complexities, and ages. The primary objective of the Khayyam Challenge is to facilitate the rigorous evaluation of LLMs that support the Persian language. Distinctive features of the Khayyam Challenge are (i) its comprehensive coverage of various topics, including literary comprehension, mathematics, sciences, logic, intelligence testing, etc., aimed at assessing different facets of LLMs such as language comprehension, reasoning, and information retrieval across various educational stages, from lower primary school to upper secondary school (ii) its inclusion of rich metadata such as human response rates, difficulty levels, and descriptive answers (iii) its utilization of new data to avoid data contamination issues prevalent in existing frameworks (iv) its use of original, non-translated data tailored for Persian speakers, ensuring the framework is free from translation challenges and errors while encompassing cultural nuances (v) its inherent scalability for future data updates and evaluations without requiring special human effort. Previous works lacked an evaluation framework that combined all of these features into a single comprehensive benchmark. Furthermore, we evaluate a wide range of existing LLMs that support the Persian language, with statistical analyses and interpretations of their outputs.
The Touché23-ValueEval Dataset for Identifying Human Values behind Arguments
Jan 31, 2023Abstract:We present the Touch\'e23-ValueEval Dataset for Identifying Human Values behind Arguments. To investigate approaches for the automated detection of human values behind arguments, we collected 9324 arguments from 6 diverse sources, covering religious texts, political discussions, free-text arguments, newspaper editorials, and online democracy platforms. Each argument was annotated by 3 crowdworkers for 54 values. The Touch\'e23-ValueEval dataset extends the Webis-ArgValues-22. In comparison to the previous dataset, the effectiveness of a 1-Baseline decreases, but that of an out-of-the-box BERT model increases. Therefore, though the classification difficulty increased as per the label distribution, the larger dataset allows for training better models.
Doxastic Extensions of Łukasiewicz Logic
Nov 04, 2021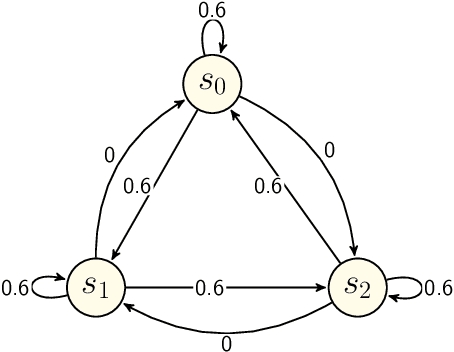
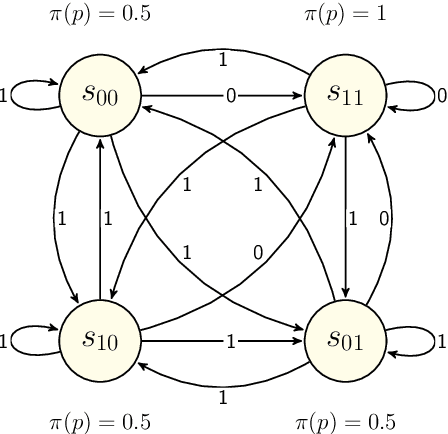
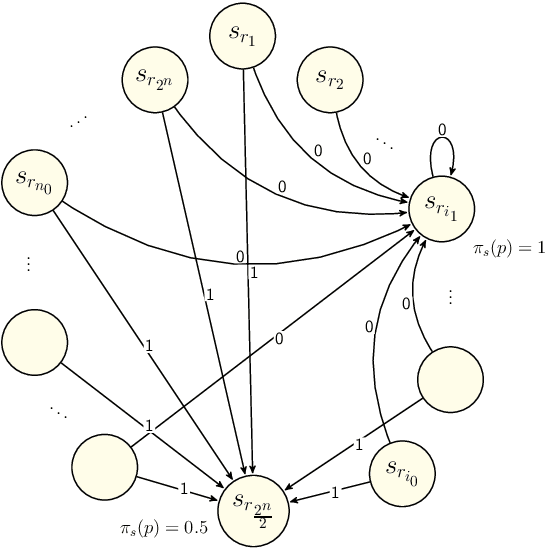
Abstract:We propose two new doxastic extensions of fuzzy \L ukasiewicz logic in which their semantics are Kripke-based with both fuzzy atomic propositions and fuzzy accessibility relations. A class of these extensions is equipped with uninformed belief operator, and the other class is based on a new notion of skeptical belief. We model a fuzzy version of muddy children problem and a CPA-security experiment using uniformed belief and skeptical belief, respectively. Moreover, we prove soundness and completeness for both of these belief extensions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge