Deeksha Dangwal
Unlocking Visual Secrets: Inverting Features with Diffusion Priors for Image Reconstruction
Dec 11, 2024Abstract:Inverting visual representations within deep neural networks (DNNs) presents a challenging and important problem in the field of security and privacy for deep learning. The main goal is to invert the features of an unidentified target image generated by a pre-trained DNN, aiming to reconstruct the original image. Feature inversion holds particular significance in understanding the privacy leakage inherent in contemporary split DNN execution techniques, as well as in various applications based on the extracted DNN features. In this paper, we explore the use of diffusion models, a promising technique for image synthesis, to enhance feature inversion quality. We also investigate the potential of incorporating alternative forms of prior knowledge, such as textual prompts and cross-frame temporal correlations, to further improve the quality of inverted features. Our findings reveal that diffusion models can effectively leverage hidden information from the DNN features, resulting in superior reconstruction performance compared to previous methods. This research offers valuable insights into how diffusion models can enhance privacy and security within applications that are reliant on DNN features.
Analysis and Mitigations of Reverse Engineering Attacks on Local Feature Descriptors
May 09, 2021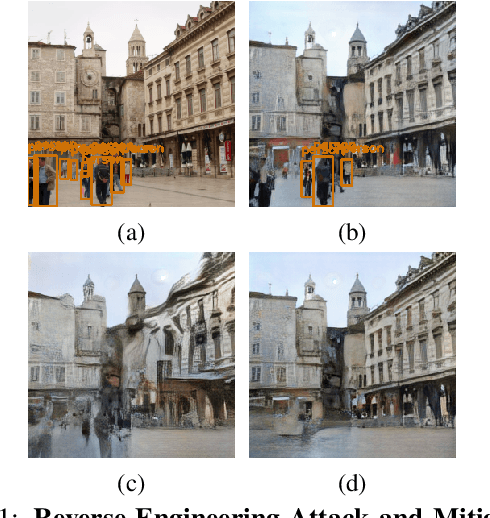
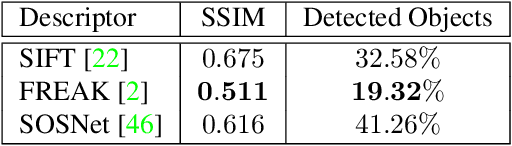
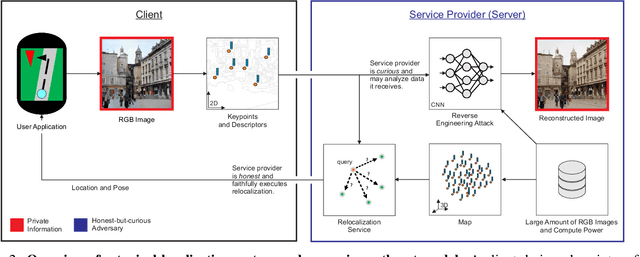
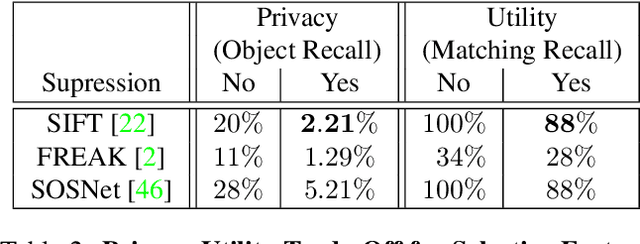
Abstract:As autonomous driving and augmented reality evolve, a practical concern is data privacy. In particular, these applications rely on localization based on user images. The widely adopted technology uses local feature descriptors, which are derived from the images and it was long thought that they could not be reverted back. However, recent work has demonstrated that under certain conditions reverse engineering attacks are possible and allow an adversary to reconstruct RGB images. This poses a potential risk to user privacy. We take this a step further and model potential adversaries using a privacy threat model. Subsequently, we show under controlled conditions a reverse engineering attack on sparse feature maps and analyze the vulnerability of popular descriptors including FREAK, SIFT and SOSNet. Finally, we evaluate potential mitigation techniques that select a subset of descriptors to carefully balance privacy reconstruction risk while preserving image matching accuracy; our results show that similar accuracy can be obtained when revealing less information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge