Dana Arad
Mechanisms of Prompt-Induced Hallucination in Vision-Language Models
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Large vision-language models (VLMs) are highly capable, yet often hallucinate by favoring textual prompts over visual evidence. We study this failure mode in a controlled object-counting setting, where the prompt overstates the number of objects in the image (e.g., asking a model to describe four waterlilies when only three are present). At low object counts, models often correct the overestimation, but as the number of objects increases, they increasingly conform to the prompt regardless of the discrepancy. Through mechanistic analysis of three VLMs, we identify a small set of attention heads whose ablation substantially reduces prompt-induced hallucinations (PIH) by at least 40% without additional training. Across models, PIH-heads mediate prompt copying in model-specific ways. We characterize these differences and show that PIH ablation increases correction toward visual evidence. Our findings offer insights into the internal mechanisms driving prompt-induced hallucinations, revealing model-specific differences in how these behaviors are implemented.
Same Task, Different Circuits: Disentangling Modality-Specific Mechanisms in VLMs
Jun 11, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language models (VLMs) show impressive abilities to answer questions on visual inputs (e.g., counting objects in an image), yet demonstrate higher accuracies when performing an analogous task on text (e.g., counting words in a text). We investigate this accuracy gap by identifying and comparing the \textit{circuits} - the task-specific computational sub-graphs - in different modalities. We show that while circuits are largely disjoint between modalities, they implement relatively similar functionalities: the differences lie primarily in processing modality-specific data positions (an image or a text sequence). Zooming in on the image data representations, we observe they become aligned with the higher-performing analogous textual representations only towards later layers, too late in processing to effectively influence subsequent positions. To overcome this, we patch the representations of visual data tokens from later layers back into earlier layers. In experiments with multiple tasks and models, this simple intervention closes a third of the performance gap between the modalities, on average. Our analysis sheds light on the multi-modal performance gap in VLMs and suggests a training-free approach for reducing it.
SAEs Are Good for Steering -- If You Select the Right Features
May 26, 2025Abstract:Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs) have been proposed as an unsupervised approach to learn a decomposition of a model's latent space. This enables useful applications such as steering - influencing the output of a model towards a desired concept - without requiring labeled data. Current methods identify SAE features to steer by analyzing the input tokens that activate them. However, recent work has highlighted that activations alone do not fully describe the effect of a feature on the model's output. In this work, we draw a distinction between two types of features: input features, which mainly capture patterns in the model's input, and output features, which have a human-understandable effect on the model's output. We propose input and output scores to characterize and locate these types of features, and show that high values for both scores rarely co-occur in the same features. These findings have practical implications: after filtering out features with low output scores, we obtain 2-3x improvements when steering with SAEs, making them competitive with supervised methods.
MIB: A Mechanistic Interpretability Benchmark
Apr 17, 2025



Abstract:How can we know whether new mechanistic interpretability methods achieve real improvements? In pursuit of meaningful and lasting evaluation standards, we propose MIB, a benchmark with two tracks spanning four tasks and five models. MIB favors methods that precisely and concisely recover relevant causal pathways or specific causal variables in neural language models. The circuit localization track compares methods that locate the model components - and connections between them - most important for performing a task (e.g., attribution patching or information flow routes). The causal variable localization track compares methods that featurize a hidden vector, e.g., sparse autoencoders (SAEs) or distributed alignment search (DAS), and locate model features for a causal variable relevant to the task. Using MIB, we find that attribution and mask optimization methods perform best on circuit localization. For causal variable localization, we find that the supervised DAS method performs best, while SAE features are not better than neurons, i.e., standard dimensions of hidden vectors. These findings illustrate that MIB enables meaningful comparisons of methods, and increases our confidence that there has been real progress in the field.
Diffusion Lens: Interpreting Text Encoders in Text-to-Image Pipelines
Mar 09, 2024
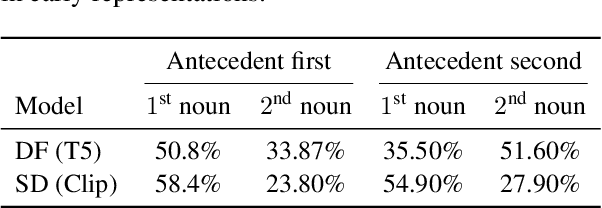
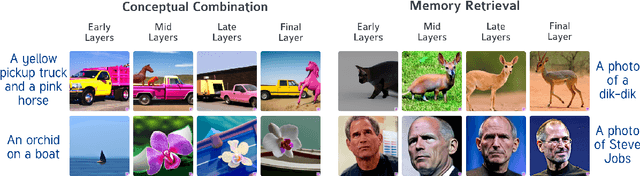
Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models (T2I) use a latent representation of a text prompt to guide the image generation process. However, the process by which the encoder produces the text representation is unknown. We propose the Diffusion Lens, a method for analyzing the text encoder of T2I models by generating images from its intermediate representations. Using the Diffusion Lens, we perform an extensive analysis of two recent T2I models. Exploring compound prompts, we find that complex scenes describing multiple objects are composed progressively and more slowly compared to simple scenes; Exploring knowledge retrieval, we find that representation of uncommon concepts requires further computation compared to common concepts, and that knowledge retrieval is gradual across layers. Overall, our findings provide valuable insights into the text encoder component in T2I pipelines.
ReFACT: Updating Text-to-Image Models by Editing the Text Encoder
Jun 01, 2023Abstract:Text-to-image models are trained on extensive amounts of data, leading them to implicitly encode factual knowledge within their parameters. While some facts are useful, others may be incorrect or become outdated (e.g., the current President of the United States). We introduce ReFACT, a novel approach for editing factual knowledge in text-to-image generative models. ReFACT updates the weights of a specific layer in the text encoder, only modifying a tiny portion of the model's parameters, and leaving the rest of the model unaffected. We empirically evaluate ReFACT on an existing benchmark, alongside RoAD, a newly curated dataset. ReFACT achieves superior performance in terms of generalization to related concepts while preserving unrelated concepts. Furthermore, ReFACT maintains image generation quality, making it a valuable tool for updating and correcting factual information in text-to-image models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge