Dmytro Kalpakchi
Collecting Visually-Grounded Dialogue with A Game Of Sorts
Sep 10, 2023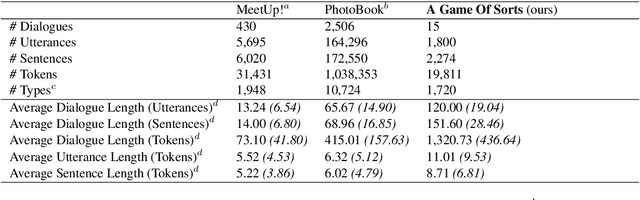
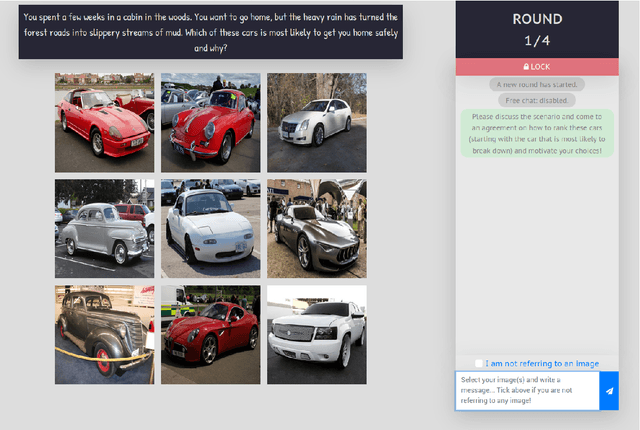
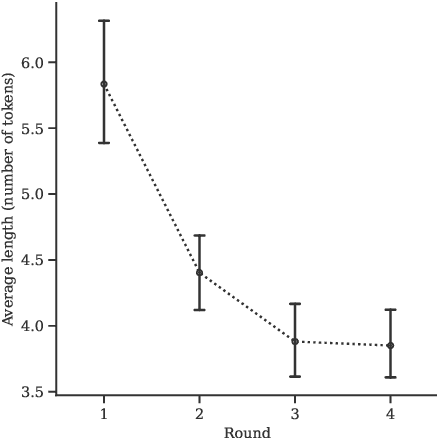
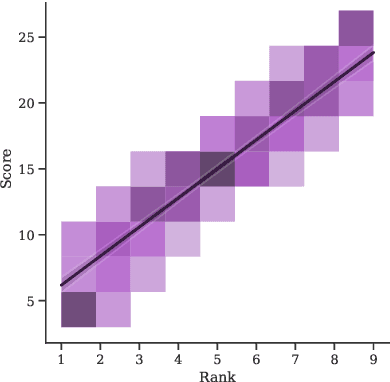
Abstract:An idealized, though simplistic, view of the referring expression production and grounding process in (situated) dialogue assumes that a speaker must merely appropriately specify their expression so that the target referent may be successfully identified by the addressee. However, referring in conversation is a collaborative process that cannot be aptly characterized as an exchange of minimally-specified referring expressions. Concerns have been raised regarding assumptions made by prior work on visually-grounded dialogue that reveal an oversimplified view of conversation and the referential process. We address these concerns by introducing a collaborative image ranking task, a grounded agreement game we call "A Game Of Sorts". In our game, players are tasked with reaching agreement on how to rank a set of images given some sorting criterion through a largely unrestricted, role-symmetric dialogue. By putting emphasis on the argumentation in this mixed-initiative interaction, we collect discussions that involve the collaborative referential process. We describe results of a small-scale data collection experiment with the proposed task. All discussed materials, which includes the collected data, the codebase, and a containerized version of the application, are publicly available.
* Published at LREC 2022
EMBRACE: Evaluation and Modifications for Boosting RACE
May 15, 2023
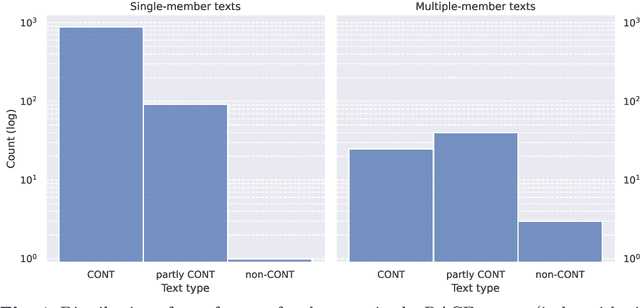


Abstract:When training and evaluating machine reading comprehension models, it is very important to work with high-quality datasets that are also representative of real-world reading comprehension tasks. This requirement includes, for instance, having questions that are based on texts of different genres and require generating inferences or reflecting on the reading material. In this article we turn our attention to RACE, a dataset of English texts and corresponding multiple-choice questions (MCQs). Each MCQ consists of a question and four alternatives (of which one is the correct answer). RACE was constructed by Chinese teachers of English for human reading comprehension and is widely used as training material for machine reading comprehension models. By construction, RACE should satisfy the aforementioned quality requirements and the purpose of this article is to check whether they are indeed satisfied. We provide a detailed analysis of the test set of RACE for high-school students (1045 texts and 3498 corresponding MCQs) including (1) an evaluation of the difficulty of each MCQ and (2) annotations for the relevant pieces of the texts (called "bases") that are used to justify the plausibility of each alternative. A considerable number of MCQs appear not to fulfill basic requirements for this type of reading comprehension tasks, so we additionally identify the high-quality subset of the evaluated RACE corpus. We also demonstrate that the distribution of the positions of the bases for the alternatives is biased towards certain parts of texts, which is not necessarily desirable when evaluating MCQ answering and generation models.
SweCTRL-Mini: a data-transparent Transformer-based large language model for controllable text generation in Swedish
May 13, 2023



Abstract:We present SweCTRL-Mini, a large Swedish language model that can be used for inference and fine-tuning on a single consumer-grade GPU. The model is based on the CTRL architecture by Keskar, McCann, Varshney, Xiong, and Socher (2019), which means that users of the SweCTRL-Mini model can control the genre of the generated text by inserting special tokens in the generation prompts. SweCTRL-Mini is trained on a subset of the Swedish part of the mC4 corpus and a set of Swedish novels. In this article, we provide (1) a detailed account of the utilized training data and text pre-processing steps, to the extent that it is possible to check whether a specific phrase/source was a part of the training data, and (2) an evaluation of the model on both discriminative tasks, using automatic evaluation methods, and generative tasks, using human referees. We also compare the generative capabilities of the model with those of GPT-3. SweCTRL-Mini is fully open and available for download.
Automatically generating question-answer pairs for assessing basic reading comprehension in Swedish
Nov 28, 2022

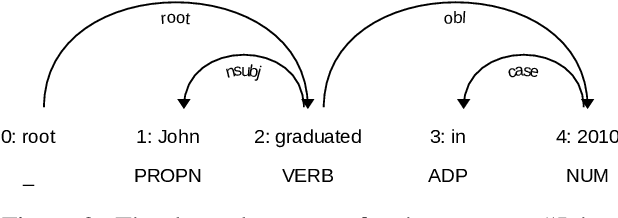
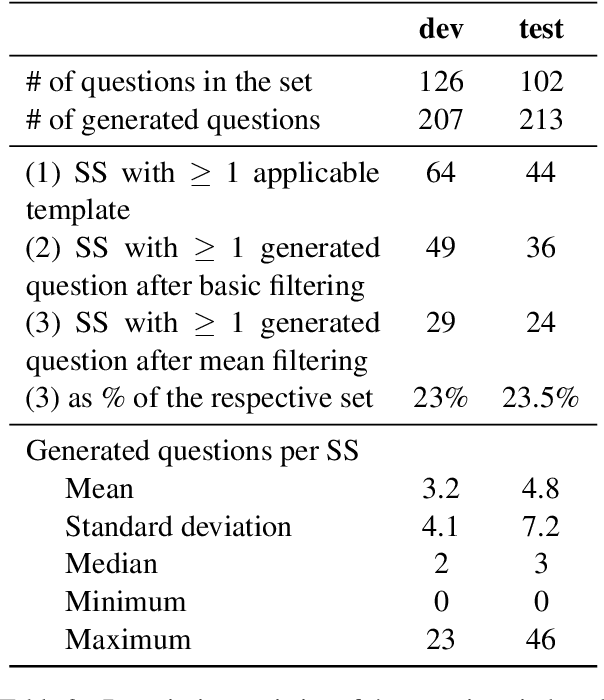
Abstract:This paper presents an evaluation of the quality of automatically generated reading comprehension questions from Swedish text, using the Quinductor method. This method is a light-weight, data-driven but non-neural method for automatic question generation (QG). The evaluation shows that Quinductor is a viable QG method that can provide a strong baseline for neural-network-based QG methods.
Minor changes make a difference: a case study on the consistency of UD-based dependency parsers
Nov 30, 2021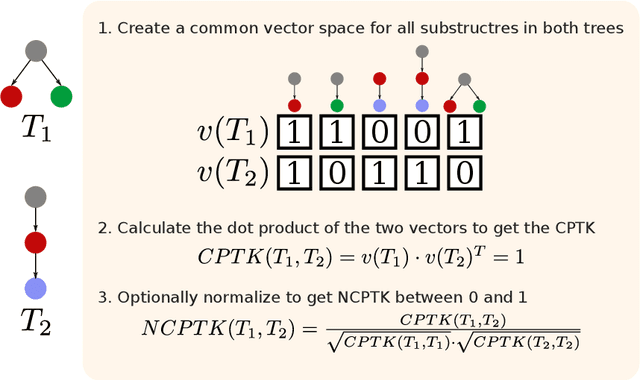
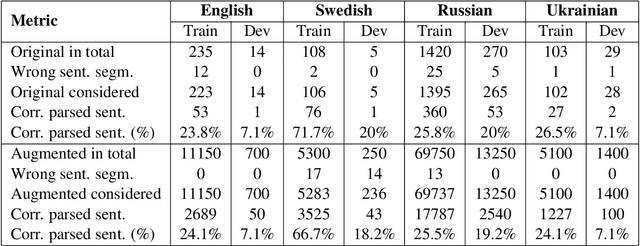
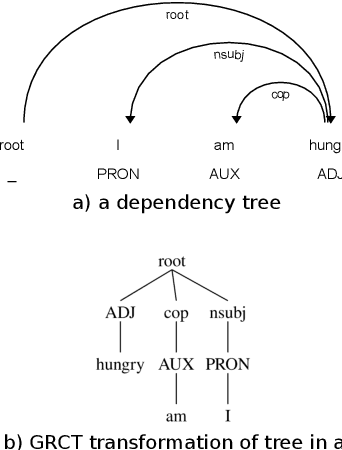
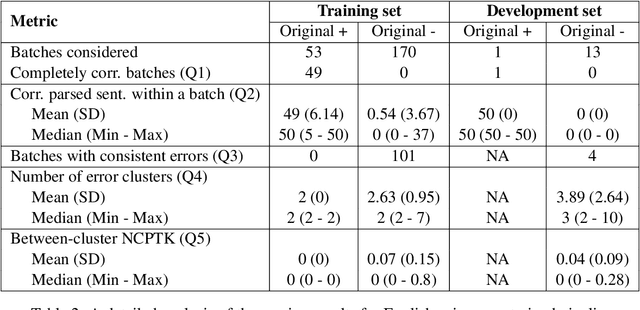
Abstract:Many downstream applications are using dependency trees, and are thus relying on dependency parsers producing correct, or at least consistent, output. However, dependency parsers are trained using machine learning, and are therefore susceptible to unwanted inconsistencies due to biases in the training data. This paper explores the effects of such biases in four languages - English, Swedish, Russian, and Ukrainian - though an experiment where we study the effect of replacing numerals in sentences. We show that such seemingly insignificant changes in the input can cause large differences in the output, and suggest that data augmentation can remedy the problems.
BERT-based distractor generation for Swedish reading comprehension questions using a small-scale dataset
Aug 09, 2021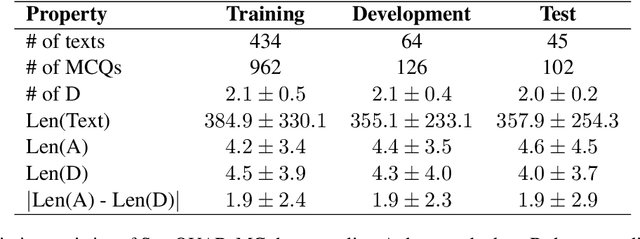
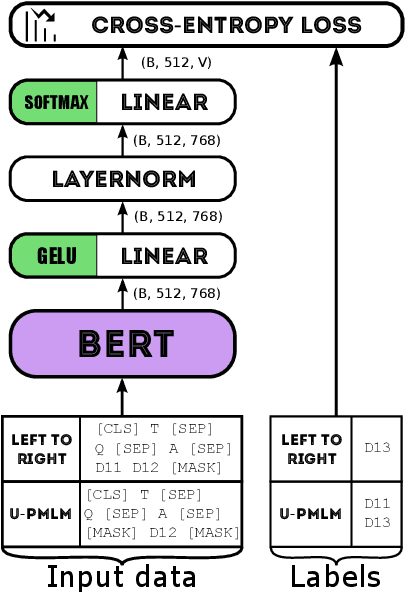
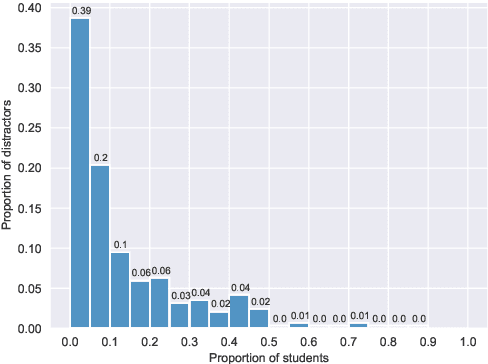
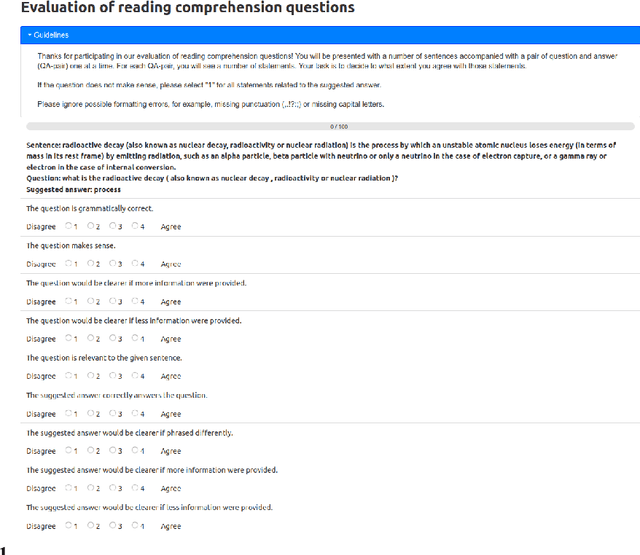
Abstract:An important part when constructing multiple-choice questions (MCQs) for reading comprehension assessment are the distractors, the incorrect but preferably plausible answer options. In this paper, we present a new BERT-based method for automatically generating distractors using only a small-scale dataset. We also release a new such dataset of Swedish MCQs (used for training the model), and propose a methodology for assessing the generated distractors. Evaluation shows that from a student's perspective, our method generated one or more plausible distractors for more than 50% of the MCQs in our test set. From a teacher's perspective, about 50% of the generated distractors were deemed appropriate. We also do a thorough analysis of the results.
Quinductor: a multilingual data-driven method for generating reading-comprehension questions using Universal Dependencies
Mar 18, 2021

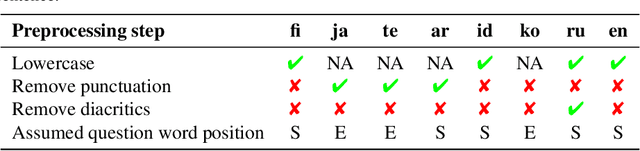
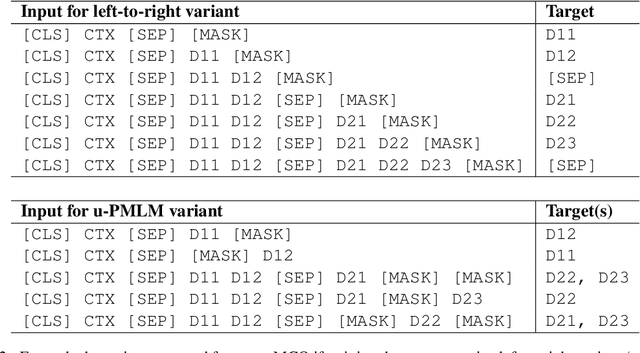
Abstract:We propose a multilingual data-driven method for generating reading comprehension questions using dependency trees. Our method provides a strong, mostly deterministic, and inexpensive-to-train baseline for less-resourced languages. While a language-specific corpus is still required, its size is nowhere near those required by modern neural question generation (QG) architectures. Our method surpasses QG baselines previously reported in the literature and shows a good performance in terms of human evaluation.
[Re] Learning to Learn By Self-Critique
Dec 05, 2019![Figure 1 for [Re] Learning to Learn By Self-Critique](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com%2Ffigures%2F2017-08-08%2F7e6471a725924938cbe0b5f9c124a46ecbcb345c%2F2-Figure1-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 2 for [Re] Learning to Learn By Self-Critique](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com%2Ffigures%2F2017-08-08%2F7e6471a725924938cbe0b5f9c124a46ecbcb345c%2F7-Table1-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 3 for [Re] Learning to Learn By Self-Critique](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com%2Ffigures%2F2017-08-08%2F7e6471a725924938cbe0b5f9c124a46ecbcb345c%2F4-Figure2-1.png&w=640&q=75)
![Figure 4 for [Re] Learning to Learn By Self-Critique](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fai2-s2-public.s3.amazonaws.com%2Ffigures%2F2017-08-08%2F7e6471a725924938cbe0b5f9c124a46ecbcb345c%2F7-Table2-1.png&w=640&q=75)
Abstract:This work is a reproducibility study of the paper of Antoniou and Storkey [2019], published at NeurIPS 2019. Our results are in parts similar to the ones reported in the original paper, supporting the central claim of the paper that the proposed novel method, called Self-Critique and Adapt (SCA), improves the performance of MAML++. The conducted additional experiments on the Caltech-UCSD Birds 200 dataset confirm the superiority of SCA compared to MAML++. In addition, the reproduced paper suggests a novel high-end version of MAML++ for which we could not reproduce the same results. We hypothesize that this is due to the many implementation details that were omitted in the original paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge