Diganta Saha
Securing Social Spaces: Harnessing Deep Learning to Eradicate Cyberbullying
Apr 01, 2024



Abstract:In today's digital world, cyberbullying is a serious problem that can harm the mental and physical health of people who use social media. This paper explains just how serious cyberbullying is and how it really affects indi-viduals exposed to it. It also stresses how important it is to find better ways to detect cyberbullying so that online spaces can be safer. Plus, it talks about how making more accurate tools to spot cyberbullying will be really helpful in the future. Our paper introduces a deep learning-based ap-proach, primarily employing BERT and BiLSTM architectures, to effective-ly address cyberbullying. This approach is designed to analyse large vol-umes of posts and predict potential instances of cyberbullying in online spaces. Our results demonstrate the superiority of the hateBERT model, an extension of BERT focused on hate speech detection, among the five mod-els, achieving an accuracy rate of 89.16%. This research is a significant con-tribution to "Computational Intelligence for Social Transformation," prom-ising a safer and more inclusive digital landscape.
Analysis and Detection of Multilingual Hate Speech Using Transformer Based Deep Learning
Jan 19, 2024Abstract:Hate speech is harmful content that directly attacks or promotes hatred against members of groups or individuals based on actual or perceived aspects of identity, such as racism, religion, or sexual orientation. This can affect social life on social media platforms as hateful content shared through social media can harm both individuals and communities. As the prevalence of hate speech increases online, the demand for automated detection as an NLP task is increasing. In this work, the proposed method is using transformer-based model to detect hate speech in social media, like twitter, Facebook, WhatsApp, Instagram, etc. The proposed model is independent of languages and has been tested on Italian, English, German, Bengali. The Gold standard datasets were collected from renowned researcher Zeerak Talat, Sara Tonelli, Melanie Siegel, and Rezaul Karim. The success rate of the proposed model for hate speech detection is higher than the existing baseline and state-of-the-art models with accuracy in Bengali dataset is 89%, in English: 91%, in German dataset 91% and in Italian dataset it is 77%. The proposed algorithm shows substantial improvement to the benchmark method.
Improvement of electronic Governance and mobile Governance in Multilingual Countries with Digital Etymology using Sanskrit Grammar
Mar 31, 2020

Abstract:With huge improvement of digital connectivity (Wifi,3G,4G) and digital devices access to internet has reached in the remotest corners now a days. Rural people can easily access web or apps from PDAs, laptops, smartphones etc. This is an opportunity of the Government to reach to the citizen in large number, get their feedback, associate them in policy decision with e governance without deploying huge man, material or resourses. But the Government of multilingual countries face a lot of problem in successful implementation of Government to Citizen (G2C) and Citizen to Government (C2G) governance as the rural people tend and prefer to interact in their native languages. Presenting equal experience over web or app to different language group of speakers is a real challenge. In this research we have sorted out the problems faced by Indo Aryan speaking netizens which is in general also applicable to any language family groups or subgroups. Then we have tried to give probable solutions using Etymology. Etymology is used to correlate the words using their ROOT forms. In 5th century BC Panini wrote Astadhyayi where he depicted sutras or rules -- how a word is changed according to person,tense,gender,number etc. Later this book was followed in Western countries also to derive their grammar of comparatively new languages. We have trained our system for automatic root extraction from the surface level or morphed form of words using Panian Gramatical rules. We have tested our system over 10000 bengali Verbs and extracted the root form with 98% accuracy. We are now working to extend the program to successfully lemmatize any words of any language and correlate them by applying those rule sets in Artificial Neural Network.
Automatic Extraction of Bengali Root Verbs using Paninian Grammar
Mar 31, 2020


Abstract:In this research work, we have proposed an algorithm based on supervised learning methodology to extract the root forms of the Bengali verbs using the grammatical rules proposed by Panini [1] in Ashtadhyayi. This methodology can be applied for the languages which are derived from Sanskrit. The proposed system has been developed based on tense, person and morphological inflections of the verbs to find their root forms. The work has been executed in two phases: first, the surface level forms or inflected forms of the verbs have been classified into a certain number of groups of similar tense and person. For this task, a standard pattern, available in Bengali language has been used. Next, a set of rules have been applied to extract the root form from the surface level forms of a verb. The system has been tested on 10000 verbs collected from the Bengali text corpus developed in the TDIL project of the Govt. of India. The accuracy of the output has been achieved 98% which is verified by a linguistic expert. Root verb identification is a key step in semantic searching, multi-sentence search query processing, understanding the meaning of a language, disambiguation of word sense, classification of the sentences etc.
Belief Base Revision for Further Improvement of Unified Answer Set Programming
Feb 27, 2020
Abstract:A belief base revision is developed. The belief base is represented using Unified Answer Set Programs which is capable of representing imprecise and uncertain information and perform nonomonotonic reasoning with them. The base revision operator is developed using Removed Set Revision strategy. The operator is characterized with respect to the postulates for base revisions operator satisfies.
Modeling Uncertainty and Imprecision in Nonmonotonic Reasoning using Fuzzy Numbers
Jan 03, 2020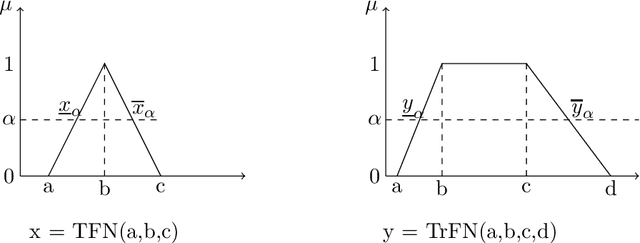
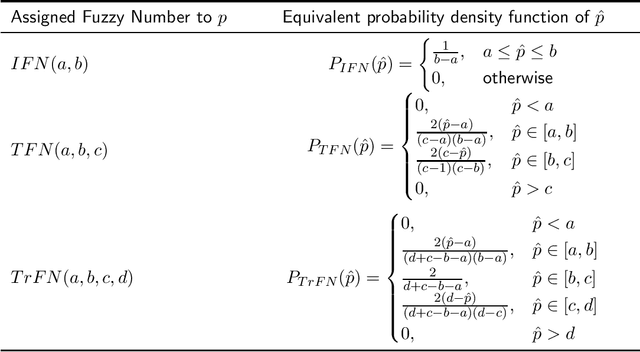

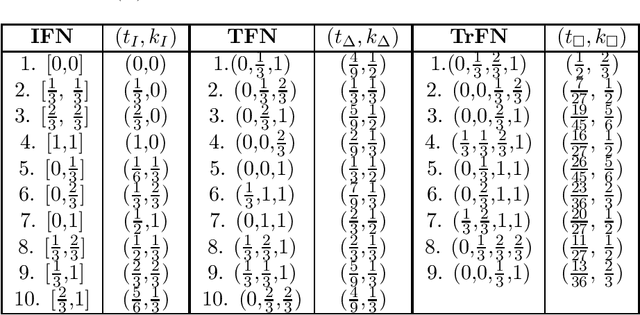
Abstract:To deal with uncertainty in reasoning, interval-valued logic has been developed. But uniform intervals cannot capture the difference in degrees of belief for different values in the interval. To salvage the problem triangular and trapezoidal fuzzy numbers are used as the set of truth values along with traditional intervals. Preorder-based truth and knowledge ordering are defined over the set of fuzzy numbers defined over $[0,1]$. Based on this enhanced set of epistemic states, an answer set framework is developed, with properly defined logical connectives. This type of framework is efficient in knowledge representation and reasoning with vague and uncertain information under nonmonotonic environment where rules may posses exceptions.
A Novel Approach to Enhance the Performance of Semantic Search in Bengali using Neural Net and other Classification Techniques
Nov 04, 2019



Abstract:Search has for a long time been an important tool for users to retrieve information. Syntactic search is matching documents or objects containing specific keywords like user-history, location, preference etc. to improve the results. However, it is often possible that the query and the best answer have no term or very less number of terms in common and syntactic search can not perform properly in such cases. Semantic search, on the other hand, resolves these issues but suffers from lack of annotation, absence of WordNet in case of low resource languages. In this work, we have demonstrated an end to end procedure to improve the performance of semantic search using semi-supervised and unsupervised learning algorithms. An available Bengali repository was chosen to have seven types of semantic properties primarily to develop the system. Performance has been tested using Support Vector Machine, Naive Bayes, Decision Tree and Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Our system has achieved the efficiency to predict the correct semantics using knowledge base over the time of learning. A repository containing around a million sentences, a product of TDIL project of Govt. of India, was used to test our system at first instance. Then the testing has been done for other languages. Being a cognitive system it may be very useful for improving user satisfaction in e-Governance or m-Governance in the multilingual environment and also for other applications.
A Unified Framework for Nonmonotonic Reasoning with Vagueness and Uncertainty
Oct 01, 2019



Abstract:An answer set programming paradigm is proposed that supports nonmonotonic reasoning with vague and uncertain information. The system can represent and reason with prioritized rules, rules with exceptions. An iterative method for answer set computation is proposed. The terminating conditions are identified for a class of logic programs using the notion of difference equations. In order to obtain the difference equations the set of rules are depicted by a signal-flow-graph like structure.
Preorder-Based Triangle: A Modified Version of Bilattice-Based Triangle for Belief Revision in Nonmonotonic Reasoning
Nov 07, 2017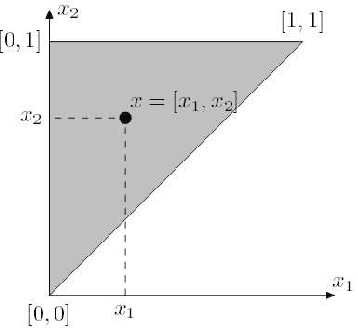
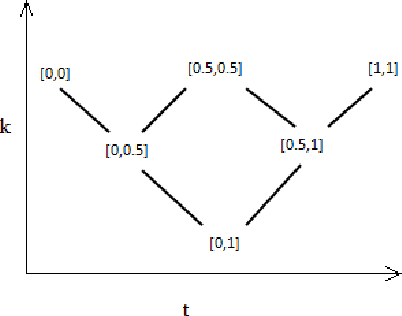
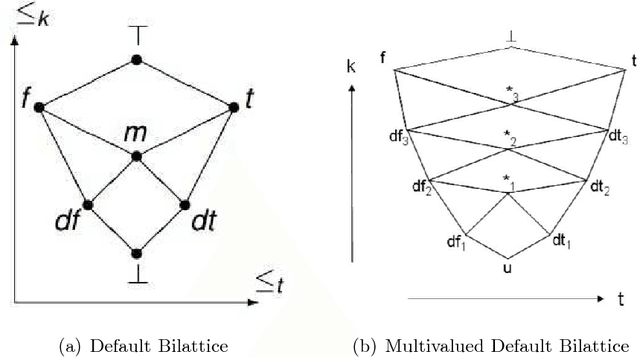
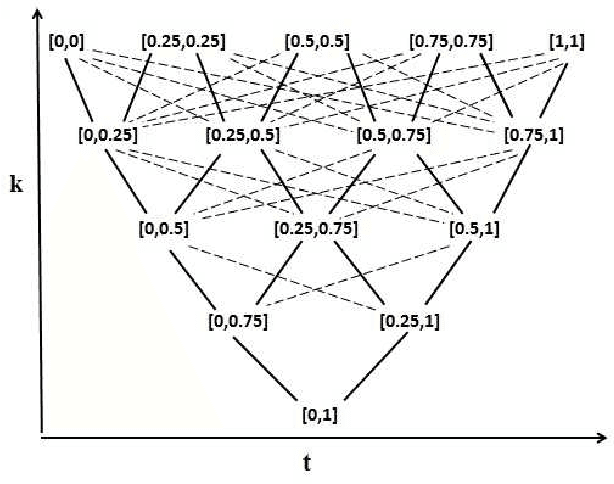
Abstract:Bilattice-based triangle provides an elegant algebraic structure for reasoning with vague and uncertain information. But the truth and knowledge ordering of intervals in bilattice-based triangle can not handle repetitive belief revisions which is an essential characteristic of nonmonotonic reasoning. Moreover the ordering induced over the intervals by the bilattice-based triangle is not sometimes intuitive. In this work, we construct an alternative algebraic structure, namely preorder-based triangle and we formulate proper logical connectives for this. It is also demonstrated that Preorder-based triangle serves to be a better alternative to the bilattice-based triangle for reasoning in application areas, that involve nonmonotonic fuzzy reasoning with uncertain information.
Detection of Slang Words in e-Data using semi-Supervised Learning
Nov 19, 2015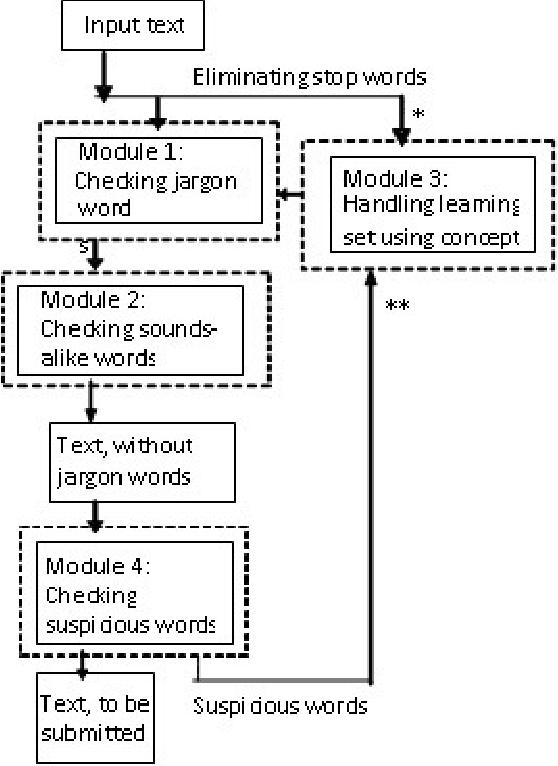
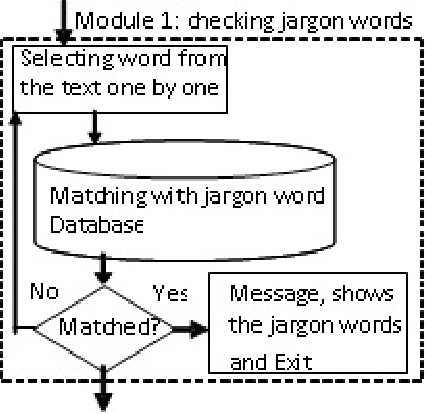
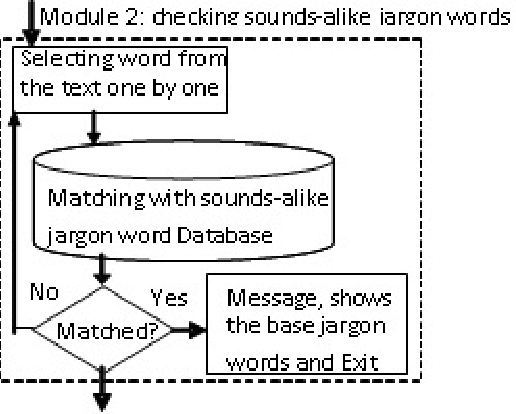
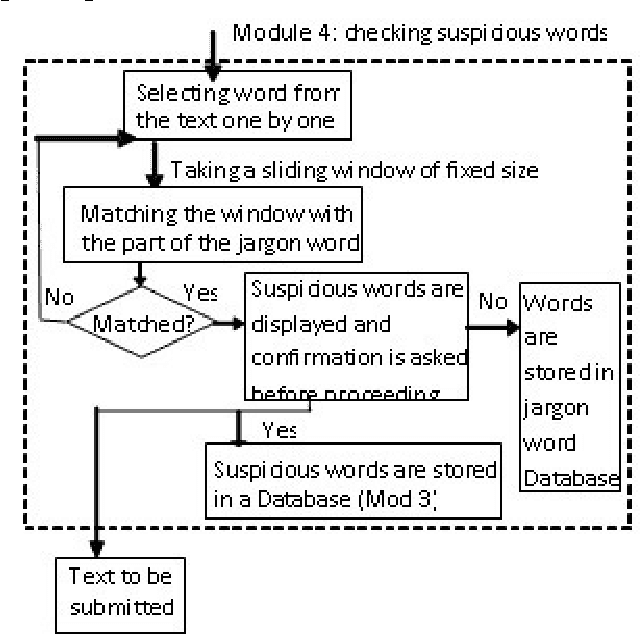
Abstract:The proposed algorithmic approach deals with finding the sense of a word in an electronic data. Now a day,in different communication mediums like internet, mobile services etc. people use few words, which are slang in nature. This approach detects those abusive words using supervised learning procedure. But in the real life scenario, the slang words are not used in complete word forms always. Most of the times, those words are used in different abbreviated forms like sounds alike forms, taboo morphemes etc. This proposed approach can detect those abbreviated forms also using semi supervised learning procedure. Using the synset and concept analysis of the text, the probability of a suspicious word to be a slang word is also evaluated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge