Chenlong Hu
Multi-Modal Multi-Granularity Tokenizer for Chu Bamboo Slip Scripts
Sep 02, 2024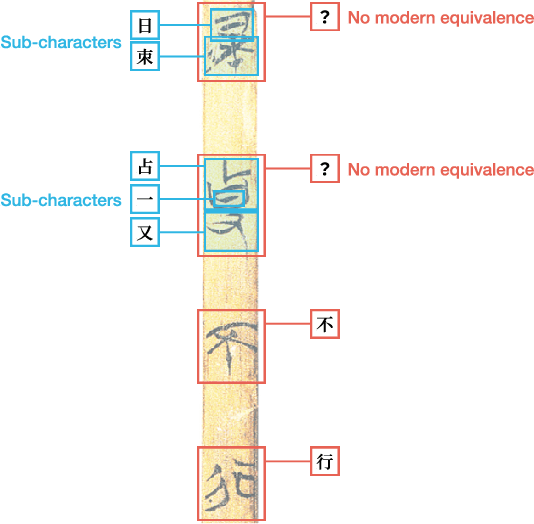
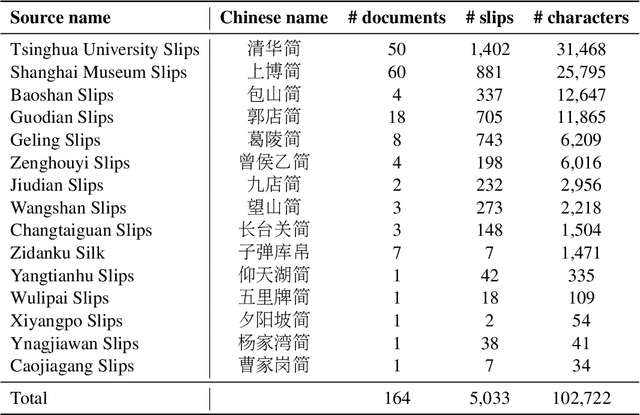
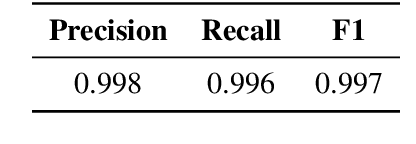
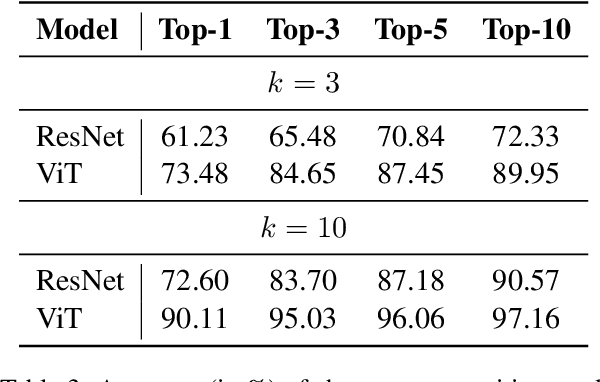
Abstract:This study presents a multi-modal multi-granularity tokenizer specifically designed for analyzing ancient Chinese scripts, focusing on the Chu bamboo slip (CBS) script used during the Spring and Autumn and Warring States period (771-256 BCE) in Ancient China. Considering the complex hierarchical structure of ancient Chinese scripts, where a single character may be a combination of multiple sub-characters, our tokenizer first adopts character detection to locate character boundaries, and then conducts character recognition at both the character and sub-character levels. Moreover, to support the academic community, we have also assembled the first large-scale dataset of CBSs with over 100K annotated character image scans. On the part-of-speech tagging task built on our dataset, using our tokenizer gives a 5.5% relative improvement in F1-score compared to mainstream sub-word tokenizers. Our work not only aids in further investigations of the specific script but also has the potential to advance research on other forms of ancient Chinese scripts.
Integration of Large Language Models in Control of EHD Pumps for Precise Color Synthesis
Jan 21, 2024
Abstract:This paper presents an innovative approach to integrating Large Language Models (LLMs) with Arduino-controlled Electrohydrodynamic (EHD) pumps for precise color synthesis in automation systems. We propose a novel framework that employs fine-tuned LLMs to interpret natural language commands and convert them into specific operational instructions for EHD pump control. This approach aims to enhance user interaction with complex hardware systems, making it more intuitive and efficient. The methodology involves four key steps: fine-tuning the language model with a dataset of color specifications and corresponding Arduino code, developing a natural language processing interface, translating user inputs into executable Arduino code, and controlling EHD pumps for accurate color mixing. Conceptual experiment results, based on theoretical assumptions, indicate a high potential for accurate color synthesis, efficient language model interpretation, and reliable EHD pump operation. This research extends the application of LLMs beyond text-based tasks, demonstrating their potential in industrial automation and control systems. While highlighting the limitations and the need for real-world testing, this study opens new avenues for AI applications in physical system control and sets a foundation for future advancements in AI-driven automation technologies.
Robust Ellipse Fitting Based on Maximum Correntropy Criterion With Variable Center
Oct 24, 2022Abstract:The presence of outliers can significantly degrade the performance of ellipse fitting methods. We develop an ellipse fitting method that is robust to outliers based on the maximum correntropy criterion with variable center (MCC-VC), where a Laplacian kernel is used. For single ellipse fitting, we formulate a non-convex optimization problem to estimate the kernel bandwidth and center and divide it into two subproblems, each estimating one parameter. We design sufficiently accurate convex approximation to each subproblem such that computationally efficient closed-form solutions are obtained. The two subproblems are solved in an alternate manner until convergence is reached. We also investigate coupled ellipses fitting. While there exist multiple ellipses fitting methods that can be used for coupled ellipses fitting, we develop a couple ellipses fitting method by exploiting the special structure. Having unknown association between data points and ellipses, we introduce an association vector for each data point and formulate a non-convex mixed-integer optimization problem to estimate the data associations, which is approximately solved by relaxing it into a second-order cone program. Using the estimated data associations, we extend the proposed method to achieve the final coupled ellipses fitting. The proposed method is shown to have significantly better performance over the existing methods in both simulated data and real images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge