Daqing Wu
ARGO: Modeling Heterogeneity in E-commerce Recommendation
Sep 14, 2021



Abstract:Nowadays, E-commerce is increasingly integrated into our daily lives. Meanwhile, shopping process has also changed incrementally from one behavior (purchase) to multiple behaviors (such as view, carting and purchase). Therefore, utilizing interaction data of auxiliary behavior data draws a lot of attention in the E-commerce recommender systems. However, all existing models ignore two kinds of intrinsic heterogeneity which are helpful to capture the difference of user preferences and the difference of item attributes. First (intra-heterogeneity), each user has multiple social identities with otherness, and these different identities can result in quite different interaction preferences. Second (inter-heterogeneity), each item can transfer an item-specific percentage of score from low-level behavior to high-level behavior for the gradual relationship among multiple behaviors. Thus, the lack of consideration of these heterogeneities damages recommendation rank performance. To model the above heterogeneities, we propose a novel method named intra- and inter-heterogeneity recommendation model (ARGO). Specifically, we embed each user into multiple vectors representing the user's identities, and the maximum of identity scores indicates the interaction preference. Besides, we regard the item-specific transition percentage as trainable transition probability between different behaviors. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets show that ARGO performs much better than the state-of-the-art in multi-behavior scenarios.
Criterion-based Heterogeneous Collaborative Filtering for Multi-behavior Implicit Recommendation
May 28, 2021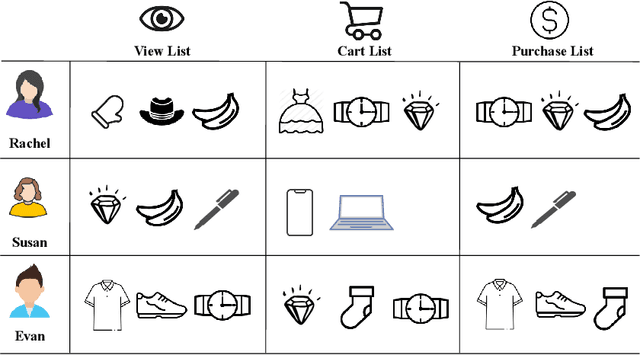

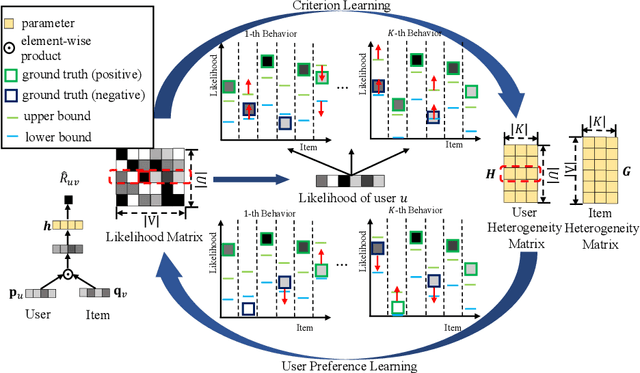

Abstract:With the increasing scale and diversification of interaction behaviors in E-commerce, more and more researchers pay attention to multi-behavior recommender systems that utilize interaction data of other auxiliary behaviors such as view and cart. To address these challenges in heterogeneous scenarios, non-sampling methods have shown superiority over negative sampling methods. However, two observations are usually ignored in existing state-of-the-art non-sampling methods based on binary regression: (1) users have different preference strengths for different items, so they cannot be measured simply by binary implicit data; (2) the dependency across multiple behaviors varies for different users and items. To tackle the above issue, we propose a novel non-sampling learning framework named \underline{C}riterion-guided \underline{H}eterogeneous \underline{C}ollaborative \underline{F}iltering (CHCF). CHCF introduces both upper and lower bounds to indicate selection criteria, which will guide user preference learning. Besides, CHCF integrates criterion learning and user preference learning into a unified framework, which can be trained jointly for the interaction prediction on target behavior. We further theoretically demonstrate that the optimization of Collaborative Metric Learning can be approximately achieved by CHCF learning framework in a non-sampling form effectively. Extensive experiments on two real-world datasets show that CHCF outperforms the state-of-the-art methods in heterogeneous scenarios.
Deep Unsupervised Hashing by Distilled Smooth Guidance
May 13, 2021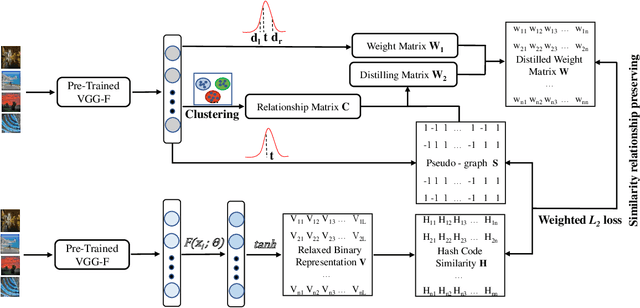
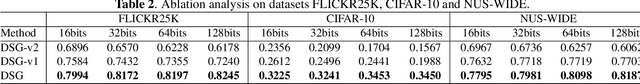
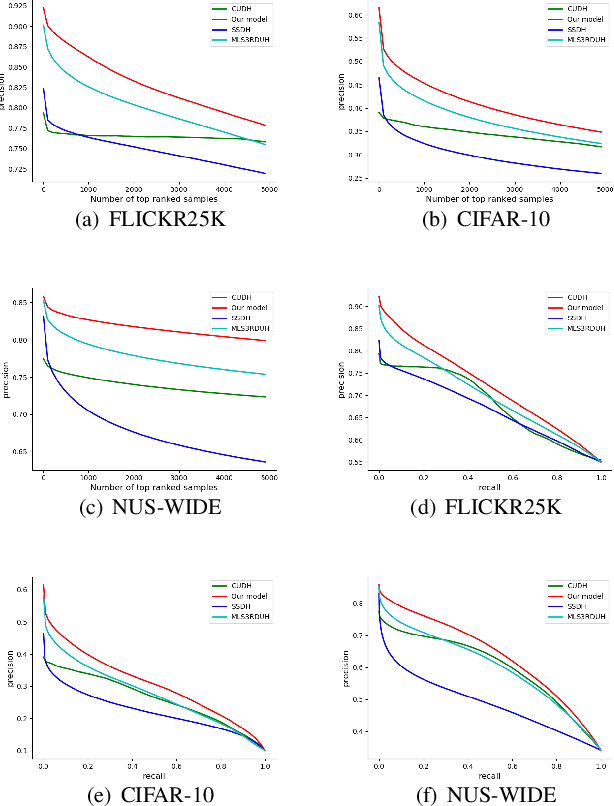
Abstract:Hashing has been widely used in approximate nearest neighbor search for its storage and computational efficiency. Deep supervised hashing methods are not widely used because of the lack of labeled data, especially when the domain is transferred. Meanwhile, unsupervised deep hashing models can hardly achieve satisfactory performance due to the lack of reliable similarity signals. To tackle this problem, we propose a novel deep unsupervised hashing method, namely Distilled Smooth Guidance (DSG), which can learn a distilled dataset consisting of similarity signals as well as smooth confidence signals. To be specific, we obtain the similarity confidence weights based on the initial noisy similarity signals learned from local structures and construct a priority loss function for smooth similarity-preserving learning. Besides, global information based on clustering is utilized to distill the image pairs by removing contradictory similarity signals. Extensive experiments on three widely used benchmark datasets show that the proposed DSG consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art search methods.
* 7 pages, 3 figures
CIMON: Towards High-quality Hash Codes
Nov 05, 2020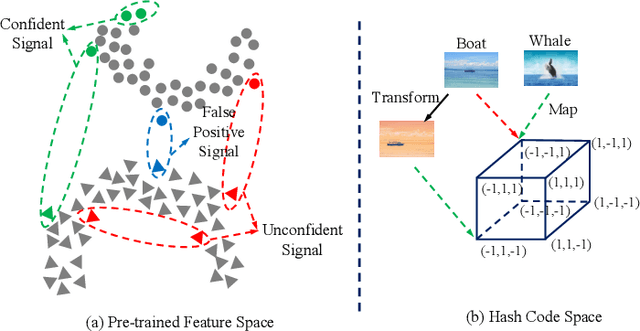
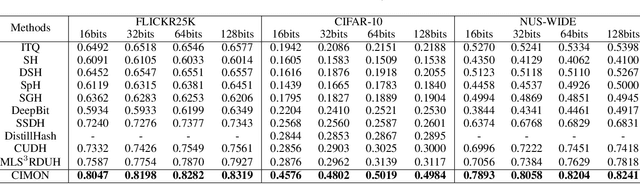
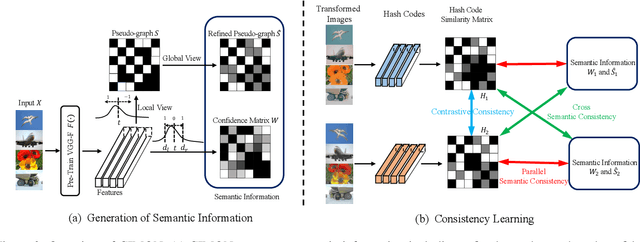
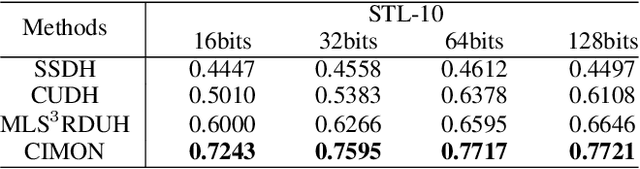
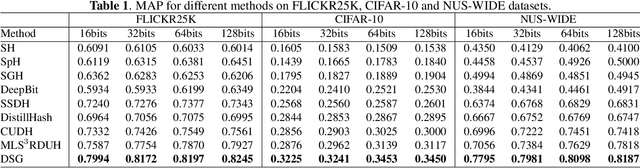
Abstract:Recently, hashing is widely-used in approximate nearest neighbor search for its storage and computational efficiency. Due to the lack of labeled data in practice, many studies focus on unsupervised hashing. Most of the unsupervised hashing methods learn to map images into semantic similarity-preserving hash codes by constructing local semantic similarity structure from the pre-trained model as guiding information, i.e., treating each point pair similar if their distance is small in feature space. However, due to the inefficient representation ability of the pre-trained model, many false positives and negatives in local semantic similarity will be introduced and lead to error propagation during hash code learning. Moreover, most of hashing methods ignore the basic characteristics of hash codes such as collisions, which will cause instability of hash codes to disturbance. In this paper, we propose a new method named Comprehensive sImilarity Mining and cOnsistency learNing (CIMON). First, we use global constraint learning and similarity statistical distribution to obtain reliable and smooth guidance. Second, image augmentation and consistency learning will be introduced to explore both semantic and contrastive consistency to derive robust hash codes with fewer collisions. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets show that the proposed method consistently outperforms a wide range of state-of-the-art methods in both retrieval performance and robustness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge