Deepesh Mehta
Balancing Discriminability and Transferability for Source-Free Domain Adaptation
Jun 16, 2022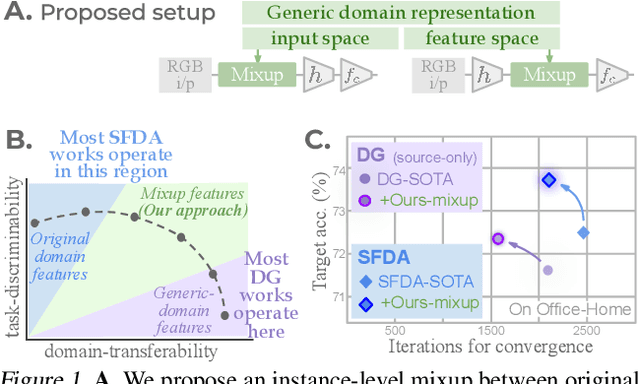
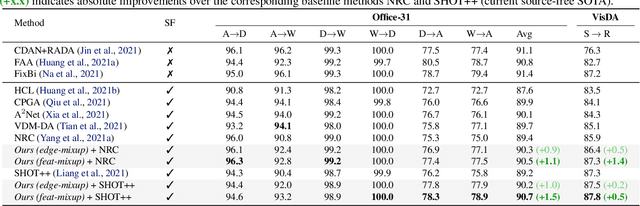
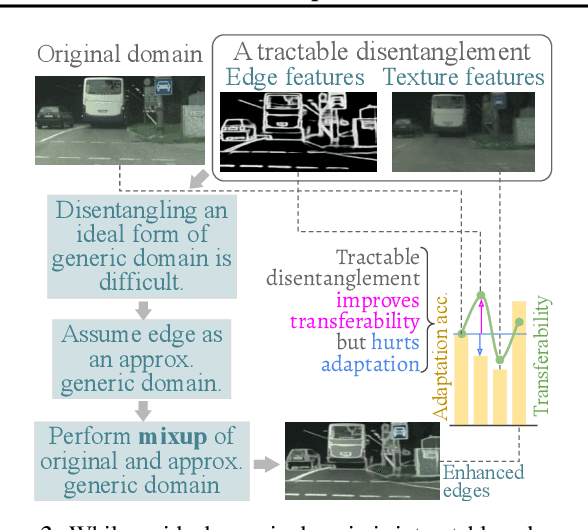
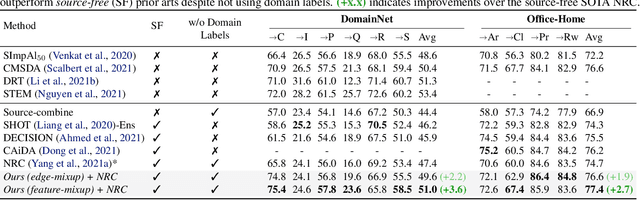
Abstract:Conventional domain adaptation (DA) techniques aim to improve domain transferability by learning domain-invariant representations; while concurrently preserving the task-discriminability knowledge gathered from the labeled source data. However, the requirement of simultaneous access to labeled source and unlabeled target renders them unsuitable for the challenging source-free DA setting. The trivial solution of realizing an effective original to generic domain mapping improves transferability but degrades task discriminability. Upon analyzing the hurdles from both theoretical and empirical standpoints, we derive novel insights to show that a mixup between original and corresponding translated generic samples enhances the discriminability-transferability trade-off while duly respecting the privacy-oriented source-free setting. A simple but effective realization of the proposed insights on top of the existing source-free DA approaches yields state-of-the-art performance with faster convergence. Beyond single-source, we also outperform multi-source prior-arts across both classification and semantic segmentation benchmarks.
GI-NNet \& RGI-NNet: Development of Robotic Grasp Pose Models, Trainable with Large as well as Limited Labelled Training Datasets, under supervised and semi supervised paradigms
Jul 15, 2021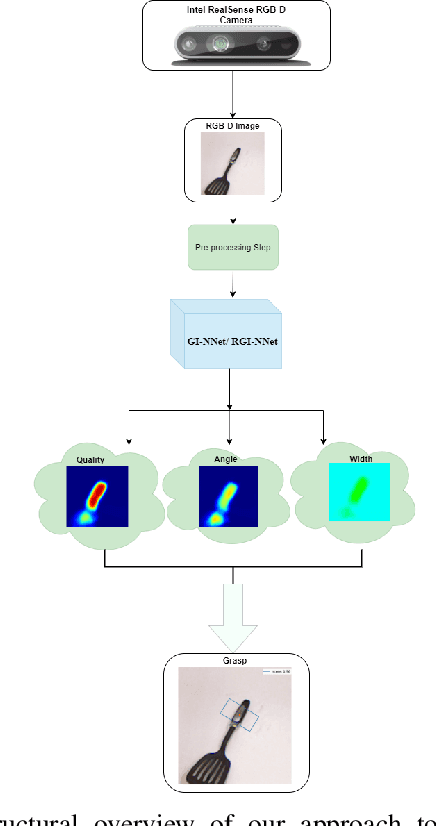
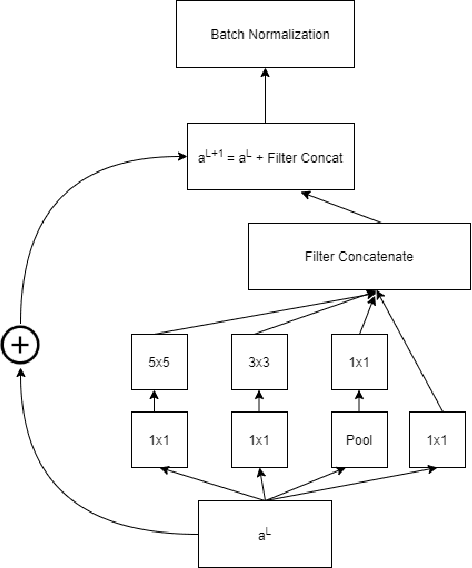
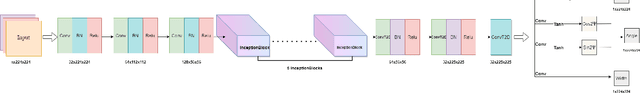
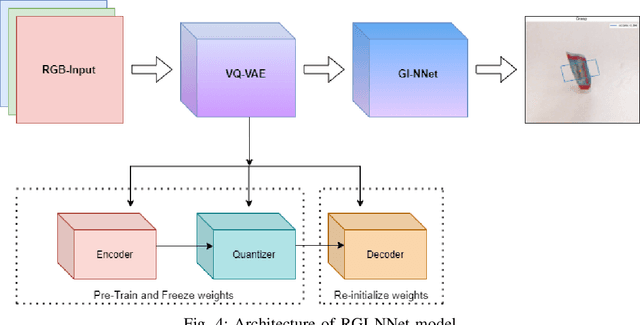
Abstract:Our way of grasping objects is challenging for efficient, intelligent and optimal grasp by COBOTs. To streamline the process, here we use deep learning techniques to help robots learn to generate and execute appropriate grasps quickly. We developed a Generative Inception Neural Network (GI-NNet) model, capable of generating antipodal robotic grasps on seen as well as unseen objects. It is trained on Cornell Grasping Dataset (CGD) and attained 98.87% grasp pose accuracy for detecting both regular and irregular shaped objects from RGB-Depth (RGB-D) images while requiring only one third of the network trainable parameters as compared to the existing approaches. However, to attain this level of performance the model requires the entire 90% of the available labelled data of CGD keeping only 10% labelled data for testing which makes it vulnerable to poor generalization. Furthermore, getting sufficient and quality labelled dataset is becoming increasingly difficult keeping in pace with the requirement of gigantic networks. To address these issues, we attach our model as a decoder with a semi-supervised learning based architecture known as Vector Quantized Variational Auto Encoder (VQVAE), which works efficiently when trained both with the available labelled and unlabelled data. The proposed model, which we name as Representation based GI-NNet (RGI-NNet), has been trained with various splits of label data on CGD with as minimum as 10% labelled dataset together with latent embedding generated from VQVAE up to 50% labelled data with latent embedding obtained from VQVAE. The performance level, in terms of grasp pose accuracy of RGI-NNet, varies between 92.13% to 95.6% which is far better than several existing models trained with only labelled dataset. For the performance verification of both GI-NNet and RGI-NNet models, we use Anukul (Baxter) hardware cobot.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge