Daniel Mollura
Mitigating domain shift in AI-based tuberculosis screening with unsupervised domain adaptation
Nov 09, 2021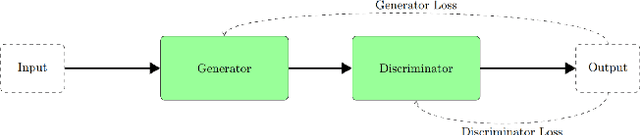
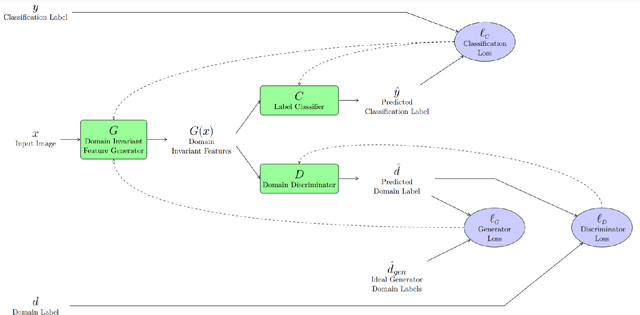
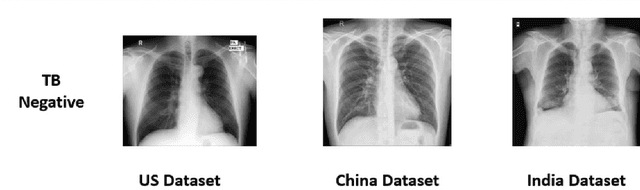
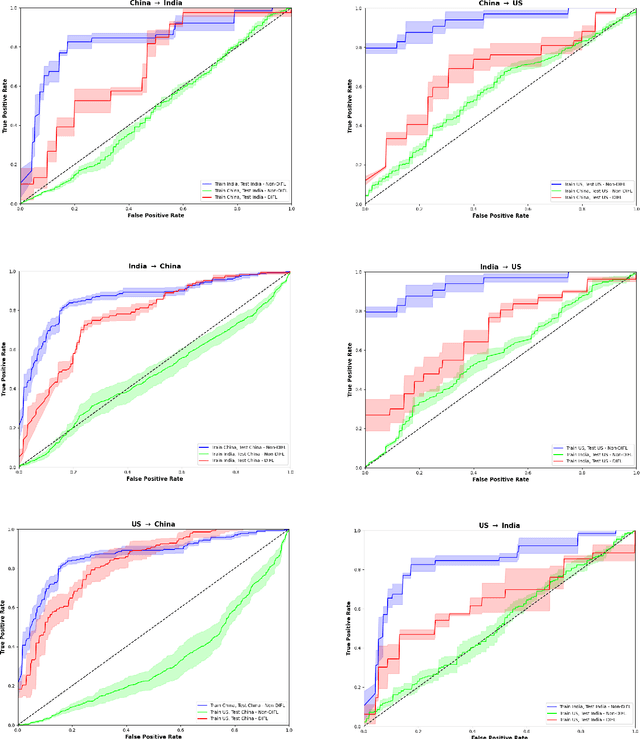
Abstract:We demonstrate that Domain Invariant Feature Learning (DIFL) can improve the out-of-domain generalizability of a deep learning Tuberculosis screening algorithm. It is well known that state of the art deep learning algorithms often have difficulty generalizing to unseen data distributions due to "domain shift". In the context of medical imaging, this could lead to unintended biases such as the inability to generalize from one patient population to another. We analyze the performance of a ResNet-50 classifier for the purposes of Tuberculosis screening using the four most popular public datasets with geographically diverse sources of imagery. We show that without domain adaptation, ResNet-50 has difficulty in generalizing between imaging distributions from a number of public Tuberculosis screening datasets with imagery from geographically distributed regions. However, with the incorporation of DIFL, the out-of-domain performance is greatly enhanced. Analysis criteria includes a comparison of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity and AUC over both the baseline, as well as the DIFL enhanced algorithms. We conclude that DIFL improves generalizability of Tuberculosis screening while maintaining acceptable accuracy over the source domain imagery when applied across a variety of public datasets.
Deep Convolutional Neural Networks for Computer-Aided Detection: CNN Architectures, Dataset Characteristics and Transfer Learning
Feb 10, 2016
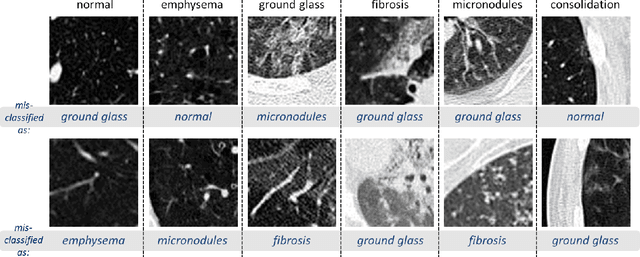
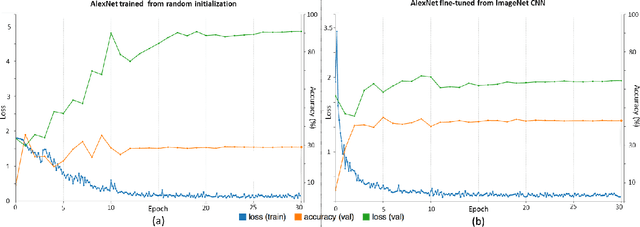

Abstract:Remarkable progress has been made in image recognition, primarily due to the availability of large-scale annotated datasets and the revival of deep CNN. CNNs enable learning data-driven, highly representative, layered hierarchical image features from sufficient training data. However, obtaining datasets as comprehensively annotated as ImageNet in the medical imaging domain remains a challenge. There are currently three major techniques that successfully employ CNNs to medical image classification: training the CNN from scratch, using off-the-shelf pre-trained CNN features, and conducting unsupervised CNN pre-training with supervised fine-tuning. Another effective method is transfer learning, i.e., fine-tuning CNN models pre-trained from natural image dataset to medical image tasks. In this paper, we exploit three important, but previously understudied factors of employing deep convolutional neural networks to computer-aided detection problems. We first explore and evaluate different CNN architectures. The studied models contain 5 thousand to 160 million parameters, and vary in numbers of layers. We then evaluate the influence of dataset scale and spatial image context on performance. Finally, we examine when and why transfer learning from pre-trained ImageNet (via fine-tuning) can be useful. We study two specific computer-aided detection (CADe) problems, namely thoraco-abdominal lymph node (LN) detection and interstitial lung disease (ILD) classification. We achieve the state-of-the-art performance on the mediastinal LN detection, with 85% sensitivity at 3 false positive per patient, and report the first five-fold cross-validation classification results on predicting axial CT slices with ILD categories. Our extensive empirical evaluation, CNN model analysis and valuable insights can be extended to the design of high performance CAD systems for other medical imaging tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge