Chia-Wei Hsu
Collaborative AI Enhances Image Understanding in Materials Science
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:The Copilot for Real-world Experimental Scientist (CRESt) system empowers researchers to control autonomous laboratories through conversational AI, providing a seamless interface for managing complex experimental workflows. We have enhanced CRESt by integrating a multi-agent collaboration mechanism that utilizes the complementary strengths of the ChatGPT and Gemini models for precise image analysis in materials science. This innovative approach significantly improves the accuracy of experimental outcomes by fostering structured debates between the AI models, which enhances decision-making processes in materials phase analysis. Additionally, to evaluate the generalizability of this approach, we tested it on a quantitative task of counting particles. Here, the collaboration between the AI models also led to improved results, demonstrating the versatility and robustness of this method. By harnessing this dual-AI framework, this approach stands as a pioneering method for enhancing experimental accuracy and efficiency in materials research, with applications extending beyond CRESt to broader scientific experimentation and analysis.
Frankenstein Optimizer: Harnessing the Potential by Revisiting Optimization Tricks
Mar 04, 2025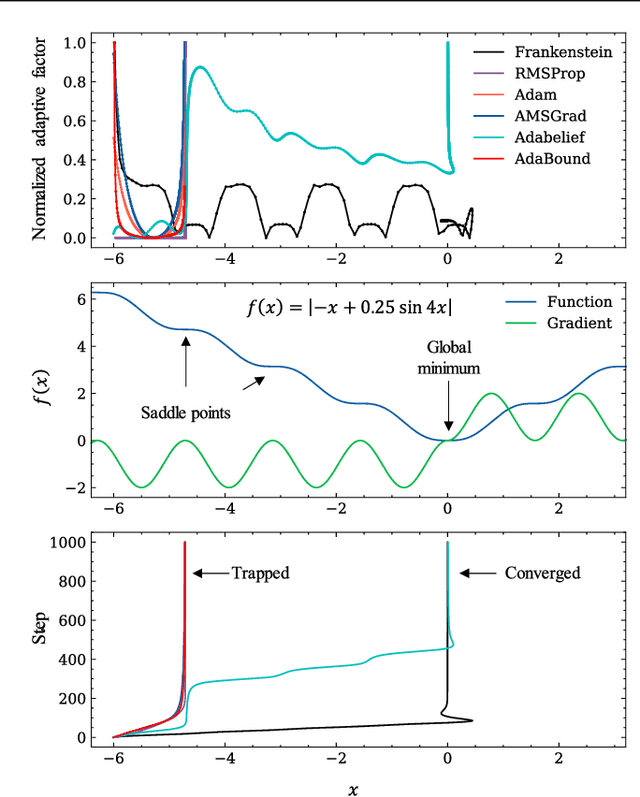
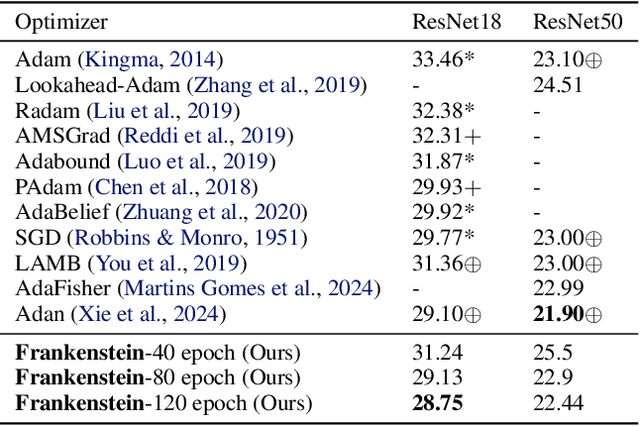
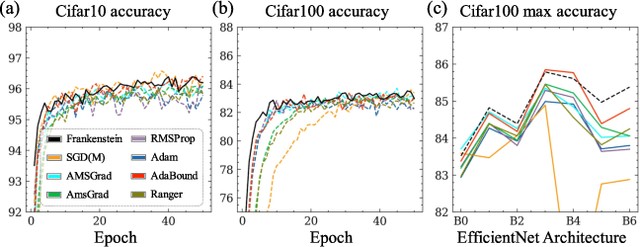
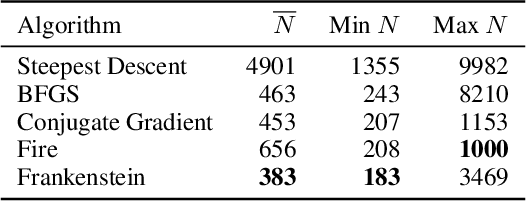
Abstract:Gradient-based optimization drives the unprecedented performance of modern deep neural network models across diverse applications. Adaptive algorithms have accelerated neural network training due to their rapid convergence rates; however, they struggle to find ``flat minima" reliably, resulting in suboptimal generalization compared to stochastic gradient descent (SGD). By revisiting various adaptive algorithms' mechanisms, we propose the Frankenstein optimizer, which combines their advantages. The proposed Frankenstein dynamically adjusts first- and second-momentum coefficients according to the optimizer's current state to directly maintain consistent learning dynamics and immediately reflect sudden gradient changes. Extensive experiments across several research domains such as computer vision, natural language processing, few-shot learning, and scientific simulations show that Frankenstein surpasses existing adaptive algorithms and SGD empirically regarding convergence speed and generalization performance. Furthermore, this research deepens our understanding of adaptive algorithms through centered kernel alignment analysis and loss landscape visualization during the learning process.
Contrastive Learning of English Language and Crystal Graphs for Multimodal Representation of Materials Knowledge
Feb 23, 2025



Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is increasingly used for the inverse design of materials, such as crystals and molecules. Existing AI research on molecules has integrated chemical structures of molecules with textual knowledge to adapt to complex instructions. However, this approach has been unattainable for crystals due to data scarcity from the biased distribution of investigated crystals and the lack of semantic supervision in peer-reviewed literature. In this work, we introduce a contrastive language-crystals model (CLaC) pre-trained on a newly synthesized dataset of 126k crystal structure-text pairs. To demonstrate the advantage of using synthetic data to overcome data scarcity, we constructed a comparable dataset extracted from academic papers. We evaluate CLaC's generalization ability through various zero-shot cross-modal tasks and downstream applications. In experiments, CLaC achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot generalization performance in understanding crystal structures, surpassing latest large language models.
1.5 million materials narratives generated by chatbots
Aug 25, 2023Abstract:The advent of artificial intelligence (AI) has enabled a comprehensive exploration of materials for various applications. However, AI models often prioritize frequently encountered materials in the scientific literature, limiting the selection of suitable candidates based on inherent physical and chemical properties. To address this imbalance, we have generated a dataset of 1,494,017 natural language-material paragraphs based on combined OQMD, Materials Project, JARVIS, COD and AFLOW2 databases, which are dominated by ab initio calculations and tend to be much more evenly distributed on the periodic table. The generated text narratives were then polled and scored by both human experts and ChatGPT-4, based on three rubrics: technical accuracy, language and structure, and relevance and depth of content, showing similar scores but with human-scored depth of content being the most lagging. The merger of multi-modality data sources and large language model (LLM) holds immense potential for AI frameworks to help the exploration and discovery of solid-state materials for specific applications.
Can ChatGPT be used to generate scientific hypotheses?
Mar 30, 2023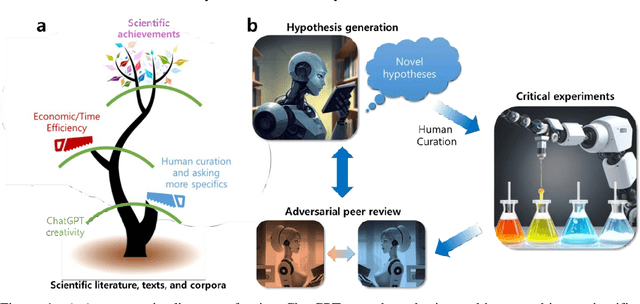
Abstract:We investigate whether large language models can perform the creative hypothesis generation that human researchers regularly do. While the error rate is high, generative AI seems to be able to effectively structure vast amounts of scientific knowledge and provide interesting and testable hypotheses. The future scientific enterprise may include synergistic efforts with a swarm of "hypothesis machines", challenged by automated experimentation and adversarial peer reviews.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge