Dongman Lee
DETACH : Decomposed Spatio-Temporal Alignment for Exocentric Video and Ambient Sensors with Staged Learning
Dec 23, 2025



Abstract:Aligning egocentric video with wearable sensors have shown promise for human action recognition, but face practical limitations in user discomfort, privacy concerns, and scalability. We explore exocentric video with ambient sensors as a non-intrusive, scalable alternative. While prior egocentric-wearable works predominantly adopt Global Alignment by encoding entire sequences into unified representations, this approach fails in exocentric-ambient settings due to two problems: (P1) inability to capture local details such as subtle motions, and (P2) over-reliance on modality-invariant temporal patterns, causing misalignment between actions sharing similar temporal patterns with different spatio-semantic contexts. To resolve these problems, we propose DETACH, a decomposed spatio-temporal framework. This explicit decomposition preserves local details, while our novel sensor-spatial features discovered via online clustering provide semantic grounding for context-aware alignment. To align the decomposed features, our two-stage approach establishes spatial correspondence through mutual supervision, then performs temporal alignment via a spatial-temporal weighted contrastive loss that adaptively handles easy negatives, hard negatives, and false negatives. Comprehensive experiments with downstream tasks on Opportunity++ and HWU-USP datasets demonstrate substantial improvements over adapted egocentric-wearable baselines.
Enhancing Regional Airbnb Trend Forecasting Using LLM-Based Embeddings of Accessibility and Human Mobility
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:The expansion of short-term rental platforms, such as Airbnb, has significantly disrupted local housing markets, often leading to increased rental prices and housing affordability issues. Accurately forecasting regional Airbnb market trends can thus offer critical insights for policymakers and urban planners aiming to mitigate these impacts. This study proposes a novel time-series forecasting framework to predict three key Airbnb indicators -- Revenue, Reservation Days, and Number of Reservations -- at the regional level. Using a sliding-window approach, the model forecasts trends 1 to 3 months ahead. Unlike prior studies that focus on individual listings at fixed time points, our approach constructs regional representations by integrating listing features with external contextual factors such as urban accessibility and human mobility. We convert structured tabular data into prompt-based inputs for a Large Language Model (LLM), producing comprehensive regional embeddings. These embeddings are then fed into advanced time-series models (RNN, LSTM, Transformer) to better capture complex spatio-temporal dynamics. Experiments on Seoul's Airbnb dataset show that our method reduces both average RMSE and MAE by approximately 48% compared to conventional baselines, including traditional statistical and machine learning models. Our framework not only improves forecasting accuracy but also offers practical insights for detecting oversupplied regions and supporting data-driven urban policy decisions.
Background Fades, Foreground Leads: Curriculum-Guided Background Pruning for Efficient Foreground-Centric Collaborative Perception
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:Collaborative perception enhances the reliability and spatial coverage of autonomous vehicles by sharing complementary information across vehicles, offering a promising solution to long-tail scenarios that challenge single-vehicle perception. However, the bandwidth constraints of vehicular networks make transmitting the entire feature map impractical. Recent methods, therefore, adopt a foreground-centric paradigm, transmitting only predicted foreground-region features while discarding the background, which encodes essential context. We propose FadeLead, a foreground-centric framework that overcomes this limitation by learning to encapsulate background context into compact foreground features during training. At the core of our design is a curricular learning strategy that leverages background cues early on but progressively prunes them away, forcing the model to internalize context into foreground representations without transmitting background itself. Extensive experiments on both simulated and real-world benchmarks show that FadeLead outperforms prior methods under different bandwidth settings, underscoring the effectiveness of context-enriched foreground sharing.
Feature Augmentation based Test-Time Adaptation
Oct 18, 2024Abstract:Test-time adaptation (TTA) allows a model to be adapted to an unseen domain without accessing the source data. Due to the nature of practical environments, TTA has a limited amount of data for adaptation. Recent TTA methods further restrict this by filtering input data for reliability, making the effective data size even smaller and limiting adaptation potential. To address this issue, We propose Feature Augmentation based Test-time Adaptation (FATA), a simple method that fully utilizes the limited amount of input data through feature augmentation. FATA employs Normalization Perturbation to augment features and adapts the model using the FATA loss, which makes the outputs of the augmented and original features similar. FATA is model-agnostic and can be seamlessly integrated into existing models without altering the model architecture. We demonstrate the effectiveness of FATA on various models and scenarios on ImageNet-C and Office-Home, validating its superiority in diverse real-world conditions.
Multiple Areal Feature Aware Transportation Demand Prediction
Aug 23, 2024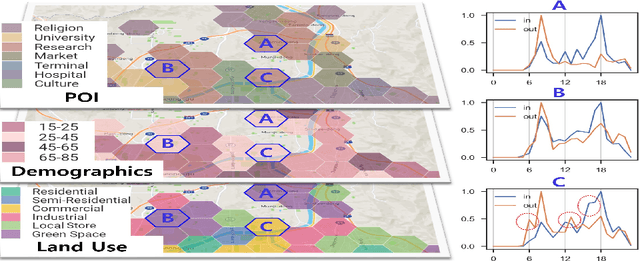
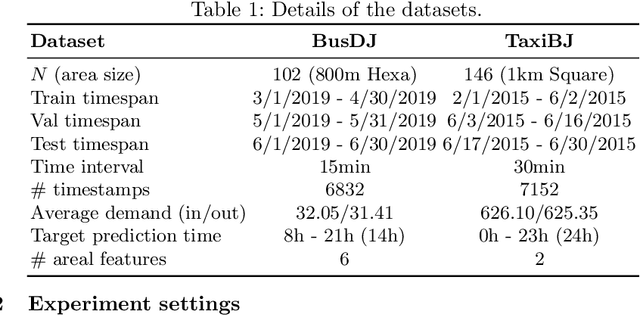
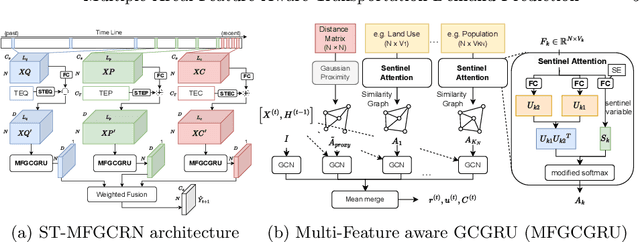
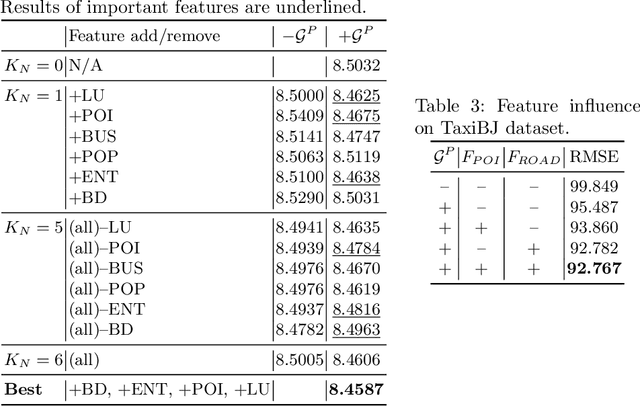
Abstract:A reliable short-term transportation demand prediction supports the authorities in improving the capability of systems by optimizing schedules, adjusting fleet sizes, and generating new transit networks. A handful of research efforts incorporate one or a few areal features while learning spatio-temporal correlation, to capture similar demand patterns between similar areas. However, urban characteristics are polymorphic, and they need to be understood by multiple areal features such as land use, sociodemographics, and place-of-interest (POI) distribution. In this paper, we propose a novel spatio-temporal multi-feature-aware graph convolutional recurrent network (ST-MFGCRN) that fuses multiple areal features during spatio-temproal understanding. Inside ST-MFGCRN, we devise sentinel attention to calculate the areal similarity matrix by allowing each area to take partial attention if the feature is not useful. We evaluate the proposed model on two real-world transportation datasets, one with our constructed BusDJ dataset and one with benchmark TaxiBJ. Results show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines up to 7\% on BusDJ and 8\% on TaxiBJ dataset.
Spatio-Temporal Road Traffic Prediction using Real-time Regional Knowledge
Aug 23, 2024Abstract:For traffic prediction in transportation services such as car-sharing and ride-hailing, mid-term road traffic prediction (within a few hours) is considered essential. However, the existing road-level traffic prediction has mainly studied how significantly micro traffic events propagate to the adjacent roads in terms of short-term prediction. On the other hand, recent attempts have been made to incorporate regional knowledge such as POIs, road characteristics, and real-time social events to help traffic prediction. However, these studies lack in understandings of different modalities of road-level and region-level spatio-temporal correlations and how to combine such knowledge. This paper proposes a novel method that embeds real-time region-level knowledge using POIs, satellite images, and real-time LTE access traces via a regional spatio-temporal module that consists of dynamic convolution and temporal attention, and conducts bipartite spatial transform attention to convert into road-level knowledge. Then the model ingests this embedded knowledge into a road-level attention-based prediction model. Experimental results on real-world road traffic prediction show that our model outperforms the baselines.
DOO-RE: A dataset of ambient sensors in a meeting room for activity recognition
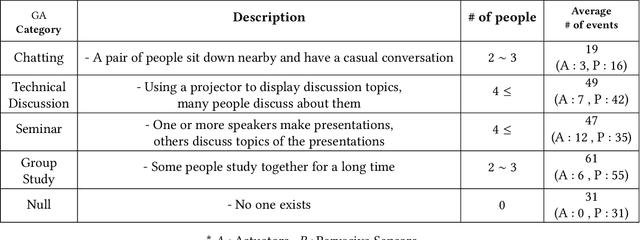
Jan 17, 2024Abstract:With the advancement of IoT technology, recognizing user activities with machine learning methods is a promising way to provide various smart services to users. High-quality data with privacy protection is essential for deploying such services in the real world. Data streams from surrounding ambient sensors are well suited to the requirement. Existing ambient sensor datasets only support constrained private spaces and those for public spaces have yet to be explored despite growing interest in research on them. To meet this need, we build a dataset collected from a meeting room equipped with ambient sensors. The dataset, DOO-RE, includes data streams from various ambient sensor types such as Sound and Projector. Each sensor data stream is segmented into activity units and multiple annotators provide activity labels through a cross-validation annotation process to improve annotation quality. We finally obtain 9 types of activities. To our best knowledge, DOO-RE is the first dataset to support the recognition of both single and group activities in a real meeting room with reliable annotations.
CLAN: A Contrastive Learning based Novelty Detection Framework for Human Activity Recognition
Jan 17, 2024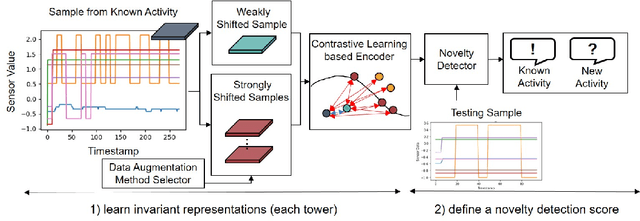
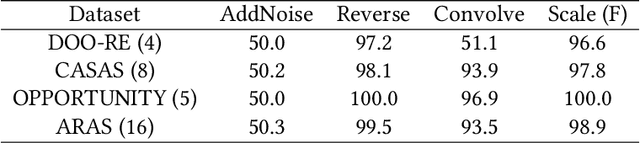
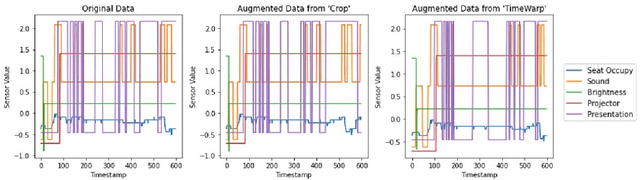
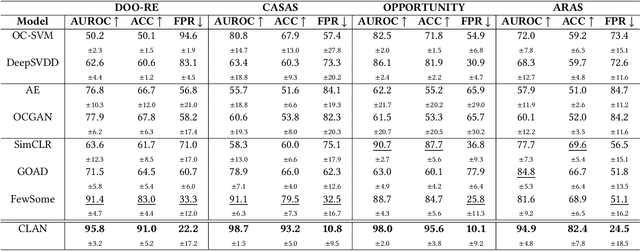
Abstract:In ambient assisted living, human activity recognition from time series sensor data mainly focuses on predefined activities, often overlooking new activity patterns. We propose CLAN, a two-tower contrastive learning-based novelty detection framework with diverse types of negative pairs for human activity recognition. It is tailored to challenges with human activity characteristics, including the significance of temporal and frequency features, complex activity dynamics, shared features across activities, and sensor modality variations. The framework aims to construct invariant representations of known activity robust to the challenges. To generate suitable negative pairs, it selects data augmentation methods according to the temporal and frequency characteristics of each dataset. It derives the key representations against meaningless dynamics by contrastive and classification losses-based representation learning and score function-based novelty detection that accommodate dynamic numbers of the different types of augmented samples. The proposed two-tower model extracts the representations in terms of time and frequency, mutually enhancing expressiveness for distinguishing between new and known activities, even when they share common features. Experiments on four real-world human activity datasets show that CLAN surpasses the best performance of existing novelty detection methods, improving by 8.3%, 13.7%, and 53.3% in AUROC, balanced accuracy, and FPR@TPR0.95 metrics respectively.
A Causality-Aware Pattern Mining Scheme for Group Activity Recognition in a Pervasive Sensor Space
Dec 01, 2023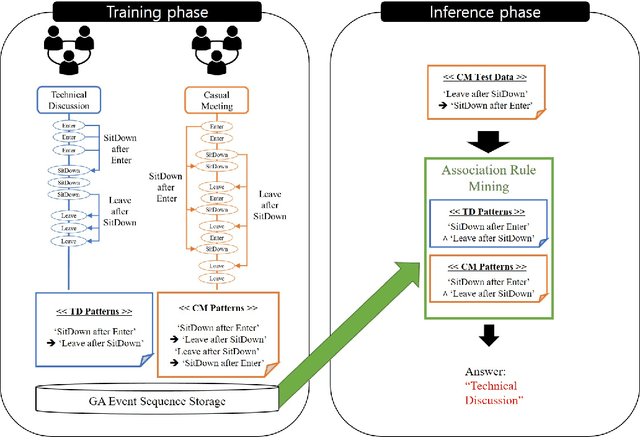
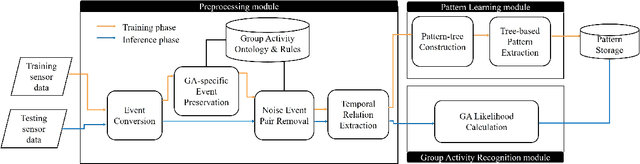
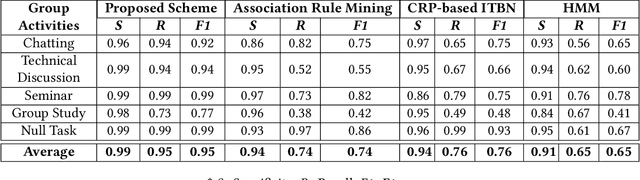
Abstract:Human activity recognition (HAR) is a key challenge in pervasive computing and its solutions have been presented based on various disciplines. Specifically, for HAR in a smart space without privacy and accessibility issues, data streams generated by deployed pervasive sensors are leveraged. In this paper, we focus on a group activity by which a group of users perform a collaborative task without user identification and propose an efficient group activity recognition scheme which extracts causality patterns from pervasive sensor event sequences generated by a group of users to support as good recognition accuracy as the state-of-the-art graphical model. To filter out irrelevant noise events from a given data stream, a set of rules is leveraged to highlight causally related events. Then, a pattern-tree algorithm extracts frequent causal patterns by means of a growing tree structure. Based on the extracted patterns, a weighted sum-based pattern matching algorithm computes the likelihoods of stored group activities to the given test event sequence by means of matched event pattern counts for group activity recognition. We evaluate the proposed scheme using the data collected from our testbed and CASAS datasets where users perform their tasks on a daily basis and validate its effectiveness in a real environment. Experiment results show that the proposed scheme performs higher recognition accuracy and with a small amount of runtime overhead than the existing schemes.
Beyond Entropy: Style Transfer Guided Single Image Continual Test-Time Adaptation
Nov 30, 2023



Abstract:Continual test-time adaptation (cTTA) methods are designed to facilitate the continual adaptation of models to dynamically changing real-world environments where computational resources are limited. Due to this inherent limitation, existing approaches fail to simultaneously achieve accuracy and efficiency. In detail, when using a single image, the instability caused by batch normalization layers and entropy loss significantly destabilizes many existing methods in real-world cTTA scenarios. To overcome these challenges, we present BESTTA, a novel single image continual test-time adaptation method guided by style transfer, which enables stable and efficient adaptation to the target environment by transferring the style of the input image to the source style. To implement the proposed method, we devise BeIN, a simple yet powerful normalization method, along with the style-guided losses. We demonstrate that BESTTA effectively adapts to the continually changing target environment, leveraging only a single image on both semantic segmentation and image classification tasks. Remarkably, despite training only two parameters in a BeIN layer consuming the least memory, BESTTA outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge