Kumar Sankar Ray
Bayesian Brain: Computation with Perception to Recognize 3D Objects
Nov 23, 2022Abstract:We mimic the cognitive ability of Human perception, based on Bayesian hypothesis, to recognize view-based 3D objects. We consider approximate Bayesian (Empirical Bayesian) for perceptual inference for recognition. We essentially handle computation with perception.
Belief Base Revision for Further Improvement of Unified Answer Set Programming
Feb 27, 2020
Abstract:A belief base revision is developed. The belief base is represented using Unified Answer Set Programs which is capable of representing imprecise and uncertain information and perform nonomonotonic reasoning with them. The base revision operator is developed using Removed Set Revision strategy. The operator is characterized with respect to the postulates for base revisions operator satisfies.
Modeling Uncertainty and Imprecision in Nonmonotonic Reasoning using Fuzzy Numbers
Jan 03, 2020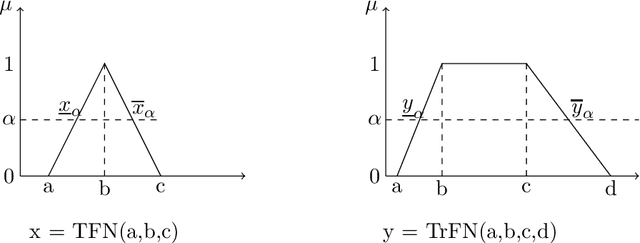
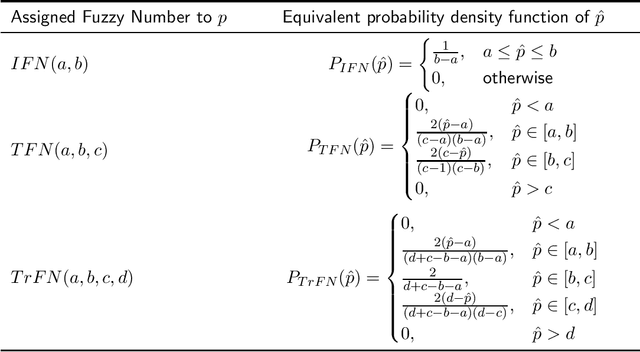

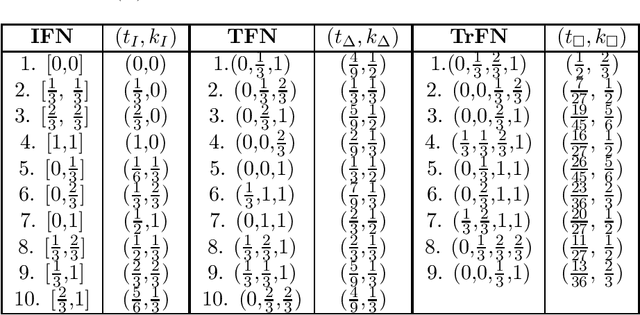
Abstract:To deal with uncertainty in reasoning, interval-valued logic has been developed. But uniform intervals cannot capture the difference in degrees of belief for different values in the interval. To salvage the problem triangular and trapezoidal fuzzy numbers are used as the set of truth values along with traditional intervals. Preorder-based truth and knowledge ordering are defined over the set of fuzzy numbers defined over $[0,1]$. Based on this enhanced set of epistemic states, an answer set framework is developed, with properly defined logical connectives. This type of framework is efficient in knowledge representation and reasoning with vague and uncertain information under nonmonotonic environment where rules may posses exceptions.
Bitopological Duality for Algebras of Fittings logic and Natural Duality extension
Dec 11, 2019Abstract:In this paper, we investigate a bitopological duality for algebras of Fitting's multi-valued logic. We also extend the natural duality theory for $\mathbb{ISP_I}(\mathcal{L})$ by developing a duality for $\mathbb{ISP}(\mathcal{L})$, where $\mathcal{L}$ is a finite algebra in which underlying lattice is bounded distributive.
A Unified Framework for Nonmonotonic Reasoning with Vagueness and Uncertainty
Oct 01, 2019



Abstract:An answer set programming paradigm is proposed that supports nonmonotonic reasoning with vague and uncertain information. The system can represent and reason with prioritized rules, rules with exceptions. An iterative method for answer set computation is proposed. The terminating conditions are identified for a class of logic programs using the notion of difference equations. In order to obtain the difference equations the set of rules are depicted by a signal-flow-graph like structure.
Preorder-Based Triangle: A Modified Version of Bilattice-Based Triangle for Belief Revision in Nonmonotonic Reasoning
Nov 07, 2017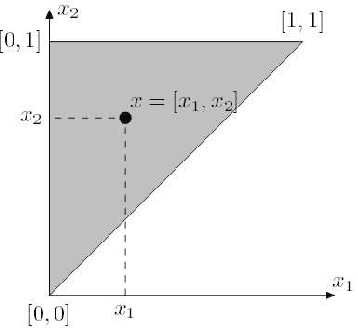
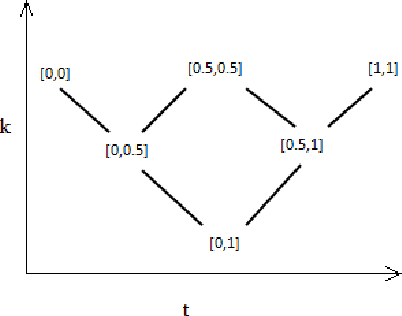
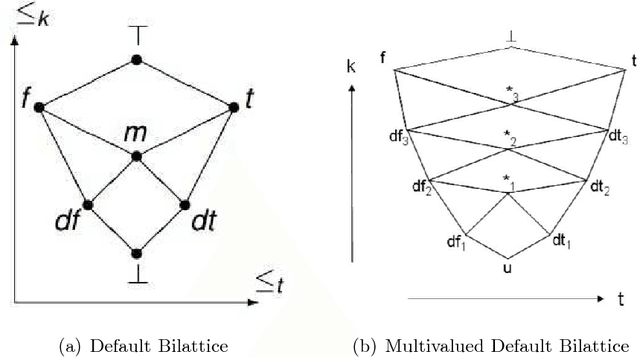
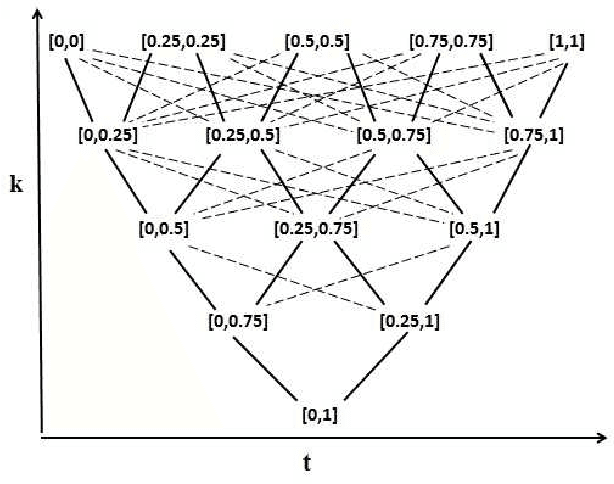
Abstract:Bilattice-based triangle provides an elegant algebraic structure for reasoning with vague and uncertain information. But the truth and knowledge ordering of intervals in bilattice-based triangle can not handle repetitive belief revisions which is an essential characteristic of nonmonotonic reasoning. Moreover the ordering induced over the intervals by the bilattice-based triangle is not sometimes intuitive. In this work, we construct an alternative algebraic structure, namely preorder-based triangle and we formulate proper logical connectives for this. It is also demonstrated that Preorder-based triangle serves to be a better alternative to the bilattice-based triangle for reasoning in application areas, that involve nonmonotonic fuzzy reasoning with uncertain information.
K+ Means : An Enhancement Over K-Means Clustering Algorithm
Jun 22, 2017Abstract:K-means (MacQueen, 1967) [1] is one of the simplest unsupervised learning algorithms that solve the well-known clustering problem. The procedure follows a simple and easy way to classify a given data set to a predefined, say K number of clusters. Determination of K is a difficult job and it is not known that which value of K can partition the objects as per our intuition. To overcome this problem we proposed K+ Means algorithm. This algorithm is an enhancement over K-Means algorithm.
Prediction of Radiation Fog by DNA Computing
Jul 07, 2015



Abstract:In this paper we propose a wet lab algorithm for prediction of radiation fog by DNA computing. The concept of DNA computing is essentially exploited for generating the classifier algorithm in the wet lab. The classifier is based on a new concept of similarity based fuzzy reasoning suitable for wet lab implementation. This new concept of similarity based fuzzy reasoning is different from conventional approach to fuzzy reasoning based on similarity measure and also replaces the logical aspect of classical fuzzy reasoning by DNA chemistry. Thus, we add a new dimension to existing forms of fuzzy reasoning by bringing it down to nanoscale. We exploit the concept of massive parallelism of DNA computing by designing this new classifier in the wet lab. This newly designed classifier is very much generalized in nature and apart from prediction of radiation fog this methodology can be applied to other types of data also. To achieve our goal we first fuzzify the given observed parameters in a form of synthetic DNA sequence which is called fuzzy DNA and which handles the vague concept of human reasoning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge