Cong Huang
A$^2$-LLM: An End-to-end Conversational Audio Avatar Large Language Model
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Developing expressive and responsive conversational digital humans is a cornerstone of next-generation human-computer interaction. While large language models (LLMs) have significantly enhanced dialogue capabilities, most current systems still rely on cascaded architectures that connect independent modules. These pipelines are often plagued by accumulated errors, high latency, and poor real-time performance. Lacking access to the underlying conversational context, these pipelines inherently prioritize rigid lip-sync over emotional depth. To address these challenges, we propose A$^2$-LLM, an end-to-end conversational audio avatar large language model that jointly reasons about language, audio prosody, and 3D facial motion within a unified framework. To facilitate training, we introduce FLAME-QA, a high-quality multimodal dataset designed to align semantic intent with expressive facial dynamics within a QA format. By leveraging deep semantic understanding, A$^2$-LLM generates emotionally rich facial movements beyond simple lip-synchronization. Experimental results demonstrate that our system achieves superior emotional expressiveness while maintaining real-time efficiency (500 ms latency, 0.7 RTF).
LangForce: Bayesian Decomposition of Vision Language Action Models via Latent Action Queries
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have shown promise in robot manipulation but often struggle to generalize to new instructions or complex multi-task scenarios. We identify a critical pathology in current training paradigms where goal-driven data collection creates a dataset bias. In such datasets, language instructions are highly predictable from visual observations alone, causing the conditional mutual information between instructions and actions to vanish, a phenomenon we term Information Collapse. Consequently, models degenerate into vision-only policies that ignore language constraints and fail in out-of-distribution (OOD) settings. To address this, we propose LangForce, a novel framework that enforces instruction following via Bayesian decomposition. By introducing learnable Latent Action Queries, we construct a dual-branch architecture to estimate both a vision-only prior $p(a \mid v)$ and a language-conditioned posterior $π(a \mid v, \ell)$. We then optimize the policy to maximize the conditional Pointwise Mutual Information (PMI) between actions and instructions. This objective effectively penalizes the vision shortcut and rewards actions that explicitly explain the language command. Without requiring new data, LangForce significantly improves generalization. Extensive experiments across on SimplerEnv and RoboCasa demonstrate substantial gains, including an 11.3% improvement on the challenging OOD SimplerEnv benchmark, validating the ability of our approach to robustly ground language in action.
BayesianVLA: Bayesian Decomposition of Vision Language Action Models via Latent Action Queries
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have shown promise in robot manipulation but often struggle to generalize to new instructions or complex multi-task scenarios. We identify a critical pathology in current training paradigms where goal-driven data collection creates a dataset bias. In such datasets, language instructions are highly predictable from visual observations alone, causing the conditional mutual information between instructions and actions to vanish, a phenomenon we term Information Collapse. Consequently, models degenerate into vision-only policies that ignore language constraints and fail in out-of-distribution (OOD) settings. To address this, we propose BayesianVLA, a novel framework that enforces instruction following via Bayesian decomposition. By introducing learnable Latent Action Queries, we construct a dual-branch architecture to estimate both a vision-only prior $p(a \mid v)$ and a language-conditioned posterior $π(a \mid v, \ell)$. We then optimize the policy to maximize the conditional Pointwise Mutual Information (PMI) between actions and instructions. This objective effectively penalizes the vision shortcut and rewards actions that explicitly explain the language command. Without requiring new data, BayesianVLA significantly improves generalization. Extensive experiments across on SimplerEnv and RoboCasa demonstrate substantial gains, including an 11.3% improvement on the challenging OOD SimplerEnv benchmark, validating the ability of our approach to robustly ground language in action.
TwinBrainVLA: Unleashing the Potential of Generalist VLMs for Embodied Tasks via Asymmetric Mixture-of-Transformers
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Standard Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models typically fine-tune a monolithic Vision-Language Model (VLM) backbone explicitly for robotic control. However, this approach creates a critical tension between maintaining high-level general semantic understanding and learning low-level, fine-grained sensorimotor skills, often leading to "catastrophic forgetting" of the model's open-world capabilities. To resolve this conflict, we introduce TwinBrainVLA, a novel architecture that coordinates a generalist VLM retaining universal semantic understanding and a specialist VLM dedicated to embodied proprioception for joint robotic control. TwinBrainVLA synergizes a frozen "Left Brain", which retains robust general visual reasoning, with a trainable "Right Brain", specialized for embodied perception, via a novel Asymmetric Mixture-of-Transformers (AsyMoT) mechanism. This design allows the Right Brain to dynamically query semantic knowledge from the frozen Left Brain and fuse it with proprioceptive states, providing rich conditioning for a Flow-Matching Action Expert to generate precise continuous controls. Extensive experiments on SimplerEnv and RoboCasa benchmarks demonstrate that TwinBrainVLA achieves superior manipulation performance compared to state-of-the-art baselines while explicitly preserving the comprehensive visual understanding capabilities of the pre-trained VLM, offering a promising direction for building general-purpose robots that simultaneously achieve high-level semantic understanding and low-level physical dexterity.
PhysBrain: Human Egocentric Data as a Bridge from Vision Language Models to Physical Intelligence
Dec 18, 2025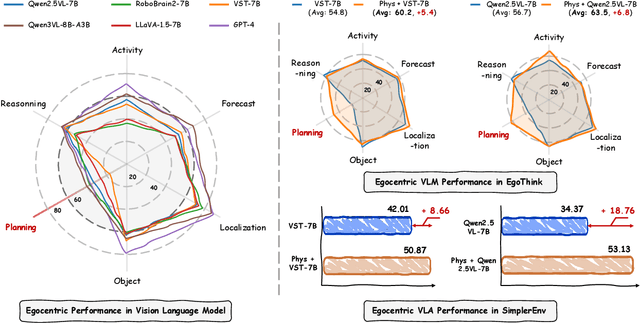
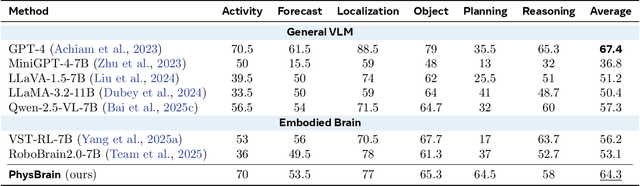
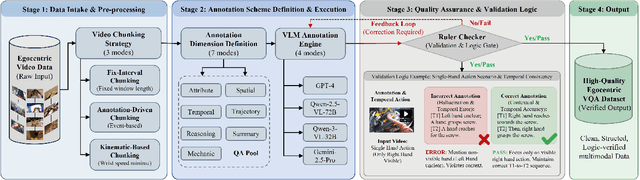
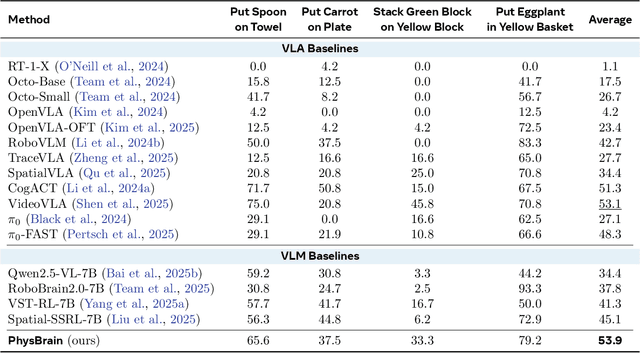
Abstract:Robotic generalization relies on physical intelligence: the ability to reason about state changes, contact-rich interactions, and long-horizon planning under egocentric perception and action. However, most VLMs are trained primarily on third-person data, creating a fundamental viewpoint mismatch for humanoid robots. Scaling robot egocentric data collection remains impractical due to high cost and limited diversity, whereas large-scale human egocentric videos offer a scalable alternative that naturally capture rich interaction context and causal structure. The key challenge is to convert raw egocentric videos into structured and reliable embodiment training supervision. Accordingly, we propose an Egocentric2Embodiment translation pipeline that transforms first-person videos into multi-level, schema-driven VQA supervision with enforced evidence grounding and temporal consistency, enabling the construction of the Egocentric2Embodiment dataset (E2E-3M) at scale. An egocentric-aware embodied brain, termed PhysBrain, is obtained by training on the E2E-3M dataset. PhysBrain exhibits substantially improved egocentric understanding, particularly for planning on EgoThink. It provides an egocentric-aware initialization that enables more sample-efficient VLA fine-tuning and higher SimplerEnv success rates (53.9\%), demonstrating effective transfer from human egocentric supervision to downstream robot control.
Bias-Restrained Prefix Representation Finetuning for Mathematical Reasoning
Nov 13, 2025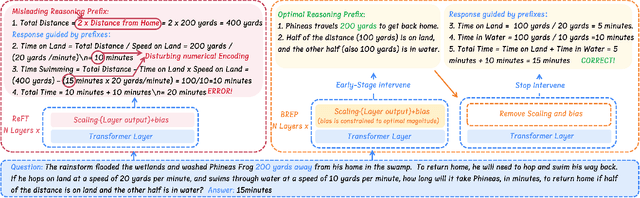
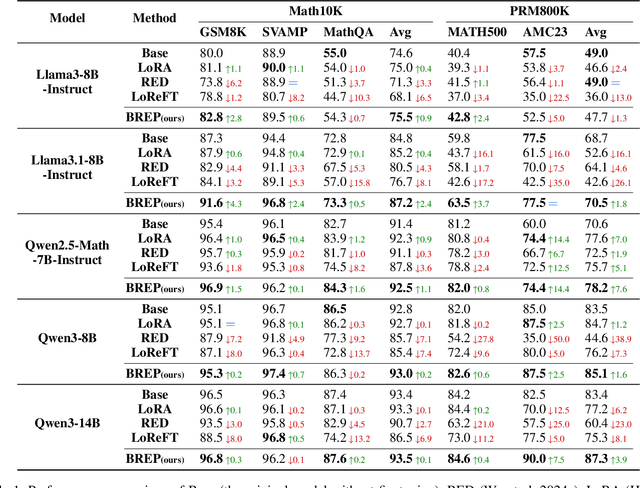
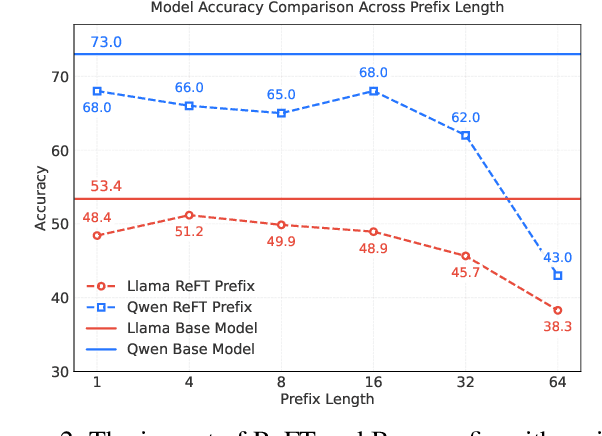
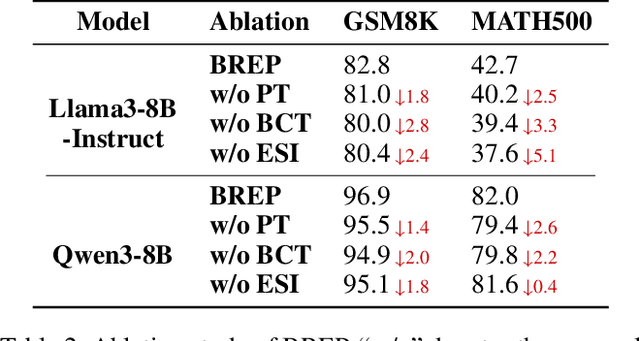
Abstract:Parameter-Efficient finetuning (PEFT) enhances model performance on downstream tasks by updating a minimal subset of parameters. Representation finetuning (ReFT) methods further improve efficiency by freezing model weights and optimizing internal representations with fewer parameters than PEFT, outperforming PEFT on several tasks. However, ReFT exhibits a significant performance decline on mathematical reasoning tasks. To address this problem, the paper demonstrates that ReFT's poor performance on mathematical tasks primarily stems from its struggle to generate effective reasoning prefixes during the early inference phase. Moreover, ReFT disturbs the numerical encoding and the error accumulats during the CoT stage. Based on these observations, this paper proposes Bias-REstrained Prefix Representation FineTuning (BREP ReFT), which enhances ReFT's mathematical reasoning capability by truncating training data to optimize the generation of initial reasoning prefixes, intervening on the early inference stage to prevent error accumulation, and constraining the intervention vectors' magnitude to avoid disturbing numerical encoding. Extensive experiments across diverse model architectures demonstrate BREP's superior effectiveness, efficiency, and robust generalization capability, outperforming both standard ReFT and weight-based PEFT methods on the task of mathematical reasoning. The source code is available at https://github.com/LiangThree/BREP.
Switching Pushing Skill Combined MPC and Deep Reinforcement Learning for Planar Non-prehensile Manipulation
Mar 30, 2023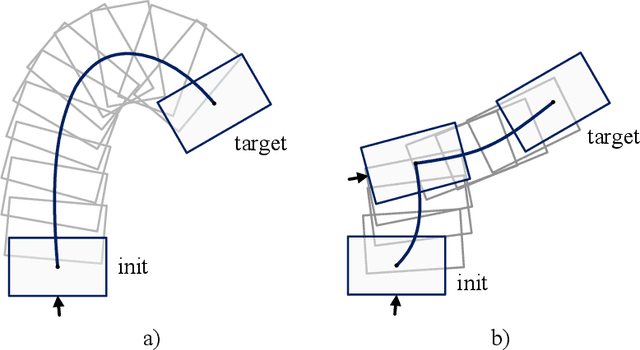
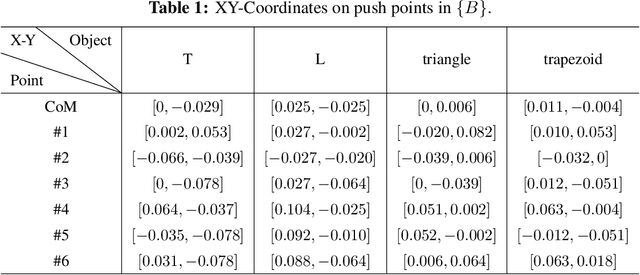
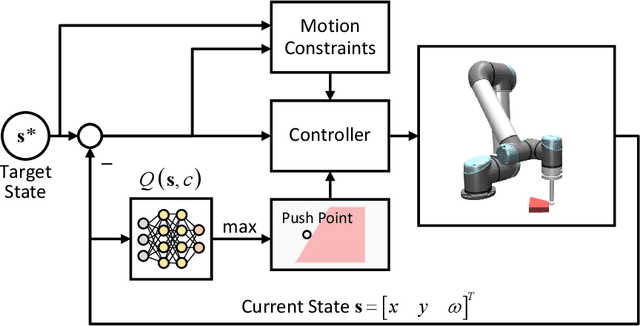

Abstract:In this paper, a novel switching pushing skill algorithm is proposed to improve the efficiency of planar non-prehensile manipulation, which draws inspiration from human pushing actions and comprises two sub-problems, i.e., discrete decision-making of pushing point and continuous feedback control of pushing action. In order to solve the sub-problems above, a combination of Model Predictive Control (MPC) and Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) method is employed. Firstly, the selection of pushing point is modeled as a Markov decision process,and an off-policy DRL method is used by reshaping the reward function to train the decision-making model for selecting pushing point from a pre-constructed set based on the current state. Secondly, a motion constraint region (MCR) is constructed for the specific pushing point based on the distance from the target, followed by utilizing the MPC controller to regulate the motion of the object within the MCR towards the target pose. The trigger condition for switching the pushing point occurs when the object reaches the boundary of the MCR under the pushing action. Subsequently, the pushing point and the controller are updated iteratively until the target pose is reached. We conducted pushing experiments on four distinct object shapes in both simulated and physical environments to evaluate our method. The results indicate that our method achieves a significantly higher training efficiency, with a training time that is only about 20% of the baseline method while maintaining around the same success rate. Moreover, our method outperforms the baseline method in terms of both training and execution efficiency of pushing operations, allowing for rapid learning of robot pushing skills.
Neural Compression-Based Feature Learning for Video Restoration
Mar 18, 2022
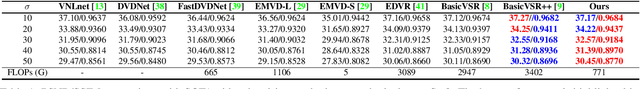


Abstract:How to efficiently utilize the temporal features is crucial, yet challenging, for video restoration. The temporal features usually contain various noisy and uncorrelated information, and they may interfere with the restoration of the current frame. This paper proposes learning noise-robust feature representations to help video restoration. We are inspired by that the neural codec is a natural denoiser. In neural codec, the noisy and uncorrelated contents which are hard to predict but cost lots of bits are more inclined to be discarded for bitrate saving. Therefore, we design a neural compression module to filter the noise and keep the most useful information in features for video restoration. To achieve robustness to noise, our compression module adopts a spatial channel-wise quantization mechanism to adaptively determine the quantization step size for each position in the latent. Experiments show that our method can significantly boost the performance on video denoising, where we obtain 0.13 dB improvement over BasicVSR++ with only 0.23x FLOPs. Meanwhile, our method also obtains SOTA results on video deraining and dehazing.
Weakly Supervised Local Attention Network for Fine-Grained Visual Classification
Aug 06, 2018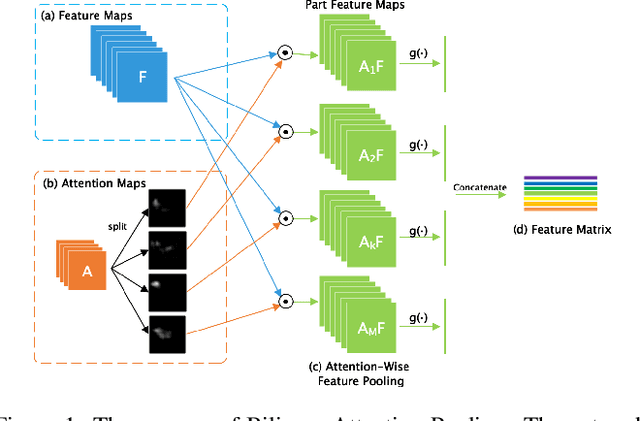
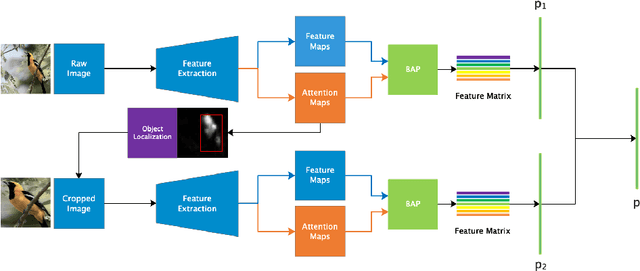

Abstract:In the fine-grained visual classification task, objects usually share similar geometric structure but present different part distribution and variant local features. Therefore, localizing and extracting discriminative local features play a crucial role in obtaining accurate performance. Existing work that first locates specific several object parts and then extracts further local features either require additional location annotation or needs to train multiple independent networks. In this paper. We propose Weakly Supervised Local Attention Network (WS-LAN) to solve the problem, which jointly generates a great many attention maps (region-of-interest maps) to indicate the location of object parts and extract sequential local features by Local Attention Pooling (LAP). Besides, we adopt attention center loss and attention dropout so that each attention map will focus on a unique object part. WS-LAN can be trained end-to-end and achieves the state-of-the-art performance on multiple fine-grained classification datasets, including CUB-200-2011, Stanford Car and FGVC-Aircraft, which demonstrated its effectiveness.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge