Leon Fadljevic
Uptrendz: API-Centric Real-time Recommendations in Multi-Domain Settings
Jan 03, 2023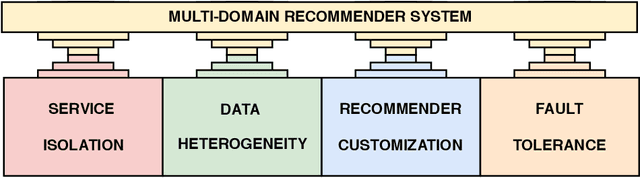
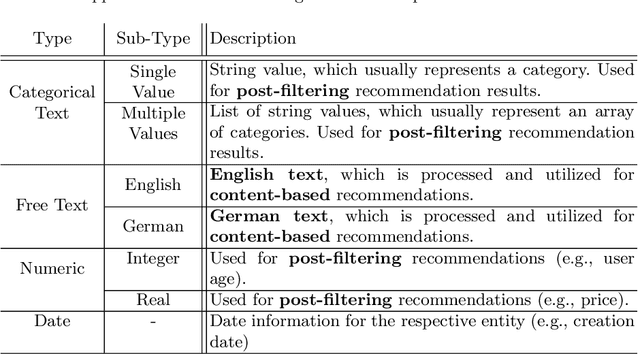
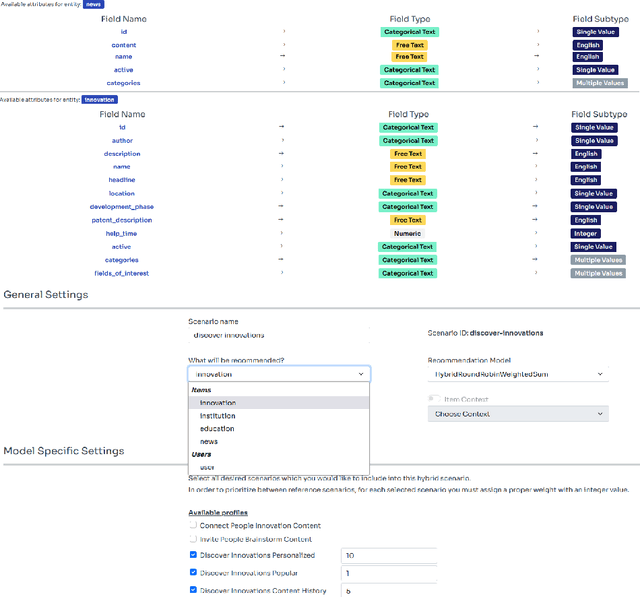

Abstract:In this work, we tackle the problem of adapting a real-time recommender system to multiple application domains, and their underlying data models and customization requirements. To do that, we present Uptrendz, a multi-domain recommendation platform that can be customized to provide real-time recommendations in an API-centric way. We demonstrate (i) how to set up a real-time movie recommender using the popular MovieLens-100k dataset, and (ii) how to simultaneously support multiple application domains based on the use-case of recommendations in entrepreneurial start-up founding. For that, we differentiate between domains on the item- and system-level. We believe that our demonstration shows a convenient way to adapt, deploy and evaluate a recommender system in an API-centric way. The source-code and documentation that demonstrates how to utilize the configured Uptrendz API is available on GitHub.
What Drives Readership? An Online Study on User Interface Types and Popularity Bias Mitigation in News Article Recommendations
Nov 29, 2021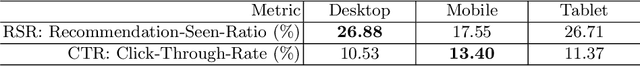
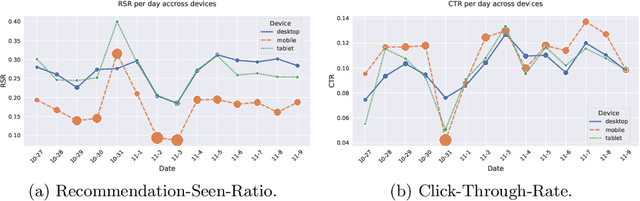
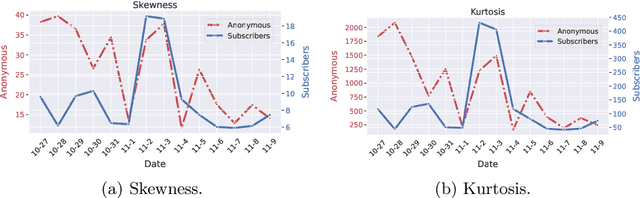
Abstract:Personalized news recommender systems support readers in finding the right and relevant articles in online news platforms. In this paper, we discuss the introduction of personalized, content-based news recommendations on DiePresse, a popular Austrian online news platform, focusing on two specific aspects: (i) user interface type, and (ii) popularity bias mitigation. Therefore, we conducted a two-weeks online study that started in October 2020, in which we analyzed the impact of recommendations on two user groups, i.e., anonymous and subscribed users, and three user interface types, i.e., on a desktop, mobile and tablet device. With respect to user interface types, we find that the probability of a recommendation to be seen is the highest for desktop devices, while the probability of interacting with recommendations is the highest for mobile devices. With respect to popularity bias mitigation, we find that personalized, content-based news recommendations can lead to a more balanced distribution of news articles' readership popularity in the case of anonymous users. Apart from that, we find that significant events (e.g., the COVID-19 lockdown announcement in Austria and the Vienna terror attack) influence the general consumption behavior of popular articles for both, anonymous and subscribed users.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge