Chi Zheng
In-the-wild Facial Expression Recognition in Extreme Poses
Nov 06, 2018Abstract:In the computer research area, facial expression recognition is a hot research problem. Recent years, the research has moved from the lab environment to in-the-wild circumstances. It is challenging, especially under extreme poses. But current expression detection systems are trying to avoid the pose effects and gain the general applicable ability. In this work, we solve the problem in the opposite approach. We consider the head poses and detect the expressions within special head poses. Our work includes two parts: detect the head pose and group it into one pre-defined head pose class; do facial expression recognize within each pose class. Our experiments show that the recognition results with pose class grouping are much better than that of direct recognition without considering poses. We combine the hand-crafted features, SIFT, LBP and geometric feature, with deep learning feature as the representation of the expressions. The handcrafted features are added into the deep learning framework along with the high level deep learning features. As a comparison, we implement SVM and random forest to as the prediction models. To train and test our methodology, we labeled the face dataset with 6 basic expressions.
An End-to-End Deep Learning Histochemical Scoring System for Breast Cancer Tissue Microarray
Jan 19, 2018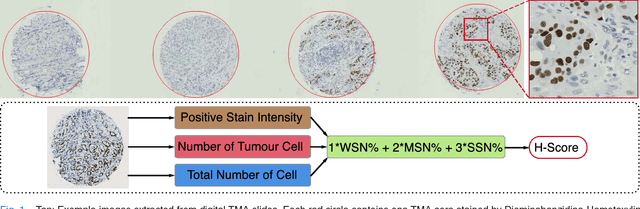
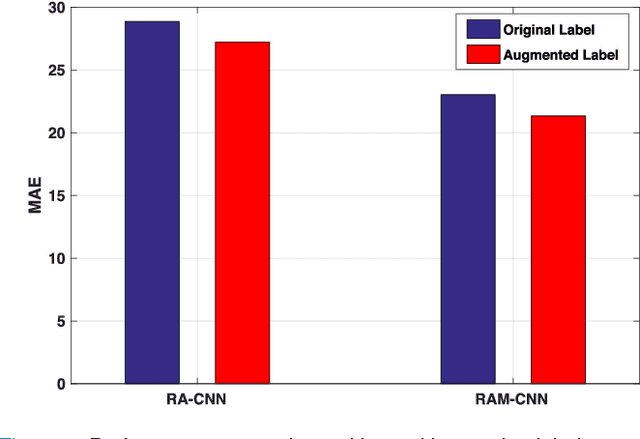
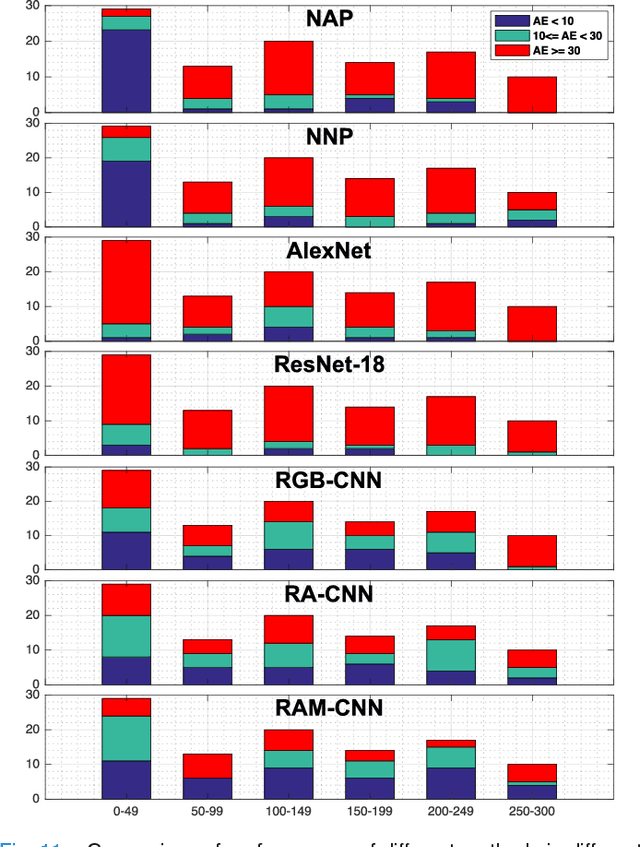
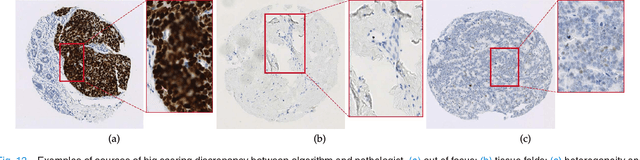
Abstract:One of the methods for stratifying different molecular classes of breast cancer is the Nottingham Prognostic Index Plus (NPI+) which uses breast cancer relevant biomarkers to stain tumour tissues prepared on tissue microarray (TMA). To determine the molecular class of the tumour, pathologists will have to manually mark the nuclei activity biomarkers through a microscope and use a semi-quantitative assessment method to assign a histochemical score (H-Score) to each TMA core. Manually marking positively stained nuclei is a time consuming, imprecise and subjective process which will lead to inter-observer and intra-observer discrepancies. In this paper, we present an end-to-end deep learning system which directly predicts the H-Score automatically. Our system imitates the pathologists' decision process and uses one fully convolutional network (FCN) to extract all nuclei region (tumour and non-tumour), a second FCN to extract tumour nuclei region, and a multi-column convolutional neural network which takes the outputs of the first two FCNs and the stain intensity description image as input and acts as the high-level decision making mechanism to directly output the H-Score of the input TMA image. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first end-to-end system that takes a TMA image as input and directly outputs a clinical score. We will present experimental results which demonstrate that the H-Scores predicted by our model have very high and statistically significant correlation with experienced pathologists' scores and that the H-Score discrepancy between our algorithm and the pathologists is on par with the inter-subject discrepancy between the pathologists.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge