Ci Li
Dessie: Disentanglement for Articulated 3D Horse Shape and Pose Estimation from Images
Oct 04, 2024Abstract:In recent years, 3D parametric animal models have been developed to aid in estimating 3D shape and pose from images and video. While progress has been made for humans, it's more challenging for animals due to limited annotated data. To address this, we introduce the first method using synthetic data generation and disentanglement to learn to regress 3D shape and pose. Focusing on horses, we use text-based texture generation and a synthetic data pipeline to create varied shapes, poses, and appearances, learning disentangled spaces. Our method, Dessie, surpasses existing 3D horse reconstruction methods and generalizes to other large animals like zebras, cows, and deer. See the project website at: \url{https://celiali.github.io/Dessie/}.
CLHOP: Combined Audio-Video Learning for Horse 3D Pose and Shape Estimation
Jul 01, 2024



Abstract:In the monocular setting, predicting 3D pose and shape of animals typically relies solely on visual information, which is highly under-constrained. In this work, we explore using audio to enhance 3D shape and motion recovery of horses from monocular video. We test our approach on two datasets: an indoor treadmill dataset for 3D evaluation and an outdoor dataset capturing diverse horse movements, the latter being a contribution to this study. Our results show that incorporating sound with visual data leads to more accurate and robust motion regression. This study is the first to investigate audio's role in 3D animal motion recovery.
Human-Centric Autonomous Systems With LLMs for User Command Reasoning
Nov 14, 2023Abstract:The evolution of autonomous driving has made remarkable advancements in recent years, evolving into a tangible reality. However, a human-centric large-scale adoption hinges on meeting a variety of multifaceted requirements. To ensure that the autonomous system meets the user's intent, it is essential to accurately discern and interpret user commands, especially in complex or emergency situations. To this end, we propose to leverage the reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to infer system requirements from in-cabin users' commands. Through a series of experiments that include different LLM models and prompt designs, we explore the few-shot multivariate binary classification accuracy of system requirements from natural language textual commands. We confirm the general ability of LLMs to understand and reason about prompts but underline that their effectiveness is conditioned on the quality of both the LLM model and the design of appropriate sequential prompts. Code and models are public with the link \url{https://github.com/KTH-RPL/DriveCmd_LLM}.
hSMAL: Detailed Horse Shape and Pose Reconstruction for Motion Pattern Recognition
Jun 18, 2021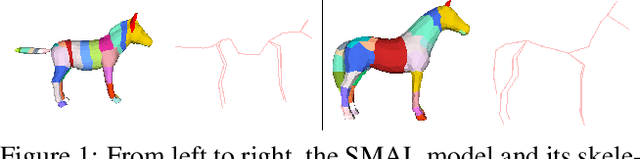
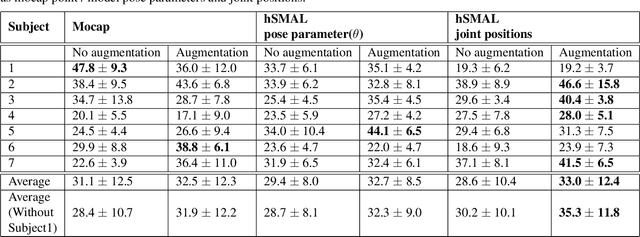
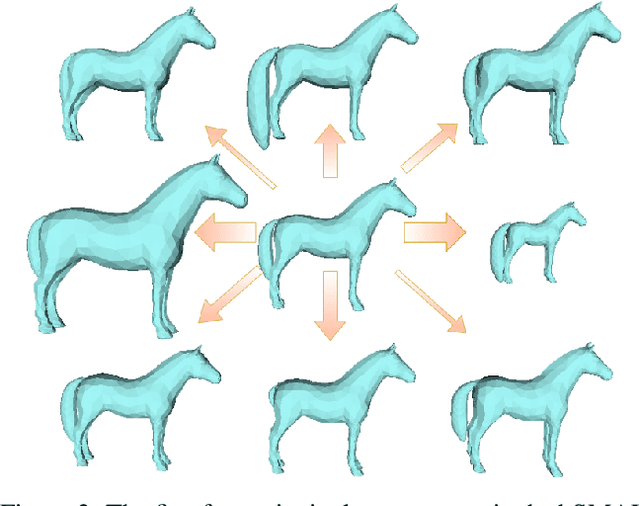
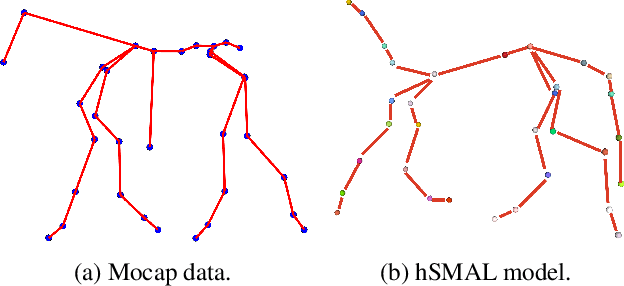
Abstract:In this paper we present our preliminary work on model-based behavioral analysis of horse motion. Our approach is based on the SMAL model, a 3D articulated statistical model of animal shape. We define a novel SMAL model for horses based on a new template, skeleton and shape space learned from $37$ horse toys. We test the accuracy of our hSMAL model in reconstructing a horse from 3D mocap data and images. We apply the hSMAL model to the problem of lameness detection from video, where we fit the model to images to recover 3D pose and train an ST-GCN network on pose data. A comparison with the same network trained on mocap points illustrates the benefit of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge