Corey Knutson
Design and Development of the MeCO Open-Source Autonomous Underwater Vehicle
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:We present MeCO, the Medium Cost Open-source autonomous underwater vehicle (AUV), a versatile autonomous vehicle designed to support research and development in underwater human-robot interaction (UHRI) and marine robotics in general. An inexpensive platform to build compared to similarly-capable AUVs, the MeCO design and software are released under open-source licenses, making it a cost effective, extensible, and open platform. It is equipped with UHRI-focused systems, such as front and side facing displays, light-based communication devices, a transducer for acoustic interaction, and stereo vision, in addition to typical AUV sensing and actuation components. Additionally, MeCO is capable of real-time deep learning inference using the latest edge computing devices, while maintaining low-latency, closed-loop control through high-performance microcontrollers. MeCO is designed from the ground up for modularity in internal electronics, external payloads, and software architecture, exploiting open-source robotics and containerarization tools. We demonstrate the diverse capabilities of MeCO through simulated, closed-water, and open-water experiments. All resources necessary to build and run MeCO, including software and hardware design, have been made publicly available.
Adaptive Landmark Color for AUV Docking in Visually Dynamic Environments
Oct 04, 2023Abstract:Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) conduct missions underwater without the need for human intervention. A docking station (DS) can extend mission times of an AUV by providing a location for the AUV to recharge its batteries and receive updated mission information. Various methods for locating and tracking a DS exist, but most rely on expensive acoustic sensors, or are vision-based, which is significantly affected by water quality. In this \doctype, we present a vision-based method that utilizes adaptive color LED markers and dynamic color filtering to maximize landmark visibility in varying water conditions. Both AUV and DS utilize cameras to determine the water background color in order to calculate the desired marker color. No communication between AUV and DS is needed to determine marker color. Experiments conducted in a pool and lake show our method performs 10 times better than static color thresholding methods as background color varies. DS detection is possible at a range of 5 meters in clear water with minimal false positives.
Design and Experiments with LoCO AUV: A Low Cost Open-Source Autonomous Underwater Vehicle
Mar 19, 2020
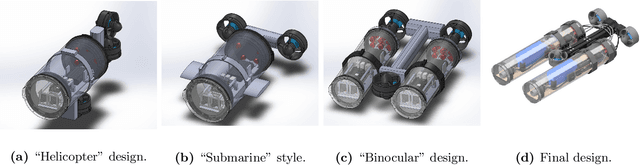

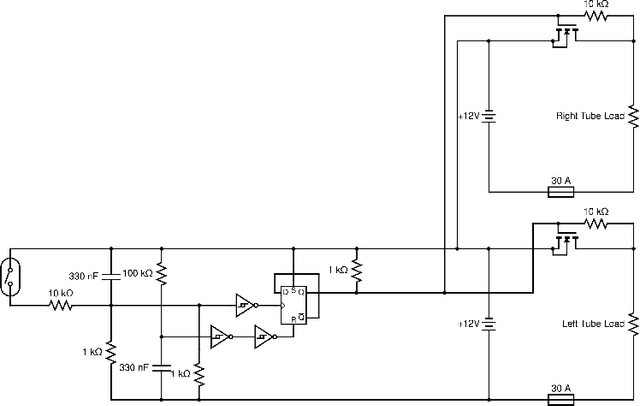
Abstract:In this paper we present LoCO AUV, a Low-Cost, Open Autonomous Underwater Vehicle. LoCO is a general-purpose, single-person-deployable, vision-guided AUV, rated to a depth of 100 meters. We discuss the open and expandable design of this underwater robot, as well as the design of a simulator in Gazebo. Additionally, we explore the platform's preliminary local motion control and state estimation abilities, which enable it to perform maneuvers autonomously. In order to demonstrate its usefulness for a variety of tasks, we implement a variety of our previously presented human-robot interaction capabilities on LoCO, including gestural control, diver following, and robot communication via motion. Finally, we discuss the practical concerns of deployment and our experiences in using this robot in pools, lakes, and the ocean. All design details, instructions on assembly, and code will be released under a permissive, open-source license.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge