Demir Arikan
Towards Motion Compensation in Autonomous Robotic Subretinal Injections
Nov 27, 2024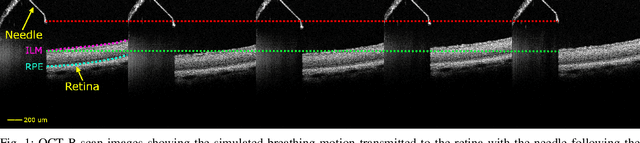
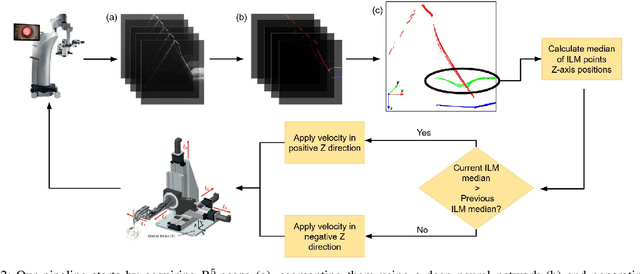

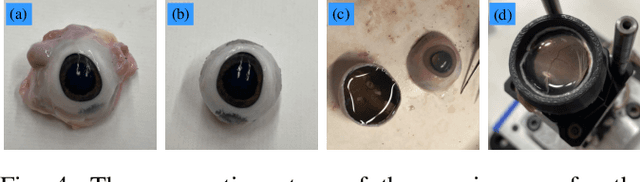
Abstract:Exudative (wet) age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is a leading cause of vision loss in older adults, typically treated with intravitreal injections. Emerging therapies, such as subretinal injections of stem cells, gene therapy, small molecules or RPE cells require precise delivery to avoid damaging delicate retinal structures. Autonomous robotic systems can potentially offer the necessary precision for these procedures. This paper presents a novel approach for motion compensation in robotic subretinal injections, utilizing real-time Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). The proposed method leverages B$^{5}$-scans, a rapid acquisition of small-volume OCT data, for dynamic tracking of retinal motion along the Z-axis, compensating for physiological movements such as breathing and heartbeat. Validation experiments on \textit{ex vivo} porcine eyes revealed challenges in maintaining a consistent tool-to-retina distance, with deviations of up to 200 $\mu m$ for 100 $\mu m$ amplitude motions and over 80 $\mu m$ for 25 $\mu m$ amplitude motions over one minute. Subretinal injections faced additional difficulties, with horizontal shifts causing the needle to move off-target and inject into the vitreous. These results highlight the need for improved motion prediction and horizontal stability to enhance the accuracy and safety of robotic subretinal procedures.
Real-time Deformation-aware Control for Autonomous Robotic Subretinal Injection under iOCT Guidance
Nov 10, 2024



Abstract:Robotic platforms provide repeatable and precise tool positioning that significantly enhances retinal microsurgery. Integration of such systems with intraoperative optical coherence tomography (iOCT) enables image-guided robotic interventions, allowing to autonomously perform advanced treatment possibilities, such as injecting therapeutic agents into the subretinal space. Yet, tissue deformations due to tool-tissue interactions are a major challenge in autonomous iOCT-guided robotic subretinal injection, impacting correct needle positioning and, thus, the outcome of the procedure. This paper presents a novel method for autonomous subretinal injection under iOCT guidance that considers tissue deformations during the insertion procedure. This is achieved through real-time segmentation and 3D reconstruction of the surgical scene from densely sampled iOCT B-scans, which we refer to as B5-scans, to monitor the positioning of the instrument regarding a virtual target layer defined at a relative position between the ILM and RPE. Our experiments on ex-vivo porcine eyes demonstrate dynamic adjustment of the insertion depth and overall improved accuracy in needle positioning compared to previous autonomous insertion approaches. Compared to a 35% success rate in subretinal bleb generation with previous approaches, our proposed method reliably and robustly created subretinal blebs in all our experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge