Chunyan Bai
Improving 3D Object Detection through Progressive Population Based Augmentation
Apr 02, 2020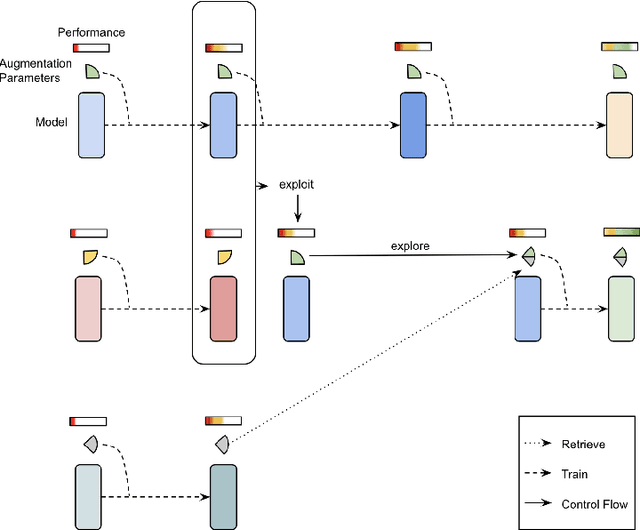
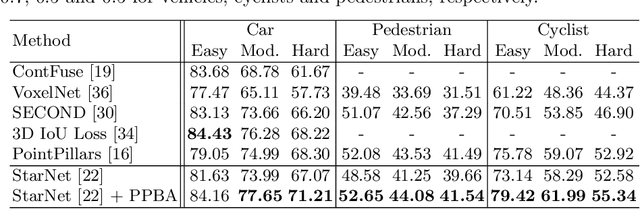
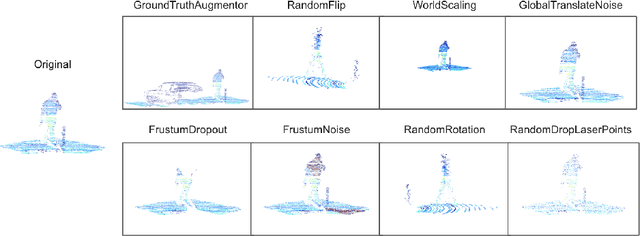

Abstract:Data augmentation has been widely adopted for object detection in 3D point clouds. All previous efforts have focused on manually designing specific data augmentation methods for individual architectures, however no work has attempted to automate the design of data augmentation in 3D detection problems -- as is common in 2D image-based computer vision. In this work, we present the first attempt to automate the design of data augmentation policies for 3D object detection. We present an algorithm, termed Progressive Population Based Augmentation (PPBA). PPBA learns to optimize augmentation strategies by narrowing down the search space and adopting the best parameters discovered in previous iterations. On the KITTI test set, PPBA improves the StarNet detector by substantial margins on the moderate difficulty category of cars, pedestrians, and cyclists, outperforming all current state-of-the-art single-stage detection models. Additional experiments on the Waymo Open Dataset indicate that PPBA continues to effectively improve 3D object detection on a 20x larger dataset compared to KITTI. The magnitude of the improvements may be comparable to advances in 3D perception architectures and the gains come without an incurred cost at inference time. In subsequent experiments, we find that PPBA may be up to 10x more data efficient than baseline 3D detection models without augmentation, highlighting that 3D detection models may achieve competitive accuracy with far fewer labeled examples.
Deep Video Generation, Prediction and Completion of Human Action Sequences
Dec 08, 2017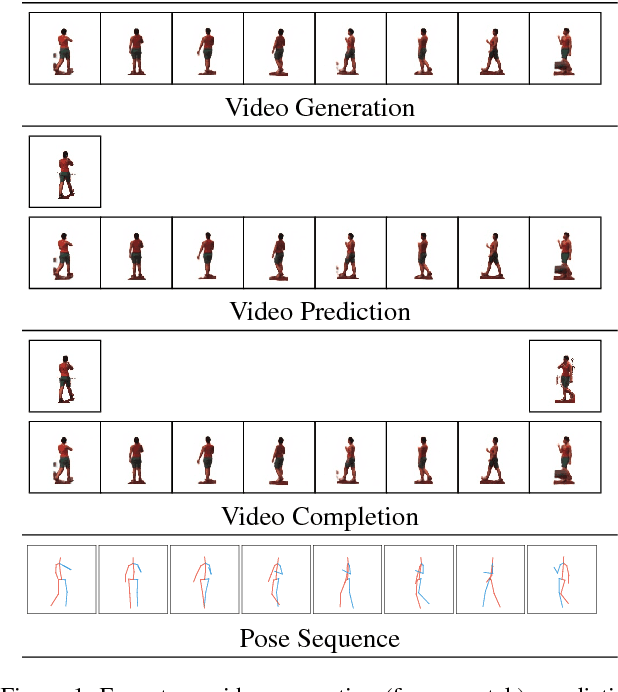
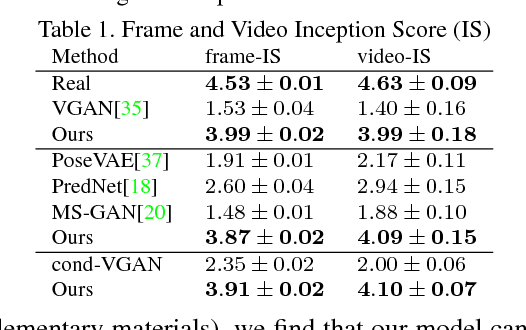
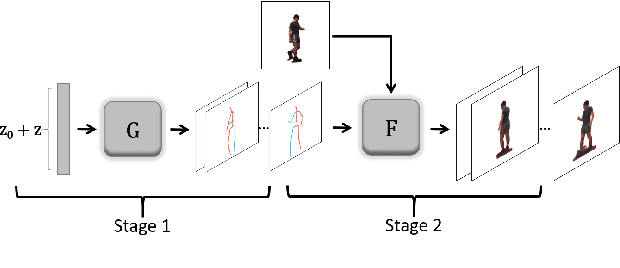
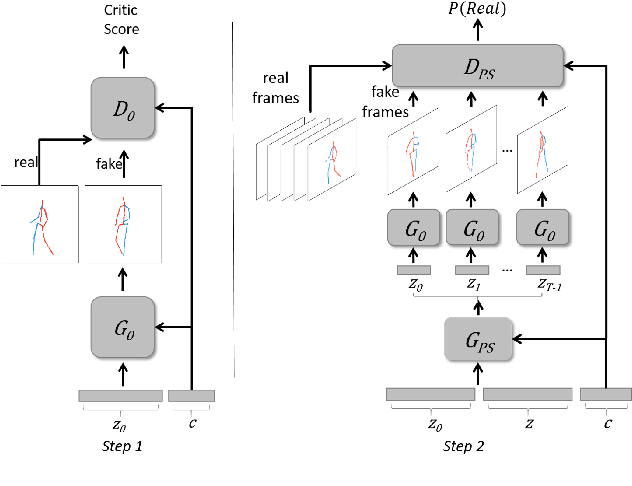
Abstract:Current deep learning results on video generation are limited while there are only a few first results on video prediction and no relevant significant results on video completion. This is due to the severe ill-posedness inherent in these three problems. In this paper, we focus on human action videos, and propose a general, two-stage deep framework to generate human action videos with no constraints or arbitrary number of constraints, which uniformly address the three problems: video generation given no input frames, video prediction given the first few frames, and video completion given the first and last frames. To make the problem tractable, in the first stage we train a deep generative model that generates a human pose sequence from random noise. In the second stage, a skeleton-to-image network is trained, which is used to generate a human action video given the complete human pose sequence generated in the first stage. By introducing the two-stage strategy, we sidestep the original ill-posed problems while producing for the first time high-quality video generation/prediction/completion results of much longer duration. We present quantitative and qualitative evaluation to show that our two-stage approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods in video generation, prediction and video completion. Our video result demonstration can be viewed at https://iamacewhite.github.io/supp/index.html
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge