David C. Steffens
Iterative Learning for Joint Image Denoising and Motion Artifact Correction of 3D Brain MRI
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:Image noise and motion artifacts greatly affect the quality of brain MRI and negatively influence downstream medical image analysis. Previous studies often focus on 2D methods that process each volumetric MR image slice-by-slice, thus losing important 3D anatomical information. Additionally, these studies generally treat image denoising and artifact correction as two standalone tasks, without considering their potential relationship, especially on low-quality images where severe noise and motion artifacts occur simultaneously. To address these issues, we propose a Joint image Denoising and motion Artifact Correction (JDAC) framework via iterative learning to handle noisy MRIs with motion artifacts, consisting of an adaptive denoising model and an anti-artifact model. In the adaptive denoising model, we first design a novel noise level estimation strategy, and then adaptively reduce the noise through a U-Net backbone with feature normalization conditioning on the estimated noise variance. The anti-artifact model employs another U-Net for eliminating motion artifacts, incorporating a novel gradient-based loss function designed to maintain the integrity of brain anatomy during the motion correction process. These two models are iteratively employed for joint image denoising and artifact correction through an iterative learning framework. An early stopping strategy depending on noise level estimation is applied to accelerate the iteration process. The denoising model is trained with 9,544 T1-weighted MRIs with manually added Gaussian noise as supervision. The anti-artifact model is trained on 552 T1-weighted MRIs with motion artifacts and paired motion-free images. Experimental results on a public dataset and a clinical study suggest the effectiveness of JDAC in both tasks of denoising and motion artifact correction, compared with several state-of-the-art methods.
Brain Anatomy Prior Modeling to Forecast Clinical Progression of Cognitive Impairment with Structural MRI
Jun 26, 2023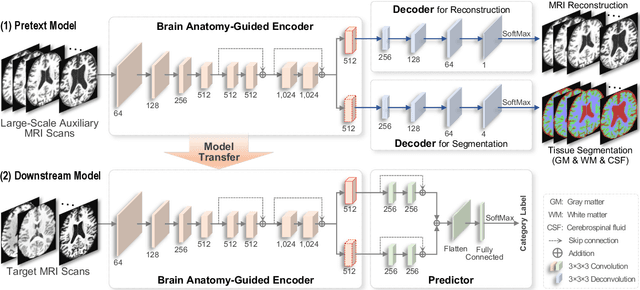
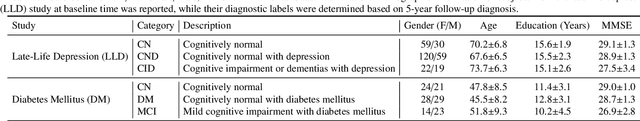
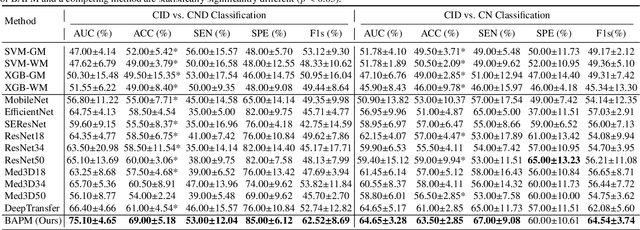
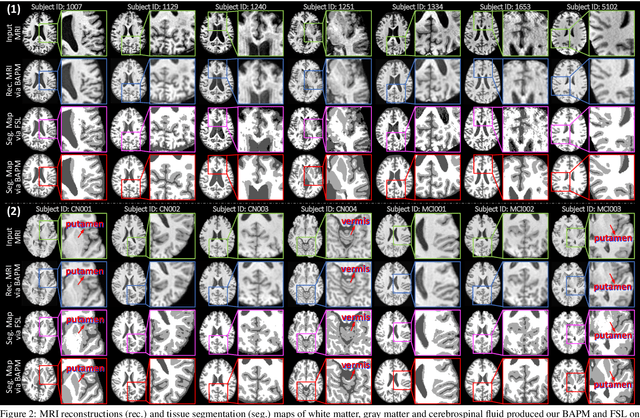
Abstract:Brain structural MRI has been widely used to assess the future progression of cognitive impairment (CI). Previous learning-based studies usually suffer from the issue of small-sized labeled training data, while there exist a huge amount of structural MRIs in large-scale public databases. Intuitively, brain anatomical structures derived from these public MRIs (even without task-specific label information) can be used to boost CI progression trajectory prediction. However, previous studies seldom take advantage of such brain anatomy prior. To this end, this paper proposes a brain anatomy prior modeling (BAPM) framework to forecast the clinical progression of cognitive impairment with small-sized target MRIs by exploring anatomical brain structures. Specifically, the BAPM consists of a pretext model and a downstream model, with a shared brain anatomy-guided encoder to model brain anatomy prior explicitly. Besides the encoder, the pretext model also contains two decoders for two auxiliary tasks (i.e., MRI reconstruction and brain tissue segmentation), while the downstream model relies on a predictor for classification. The brain anatomy-guided encoder is pre-trained with the pretext model on 9,344 auxiliary MRIs without diagnostic labels for anatomy prior modeling. With this encoder frozen, the downstream model is then fine-tuned on limited target MRIs for prediction. We validate the BAPM on two CI-related studies with T1-weighted MRIs from 448 subjects. Experimental results suggest the effectiveness of BAPM in (1) four CI progression prediction tasks, (2) MR image reconstruction, and (3) brain tissue segmentation, compared with several state-of-the-art methods.
Hybrid Representation Learning for Cognitive Diagnosis in Late-Life Depression Over 5 Years with Structural MRI
Dec 24, 2022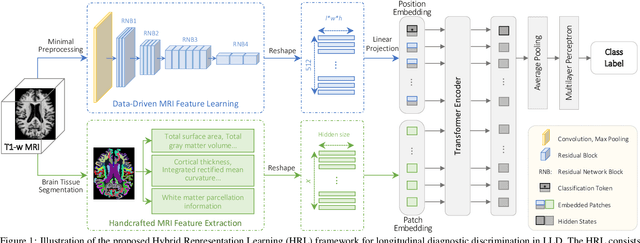
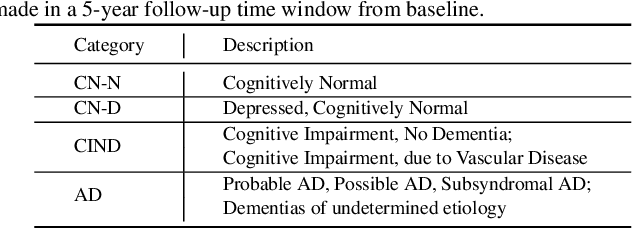
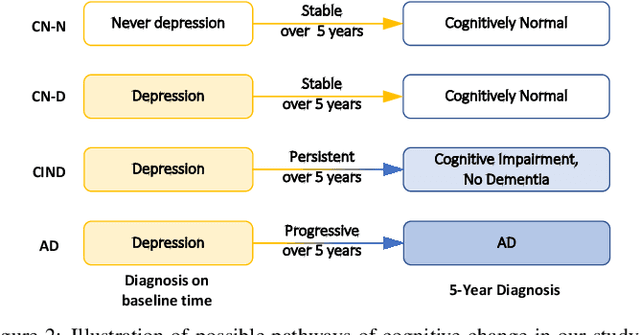
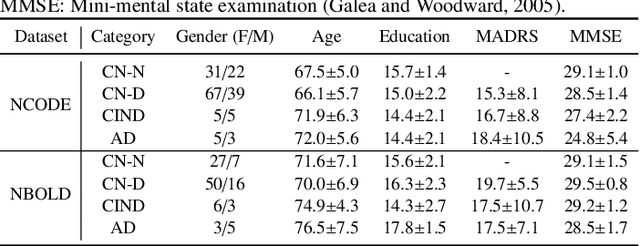
Abstract:Late-life depression (LLD) is a highly prevalent mood disorder occurring in older adults and is frequently accompanied by cognitive impairment (CI). Studies have shown that LLD may increase the risk of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the heterogeneity of presentation of geriatric depression suggests that multiple biological mechanisms may underlie it. Current biological research on LLD progression incorporates machine learning that combines neuroimaging data with clinical observations. There are few studies on incident cognitive diagnostic outcomes in LLD based on structural MRI (sMRI). In this paper, we describe the development of a hybrid representation learning (HRL) framework for predicting cognitive diagnosis over 5 years based on T1-weighted sMRI data. Specifically, we first extract prediction-oriented MRI features via a deep neural network, and then integrate them with handcrafted MRI features via a Transformer encoder for cognitive diagnosis prediction. Two tasks are investigated in this work, including (1) identifying cognitively normal subjects with LLD and never-depressed older healthy subjects, and (2) identifying LLD subjects who developed CI (or even AD) and those who stayed cognitively normal over five years. To the best of our knowledge, this is among the first attempts to study the complex heterogeneous progression of LLD based on task-oriented and handcrafted MRI features. We validate the proposed HRL on 294 subjects with T1-weighted MRIs from two clinically harmonized studies. Experimental results suggest that the HRL outperforms several classical machine learning and state-of-the-art deep learning methods in LLD identification and prediction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge