Damien Lefortier
Attribution Modeling Increases Efficiency of Bidding in Display Advertising
Jul 21, 2017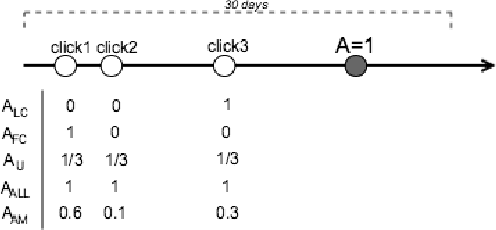
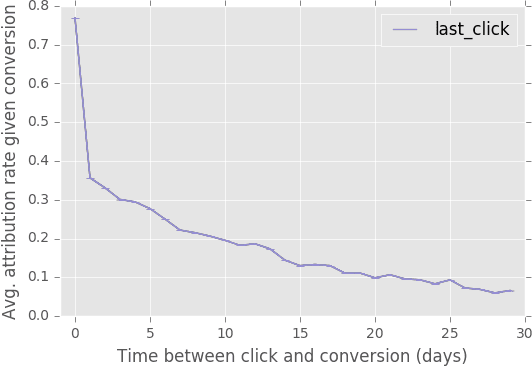
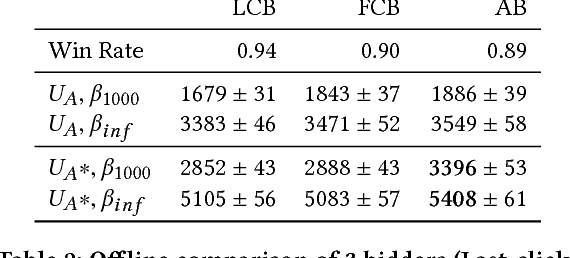
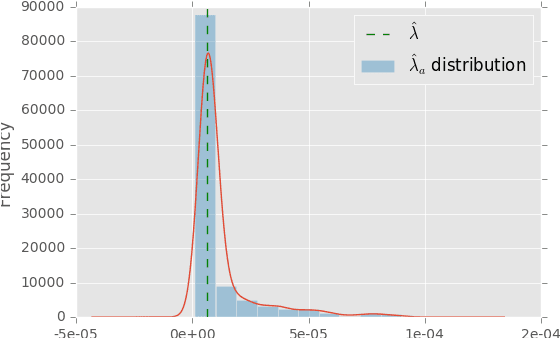
Abstract:Predicting click and conversion probabilities when bidding on ad exchanges is at the core of the programmatic advertising industry. Two separated lines of previous works respectively address i) the prediction of user conversion probability and ii) the attribution of these conversions to advertising events (such as clicks) after the fact. We argue that attribution modeling improves the efficiency of the bidding policy in the context of performance advertising. Firstly we explain the inefficiency of the standard bidding policy with respect to attribution. Secondly we learn and utilize an attribution model in the bidder itself and show how it modifies the average bid after a click. Finally we produce evidence of the effectiveness of the proposed method on both offline and online experiments with data spanning several weeks of real traffic from Criteo, a leader in performance advertising.
Cost-sensitive Learning for Utility Optimization in Online Advertising Auctions
Jul 12, 2017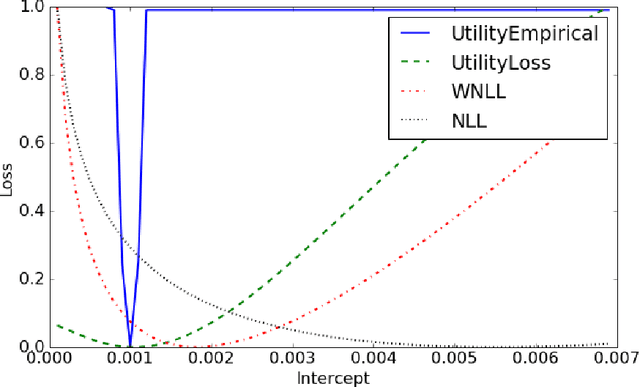
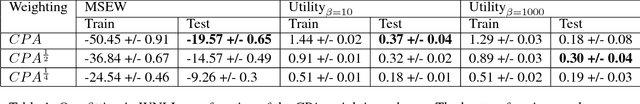
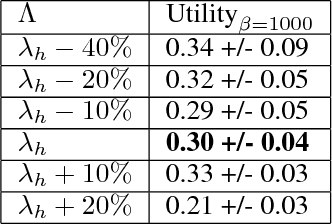

Abstract:One of the most challenging problems in computational advertising is the prediction of click-through and conversion rates for bidding in online advertising auctions. An unaddressed problem in previous approaches is the existence of highly non-uniform misprediction costs. While for model evaluation these costs have been taken into account through recently proposed business-aware offline metrics -- such as the Utility metric which measures the impact on advertiser profit -- this is not the case when training the models themselves. In this paper, to bridge the gap, we formally analyze the relationship between optimizing the Utility metric and the log loss, which is considered as one of the state-of-the-art approaches in conversion modeling. Our analysis motivates the idea of weighting the log loss with the business value of the predicted outcome. We present and analyze a new cost weighting scheme and show that significant gains in offline and online performance can be achieved.
Large-scale Validation of Counterfactual Learning Methods: A Test-Bed
Jun 25, 2017
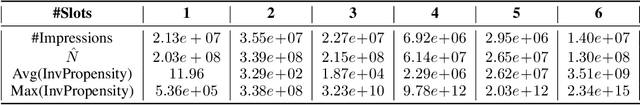
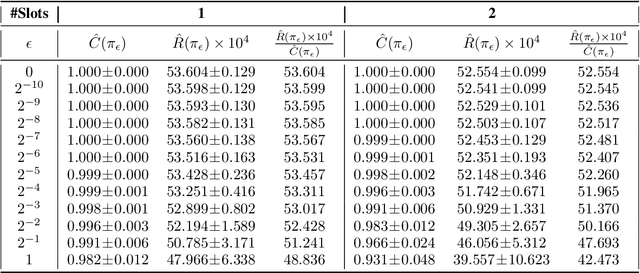
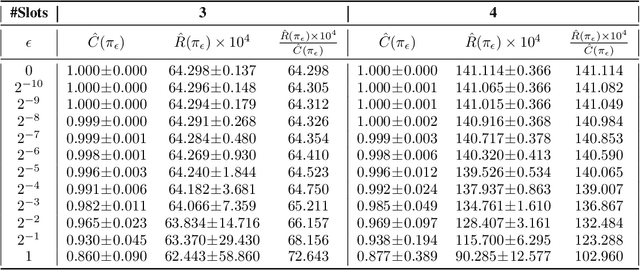
Abstract:The ability to perform effective off-policy learning would revolutionize the process of building better interactive systems, such as search engines and recommendation systems for e-commerce, computational advertising and news. Recent approaches for off-policy evaluation and learning in these settings appear promising. With this paper, we provide real-world data and a standardized test-bed to systematically investigate these algorithms using data from display advertising. In particular, we consider the problem of filling a banner ad with an aggregate of multiple products the user may want to purchase. This paper presents our test-bed, the sanity checks we ran to ensure its validity, and shows results comparing state-of-the-art off-policy learning methods like doubly robust optimization, POEM, and reductions to supervised learning using regression baselines. Our results show experimental evidence that recent off-policy learning methods can improve upon state-of-the-art supervised learning techniques on a large-scale real-world data set.
Field-aware Factorization Machines in a Real-world Online Advertising System
Feb 23, 2017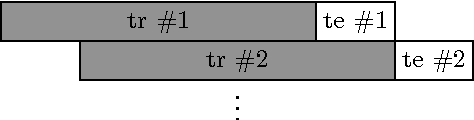


Abstract:Predicting user response is one of the core machine learning tasks in computational advertising. Field-aware Factorization Machines (FFM) have recently been established as a state-of-the-art method for that problem and in particular won two Kaggle challenges. This paper presents some results from implementing this method in a production system that predicts click-through and conversion rates for display advertising and shows that this method it is not only effective to win challenges but is also valuable in a real-world prediction system. We also discuss some specific challenges and solutions to reduce the training time, namely the use of an innovative seeding algorithm and a distributed learning mechanism.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge