Dieter Theiler
Reproducibility in Machine Learning-based Research: Overview, Barriers and Drivers
Jun 20, 2024Abstract:Research in various fields is currently experiencing challenges regarding the reproducibility of results. This problem is also prevalent in machine learning (ML) research. The issue arises primarily due to unpublished data and/or source code and the sensitivity of ML training conditions. Although different solutions have been proposed to address this issue, such as using ML platforms, the level of reproducibility in ML-driven research remains unsatisfactory. Therefore, in this article, we discuss the reproducibility of ML-driven research with three main aims: (i) identify the barriers to reproducibility when applying ML in research as well as categorize the barriers to different types of reproducibility (description, code, data, and experiment reproducibility), (ii) identify potential drivers such as tools, practices, and interventions that support ML reproducibility as well as distinguish between technology-driven drivers, procedural drivers, and drivers related to awareness and education, and (iii) map the drivers to the barriers. With this work, we hope to provide insights and contribute to the decision-making process regarding the adoption of different solutions to support ML reproducibility.
Reproducibility in Machine Learning-Driven Research
Jul 19, 2023
Abstract:Research is facing a reproducibility crisis, in which the results and findings of many studies are difficult or even impossible to reproduce. This is also the case in machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) research. Often, this is the case due to unpublished data and/or source-code, and due to sensitivity to ML training conditions. Although different solutions to address this issue are discussed in the research community such as using ML platforms, the level of reproducibility in ML-driven research is not increasing substantially. Therefore, in this mini survey, we review the literature on reproducibility in ML-driven research with three main aims: (i) reflect on the current situation of ML reproducibility in various research fields, (ii) identify reproducibility issues and barriers that exist in these research fields applying ML, and (iii) identify potential drivers such as tools, practices, and interventions that support ML reproducibility. With this, we hope to contribute to decisions on the viability of different solutions for supporting ML reproducibility.
Uptrendz: API-Centric Real-time Recommendations in Multi-Domain Settings
Jan 03, 2023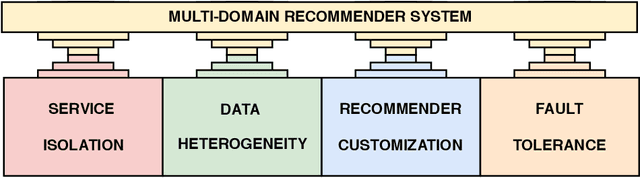
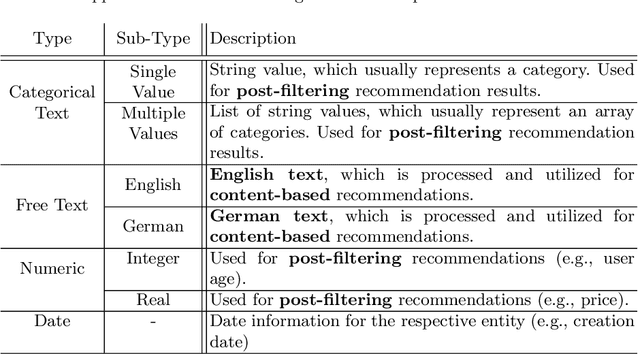
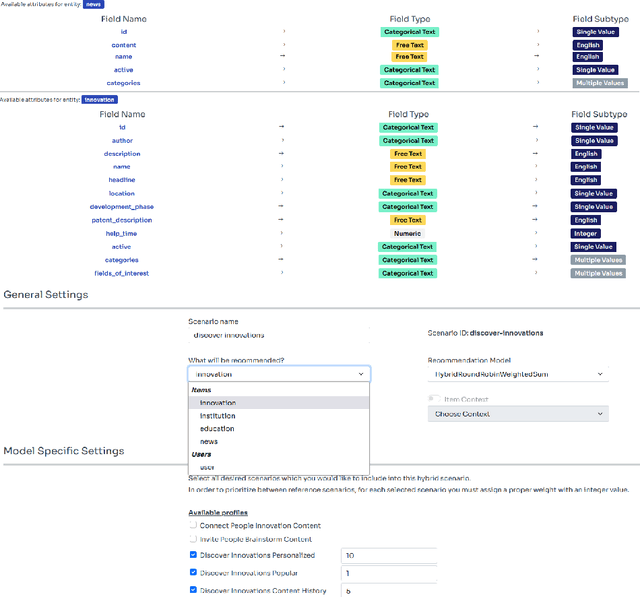

Abstract:In this work, we tackle the problem of adapting a real-time recommender system to multiple application domains, and their underlying data models and customization requirements. To do that, we present Uptrendz, a multi-domain recommendation platform that can be customized to provide real-time recommendations in an API-centric way. We demonstrate (i) how to set up a real-time movie recommender using the popular MovieLens-100k dataset, and (ii) how to simultaneously support multiple application domains based on the use-case of recommendations in entrepreneurial start-up founding. For that, we differentiate between domains on the item- and system-level. We believe that our demonstration shows a convenient way to adapt, deploy and evaluate a recommender system in an API-centric way. The source-code and documentation that demonstrates how to utilize the configured Uptrendz API is available on GitHub.
Evaluating Tag Recommendations for E-Book Annotation Using a Semantic Similarity Metric
Aug 12, 2019


Abstract:In this paper, we present our work to support publishers and editors in finding descriptive tags for e-books through tag recommendations. We propose a hybrid tag recommendation system for e-books, which leverages search query terms from Amazon users and e-book metadata, which is assigned by publishers and editors. Our idea is to mimic the vocabulary of users in Amazon, who search for and review e-books, and to combine these search terms with editor tags in a hybrid tag recommendation approach. In total, we evaluate 19 tag recommendation algorithms on the review content of Amazon users, which reflects the readers' vocabulary. Our results show that we can improve the performance of tag recommender systems for e-books both concerning tag recommendation accuracy, diversity as well as a novel semantic similarity metric, which we also propose in this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge