Mariia Zyrianova
EMBRACE: Evaluation and Modifications for Boosting RACE
May 15, 2023
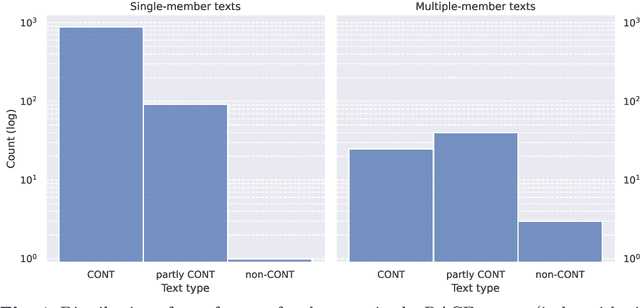


Abstract:When training and evaluating machine reading comprehension models, it is very important to work with high-quality datasets that are also representative of real-world reading comprehension tasks. This requirement includes, for instance, having questions that are based on texts of different genres and require generating inferences or reflecting on the reading material. In this article we turn our attention to RACE, a dataset of English texts and corresponding multiple-choice questions (MCQs). Each MCQ consists of a question and four alternatives (of which one is the correct answer). RACE was constructed by Chinese teachers of English for human reading comprehension and is widely used as training material for machine reading comprehension models. By construction, RACE should satisfy the aforementioned quality requirements and the purpose of this article is to check whether they are indeed satisfied. We provide a detailed analysis of the test set of RACE for high-school students (1045 texts and 3498 corresponding MCQs) including (1) an evaluation of the difficulty of each MCQ and (2) annotations for the relevant pieces of the texts (called "bases") that are used to justify the plausibility of each alternative. A considerable number of MCQs appear not to fulfill basic requirements for this type of reading comprehension tasks, so we additionally identify the high-quality subset of the evaluated RACE corpus. We also demonstrate that the distribution of the positions of the bases for the alternatives is biased towards certain parts of texts, which is not necessarily desirable when evaluating MCQ answering and generation models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge