David Freeman
Predictive Response Optimization: Using Reinforcement Learning to Fight Online Social Network Abuse
Feb 24, 2025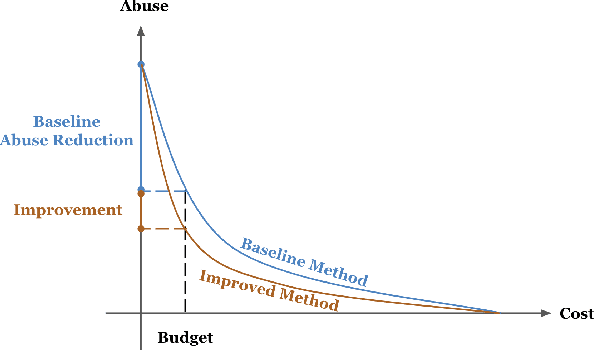
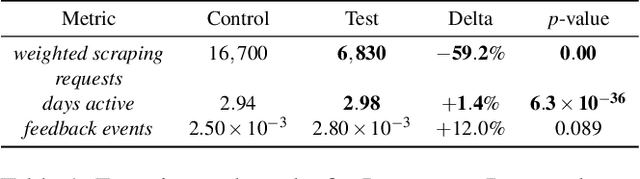
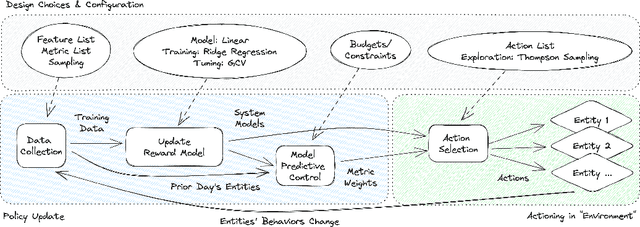
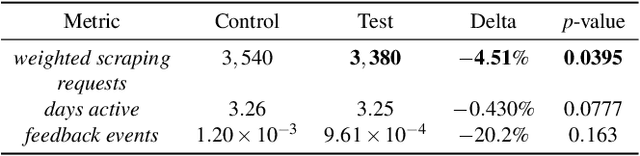
Abstract:Detecting phishing, spam, fake accounts, data scraping, and other malicious activity in online social networks (OSNs) is a problem that has been studied for well over a decade, with a number of important results. Nearly all existing works on abuse detection have as their goal producing the best possible binary classifier; i.e., one that labels unseen examples as "benign" or "malicious" with high precision and recall. However, no prior published work considers what comes next: what does the service actually do after it detects abuse? In this paper, we argue that detection as described in previous work is not the goal of those who are fighting OSN abuse. Rather, we believe the goal to be selecting actions (e.g., ban the user, block the request, show a CAPTCHA, or "collect more evidence") that optimize a tradeoff between harm caused by abuse and impact on benign users. With this framing, we see that enlarging the set of possible actions allows us to move the Pareto frontier in a way that is unattainable by simply tuning the threshold of a binary classifier. To demonstrate the potential of our approach, we present Predictive Response Optimization (PRO), a system based on reinforcement learning that utilizes available contextual information to predict future abuse and user-experience metrics conditioned on each possible action, and select actions that optimize a multi-dimensional tradeoff between abuse/harm and impact on user experience. We deployed versions of PRO targeted at stopping automated activity on Instagram and Facebook. In both cases our experiments showed that PRO outperforms a baseline classification system, reducing abuse volume by 59% and 4.5% (respectively) with no negative impact to users. We also present several case studies that demonstrate how PRO can quickly and automatically adapt to changes in business constraints, system behavior, and/or adversarial tactics.
"Real Attackers Don't Compute Gradients": Bridging the Gap Between Adversarial ML Research and Practice
Dec 29, 2022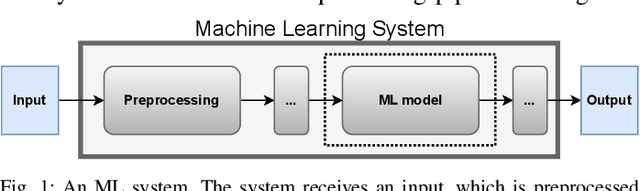
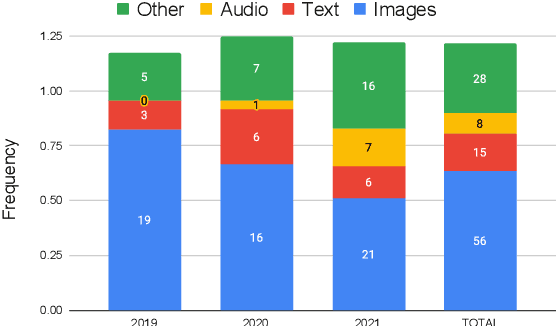
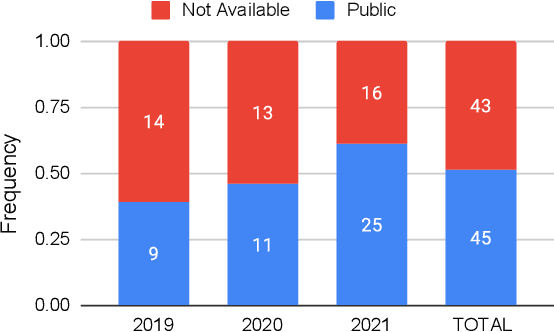
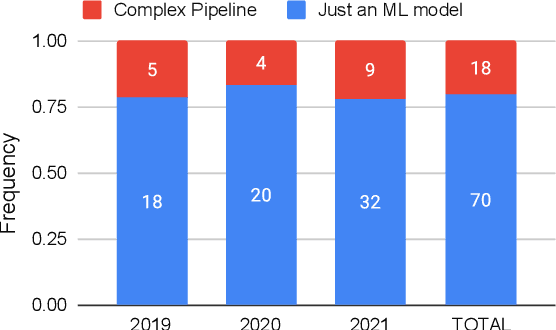
Abstract:Recent years have seen a proliferation of research on adversarial machine learning. Numerous papers demonstrate powerful algorithmic attacks against a wide variety of machine learning (ML) models, and numerous other papers propose defenses that can withstand most attacks. However, abundant real-world evidence suggests that actual attackers use simple tactics to subvert ML-driven systems, and as a result security practitioners have not prioritized adversarial ML defenses. Motivated by the apparent gap between researchers and practitioners, this position paper aims to bridge the two domains. We first present three real-world case studies from which we can glean practical insights unknown or neglected in research. Next we analyze all adversarial ML papers recently published in top security conferences, highlighting positive trends and blind spots. Finally, we state positions on precise and cost-driven threat modeling, collaboration between industry and academia, and reproducible research. We believe that our positions, if adopted, will increase the real-world impact of future endeavours in adversarial ML, bringing both researchers and practitioners closer to their shared goal of improving the security of ML systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge