Christian Uhl
Dimension reduction methods, persistent homology and machine learning for EEG signal analysis of Interictal Epileptic Discharges
Feb 18, 2025

Abstract:Recognizing specific events in medical data requires trained personnel. To aid the classification, machine learning algorithms can be applied. In this context, medical records are usually high-dimensional, although a lower dimension can also reflect the dynamics of the signal. In this study, electroencephalogram data with Interictal Epileptic Discharges (IEDs) are investigated. First, the dimensions are reduced using Dynamical Component Analysis (DyCA) and Principal Component Analysis (PCA), respectively. The reduced data are examined using topological data analysis (TDA), specifically using a persistent homology algorithm. The persistent homology results are used for targeted feature generation. The features are used to train and evaluate a Support Vector Machine (SVM) to distinguish IEDs from background activities.
Learning-Based Autonomous Navigation, Benchmark Environments and Simulation Framework for Endovascular Interventions
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Endovascular interventions are a life-saving treatment for many diseases, yet suffer from drawbacks such as radiation exposure and potential scarcity of proficient physicians. Robotic assistance during these interventions could be a promising support towards these problems. Research focusing on autonomous endovascular interventions utilizing artificial intelligence-based methodologies is gaining popularity. However, variability in assessment environments hinders the ability to compare and contrast the efficacy of different approaches, primarily due to each study employing a unique evaluation framework. In this study, we present deep reinforcement learning-based autonomous endovascular device navigation on three distinct digital benchmark interventions: BasicWireNav, ArchVariety, and DualDeviceNav. The benchmark interventions were implemented with our modular simulation framework stEVE (simulated EndoVascular Environment). Autonomous controllers were trained solely in simulation and evaluated in simulation and on physical test benches with camera and fluoroscopy feedback. Autonomous control for BasicWireNav and ArchVariety reached high success rates and was successfully transferred from the simulated training environment to the physical test benches, while autonomous control for DualDeviceNav reached a moderate success rate. The experiments demonstrate the feasibility of stEVE and its potential for transferring controllers trained in simulation to real-world scenarios. Nevertheless, they also reveal areas that offer opportunities for future research. This study demonstrates the transferability of autonomous controllers from simulation to the real world in endovascular navigation and lowers the entry barriers and increases the comparability of research on endovascular assistance systems by providing open-source training scripts, benchmarks and the stEVE framework.
Dynamical Component Analysis (DyCA) and its application on epileptic EEG
Feb 05, 2019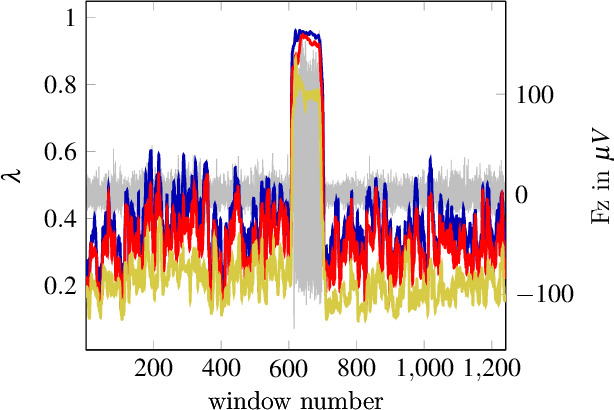
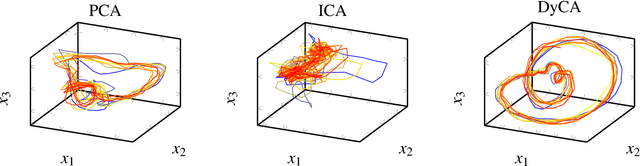
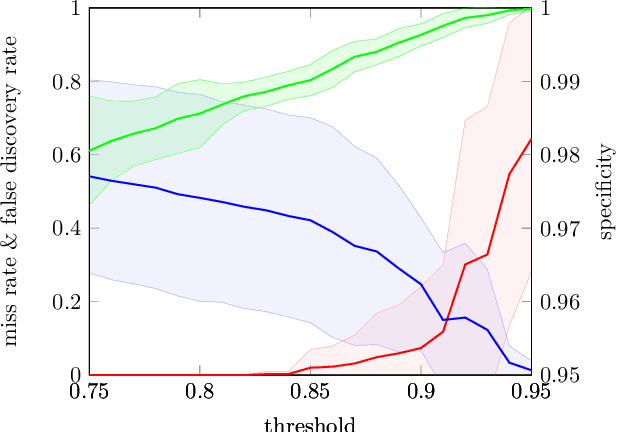

Abstract:Dynamical Component Analysis (DyCA) is a recently-proposed method to detect projection vectors to reduce the dimensionality of multi-variate deterministic datasets. It is based on the solution of a generalized eigenvalue problem and therefore straight forward to implement. DyCA is introduced and applied to EEG data of epileptic seizures. The obtained eigenvectors are used to project the signal and the corresponding trajectories in phase space are compared with PCA and ICA-projections. The eigenvalues of DyCA are utilized for seizure detection and the obtained results in terms of specificity, false discovery rate and miss rate are compared to other seizure detection algorithms.
Dynamical Component Analysis (DyCA): Dimensionality Reduction For High-Dimensional Deterministic Time-Series
Jul 26, 2018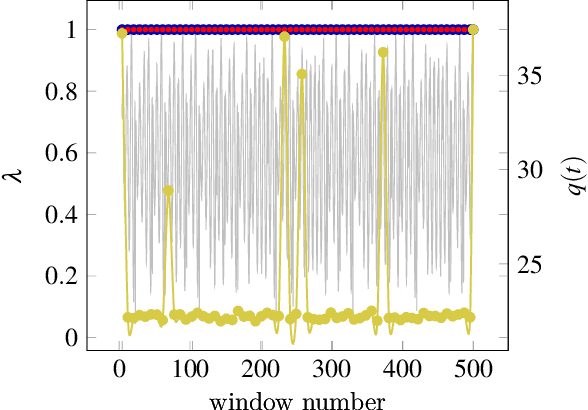
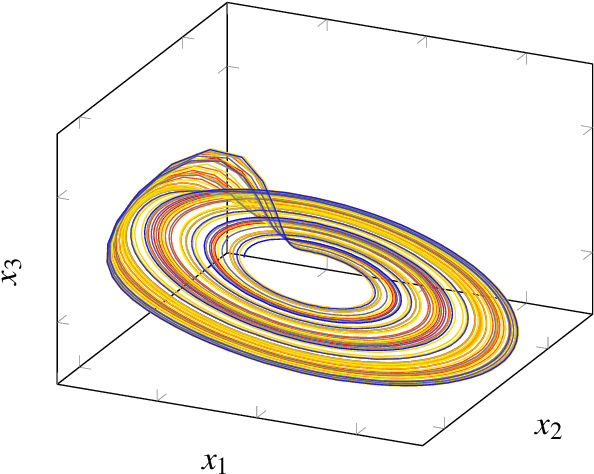

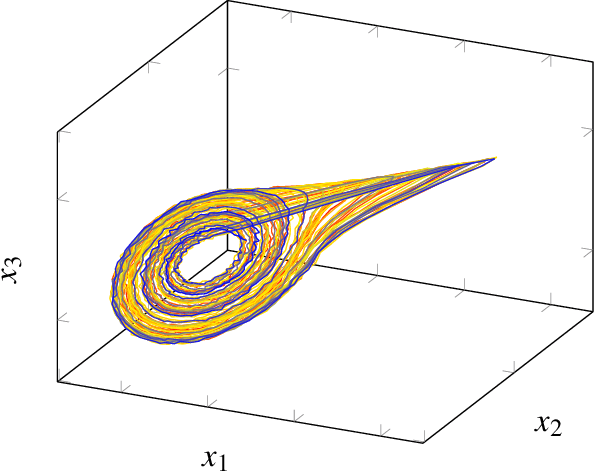
Abstract:Multivariate signal processing is often based on dimensionality reduction techniques. We propose a new method, Dynamical Component Analysis (DyCA), leading to a classification of the underlying dynamics and - for a certain type of dynamics - to a signal subspace representing the dynamics of the data. In this paper the algorithm is derived leading to a generalized eigenvalue problem of correlation matrices. The application of the DyCA on high-dimensional chaotic signals is presented both for simulated data as well as real EEG data of epileptic seizures.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge