Dian Qin
Hilbert Distillation for Cross-Dimensionality Networks
Nov 08, 2022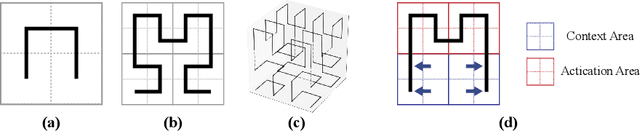
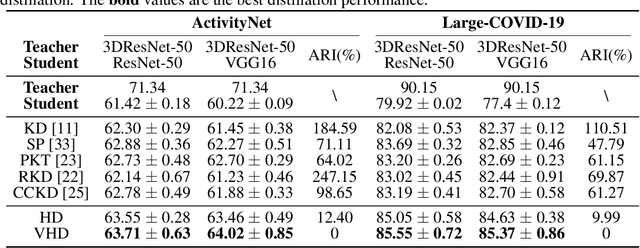
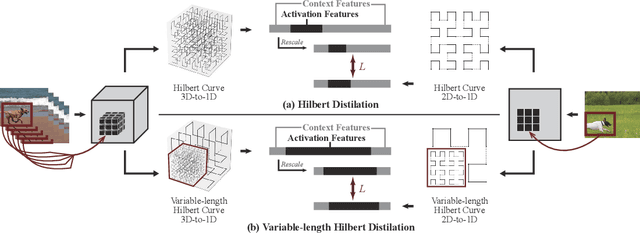
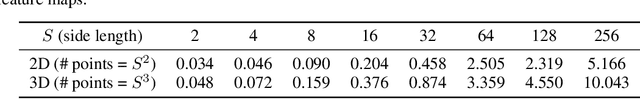
Abstract:3D convolutional neural networks have revealed superior performance in processing volumetric data such as video and medical imaging. However, the competitive performance by leveraging 3D networks results in huge computational costs, which are far beyond that of 2D networks. In this paper, we propose a novel Hilbert curve-based cross-dimensionality distillation approach that facilitates the knowledge of 3D networks to improve the performance of 2D networks. The proposed Hilbert Distillation (HD) method preserves the structural information via the Hilbert curve, which maps high-dimensional (>=2) representations to one-dimensional continuous space-filling curves. Since the distilled 2D networks are supervised by the curves converted from dimensionally heterogeneous 3D features, the 2D networks are given an informative view in terms of learning structural information embedded in well-trained high-dimensional representations. We further propose a Variable-length Hilbert Distillation (VHD) method to dynamically shorten the walking stride of the Hilbert curve in activation feature areas and lengthen the stride in context feature areas, forcing the 2D networks to pay more attention to learning from activation features. The proposed algorithm outperforms the current state-of-the-art distillation techniques adapted to cross-dimensionality distillation on two classification tasks. Moreover, the distilled 2D networks by the proposed method achieve competitive performance with the original 3D networks, indicating the lightweight distilled 2D networks could potentially be the substitution of cumbersome 3D networks in the real-world scenario.
Efficient Medical Image Segmentation Based on Knowledge Distillation
Aug 23, 2021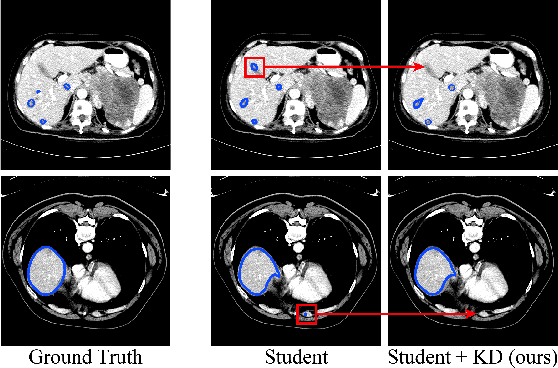
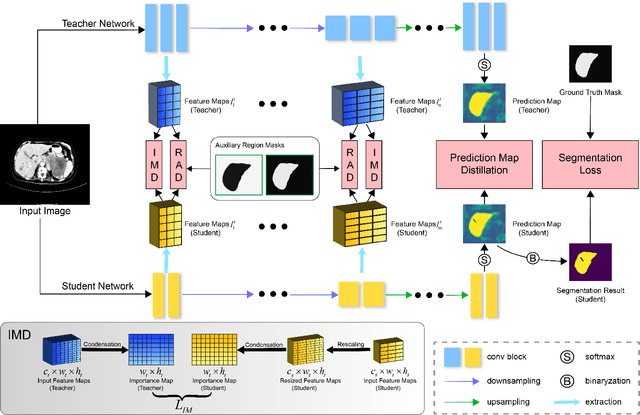
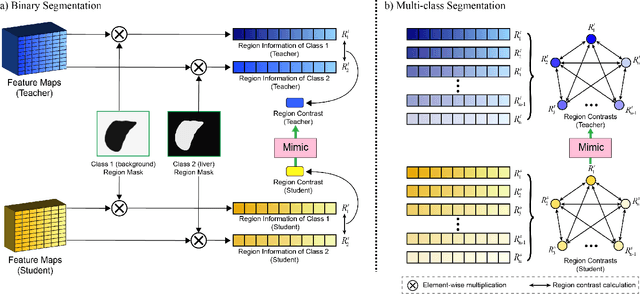
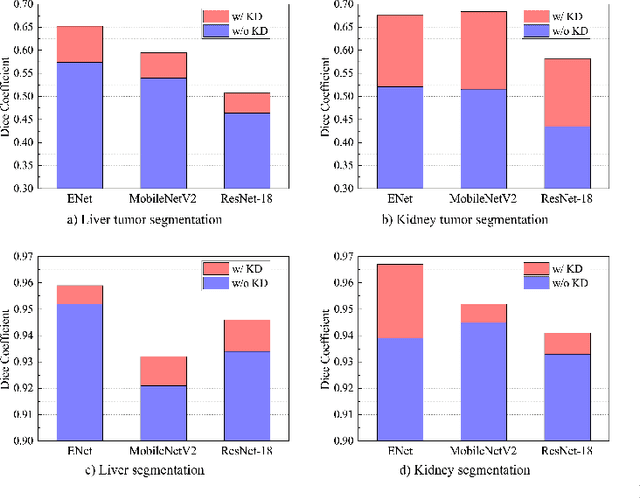
Abstract:Recent advances have been made in applying convolutional neural networks to achieve more precise prediction results for medical image segmentation problems. However, the success of existing methods has highly relied on huge computational complexity and massive storage, which is impractical in the real-world scenario. To deal with this problem, we propose an efficient architecture by distilling knowledge from well-trained medical image segmentation networks to train another lightweight network. This architecture empowers the lightweight network to get a significant improvement on segmentation capability while retaining its runtime efficiency. We further devise a novel distillation module tailored for medical image segmentation to transfer semantic region information from teacher to student network. It forces the student network to mimic the extent of difference of representations calculated from different tissue regions. This module avoids the ambiguous boundary problem encountered when dealing with medical imaging but instead encodes the internal information of each semantic region for transferring. Benefited from our module, the lightweight network could receive an improvement of up to 32.6% in our experiment while maintaining its portability in the inference phase. The entire structure has been verified on two widely accepted public CT datasets LiTS17 and KiTS19. We demonstrate that a lightweight network distilled by our method has non-negligible value in the scenario which requires relatively high operating speed and low storage usage.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge