Deeksha Varshney
Deriving Strategic Market Insights with Large Language Models: A Benchmark for Forward Counterfactual Generation
May 26, 2025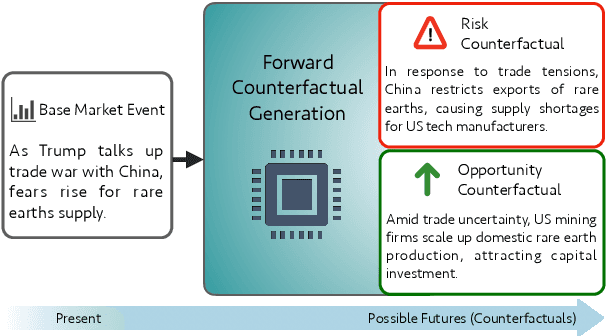
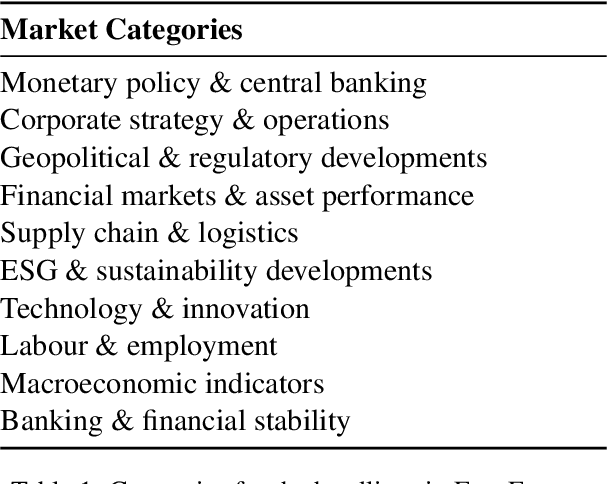
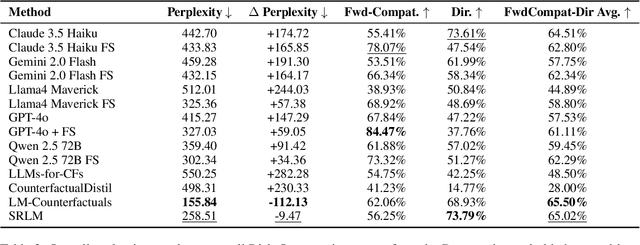
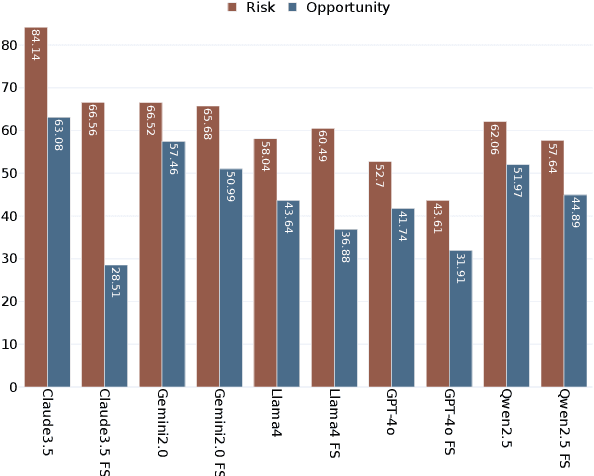
Abstract:Counterfactual reasoning typically involves considering alternatives to actual events. While often applied to understand past events, a distinct form-forward counterfactual reasoning-focuses on anticipating plausible future developments. This type of reasoning is invaluable in dynamic financial markets, where anticipating market developments can powerfully unveil potential risks and opportunities for stakeholders, guiding their decision-making. However, performing this at scale is challenging due to the cognitive demands involved, underscoring the need for automated solutions. Large Language Models (LLMs) offer promise, but remain unexplored for this application. To address this gap, we introduce a novel benchmark, Fin-Force-FINancial FORward Counterfactual Evaluation. By curating financial news headlines and providing structured evaluation, Fin-Force supports LLM based forward counterfactual generation. This paves the way for scalable and automated solutions for exploring and anticipating future market developments, thereby providing structured insights for decision-making. Through experiments on Fin-Force, we evaluate state-of-the-art LLMs and counterfactual generation methods, analyzing their limitations and proposing insights for future research.
ClimaEmpact: Domain-Aligned Small Language Models and Datasets for Extreme Weather Analytics
Apr 27, 2025Abstract:Accurate assessments of extreme weather events are vital for research and policy, yet localized and granular data remain scarce in many parts of the world. This data gap limits our ability to analyze potential outcomes and implications of extreme weather events, hindering effective decision-making. Large Language Models (LLMs) can process vast amounts of unstructured text data, extract meaningful insights, and generate detailed assessments by synthesizing information from multiple sources. Furthermore, LLMs can seamlessly transfer their general language understanding to smaller models, enabling these models to retain key knowledge while being fine-tuned for specific tasks. In this paper, we propose Extreme Weather Reasoning-Aware Alignment (EWRA), a method that enhances small language models (SLMs) by incorporating structured reasoning paths derived from LLMs, and ExtremeWeatherNews, a large dataset of extreme weather event-related news articles. EWRA and ExtremeWeatherNews together form the overall framework, ClimaEmpact, that focuses on addressing three critical extreme-weather tasks: categorization of tangible vulnerabilities/impacts, topic labeling, and emotion analysis. By aligning SLMs with advanced reasoning strategies on ExtremeWeatherNews (and its derived dataset ExtremeAlign used specifically for SLM alignment), EWRA improves the SLMs' ability to generate well-grounded and domain-specific responses for extreme weather analytics. Our results show that the approach proposed guides SLMs to output domain-aligned responses, surpassing the performance of task-specific models and offering enhanced real-world applicability for extreme weather analytics.
Towards Robust ESG Analysis Against Greenwashing Risks: Aspect-Action Analysis with Cross-Category Generalization
Feb 20, 2025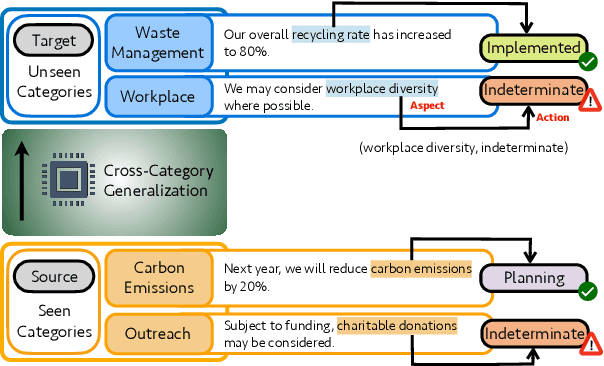
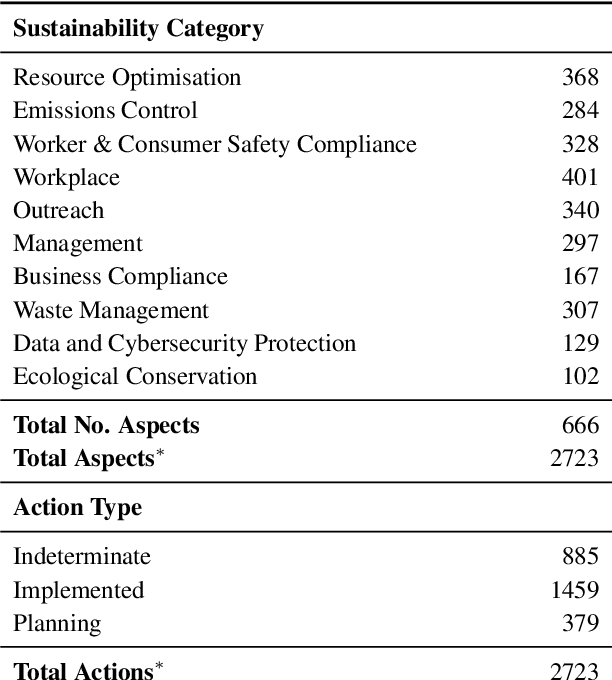
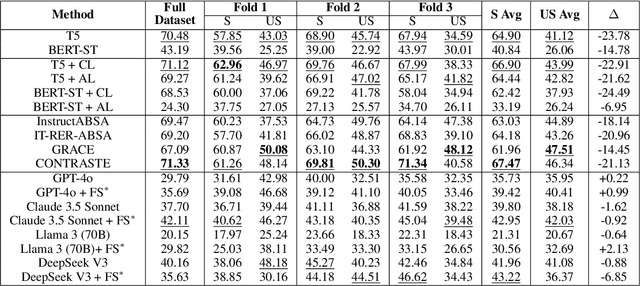
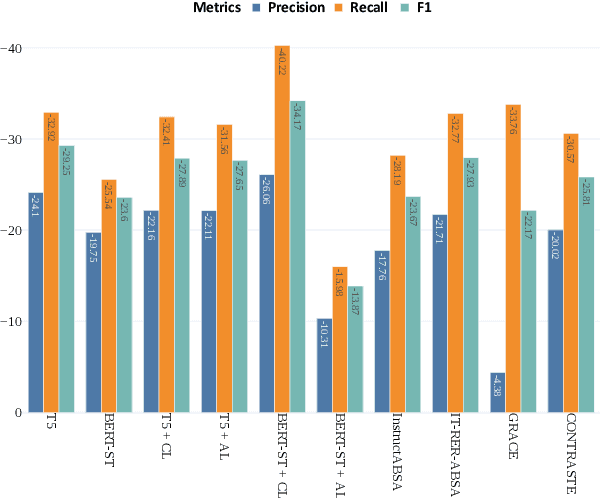
Abstract:Sustainability reports are key for evaluating companies' environmental, social and governance, ESG performance, but their content is increasingly obscured by greenwashing - sustainability claims that are misleading, exaggerated, and fabricated. Yet, existing NLP approaches for ESG analysis lack robustness against greenwashing risks, often extracting insights that reflect misleading or exaggerated sustainability claims rather than objective ESG performance. To bridge this gap, we introduce A3CG - Aspect-Action Analysis with Cross-Category Generalization, as a novel dataset to improve the robustness of ESG analysis amid the prevalence of greenwashing. By explicitly linking sustainability aspects with their associated actions, A3CG facilitates a more fine-grained and transparent evaluation of sustainability claims, ensuring that insights are grounded in verifiable actions rather than vague or misleading rhetoric. Additionally, A3CG emphasizes cross-category generalization. This ensures robust model performance in aspect-action analysis even when companies change their reports to selectively favor certain sustainability areas. Through experiments on A3CG, we analyze state-of-the-art supervised models and LLMs, uncovering their limitations and outlining key directions for future research.
Distraction-free Embeddings for Robust VQA
Aug 31, 2023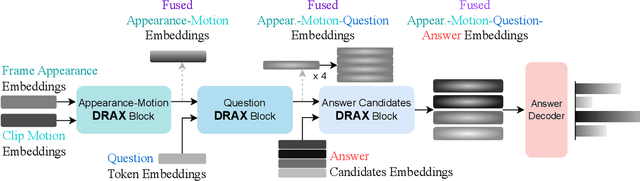
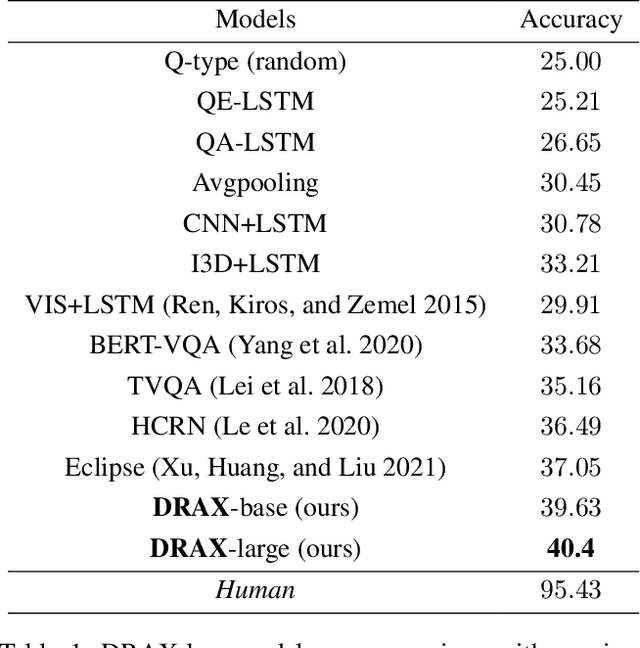
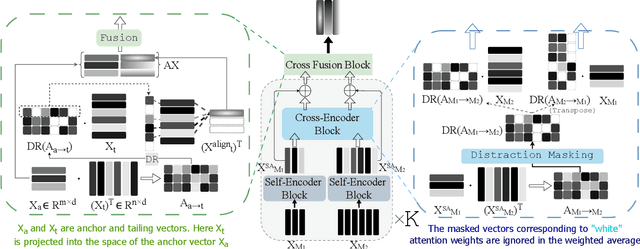
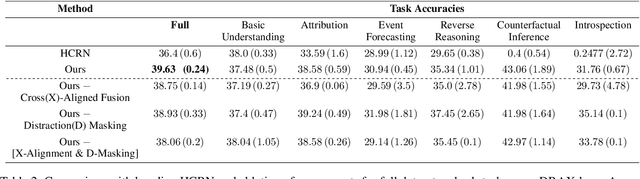
Abstract:The generation of effective latent representations and their subsequent refinement to incorporate precise information is an essential prerequisite for Vision-Language Understanding (VLU) tasks such as Video Question Answering (VQA). However, most existing methods for VLU focus on sparsely sampling or fine-graining the input information (e.g., sampling a sparse set of frames or text tokens), or adding external knowledge. We present a novel "DRAX: Distraction Removal and Attended Cross-Alignment" method to rid our cross-modal representations of distractors in the latent space. We do not exclusively confine the perception of any input information from various modalities but instead use an attention-guided distraction removal method to increase focus on task-relevant information in latent embeddings. DRAX also ensures semantic alignment of embeddings during cross-modal fusions. We evaluate our approach on a challenging benchmark (SUTD-TrafficQA dataset), testing the framework's abilities for feature and event queries, temporal relation understanding, forecasting, hypothesis, and causal analysis through extensive experiments.
Commonsense and Named Entity Aware Knowledge Grounded Dialogue Generation
May 27, 2022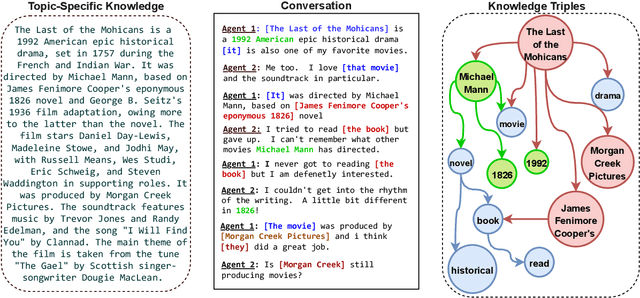

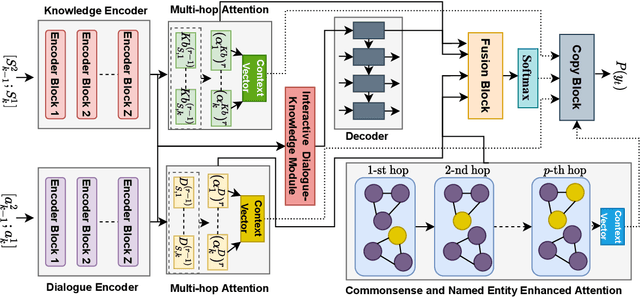

Abstract:Grounding dialogue on external knowledge and interpreting linguistic patterns in dialogue history context, such as ellipsis, anaphora, and co-references is critical for dialogue comprehension and generation. In this paper, we present a novel open-domain dialogue generation model which effectively utilizes the large-scale commonsense and named entity based knowledge in addition to the unstructured topic-specific knowledge associated with each utterance. We enhance the commonsense knowledge with named entity-aware structures using co-references. Our proposed model utilizes a multi-hop attention layer to preserve the most accurate and critical parts of the dialogue history and the associated knowledge. In addition, we employ a Commonsense and Named Entity Enhanced Attention Module, which starts with the extracted triples from various sources and gradually finds the relevant supporting set of triples using multi-hop attention with the query vector obtained from the interactive dialogue-knowledge module. Empirical results on two benchmark dataset demonstrate that our model significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in terms of both automatic evaluation metrics and human judgment. Our code is publicly available at \href{https://github.com/deekshaVarshney/CNTF}{https://github.com/deekshaVarshney/CNTF}; \href{https://www.iitp.ac.in/~ai-nlp-ml/resources/codes/CNTF.zip}{https://www.iitp.ac.in/-ai-nlp-ml/resources/ codes/CNTF.zip}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge