Charlotte Pouw
A Linguistically Motivated Analysis of Intonational Phrasing in Text-to-Speech Systems: Revealing Gaps in Syntactic Sensitivity
May 28, 2025Abstract:We analyze the syntactic sensitivity of Text-to-Speech (TTS) systems using methods inspired by psycholinguistic research. Specifically, we focus on the generation of intonational phrase boundaries, which can often be predicted by identifying syntactic boundaries within a sentence. We find that TTS systems struggle to accurately generate intonational phrase boundaries in sentences where syntactic boundaries are ambiguous (e.g., garden path sentences or sentences with attachment ambiguity). In these cases, systems need superficial cues such as commas to place boundaries at the correct positions. In contrast, for sentences with simpler syntactic structures, we find that systems do incorporate syntactic cues beyond surface markers. Finally, we finetune models on sentences without commas at the syntactic boundary positions, encouraging them to focus on more subtle linguistic cues. Our findings indicate that this leads to more distinct intonation patterns that better reflect the underlying structure.
Perception of Phonological Assimilation by Neural Speech Recognition Models
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:Human listeners effortlessly compensate for phonological changes during speech perception, often unconsciously inferring the intended sounds. For example, listeners infer the underlying /n/ when hearing an utterance such as "clea[m] pan", where [m] arises from place assimilation to the following labial [p]. This article explores how the neural speech recognition model Wav2Vec2 perceives assimilated sounds, and identifies the linguistic knowledge that is implemented by the model to compensate for assimilation during Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). Using psycholinguistic stimuli, we systematically analyze how various linguistic context cues influence compensation patterns in the model's output. Complementing these behavioral experiments, our probing experiments indicate that the model shifts its interpretation of assimilated sounds from their acoustic form to their underlying form in its final layers. Finally, our causal intervention experiments suggest that the model relies on minimal phonological context cues to accomplish this shift. These findings represent a step towards better understanding the similarities and differences in phonological processing between neural ASR models and humans.
ChapGTP, ILLC's Attempt at Raising a BabyLM: Improving Data Efficiency by Automatic Task Formation
Oct 17, 2023Abstract:We present the submission of the ILLC at the University of Amsterdam to the BabyLM challenge (Warstadt et al., 2023), in the strict-small track. Our final model, ChapGTP, is a masked language model that was trained for 200 epochs, aided by a novel data augmentation technique called Automatic Task Formation. We discuss in detail the performance of this model on the three evaluation suites: BLiMP, (Super)GLUE, and MSGS. Furthermore, we present a wide range of methods that were ultimately not included in the model, but may serve as inspiration for training LMs in low-resource settings.
Cross-Lingual Transfer of Cognitive Processing Complexity
Feb 27, 2023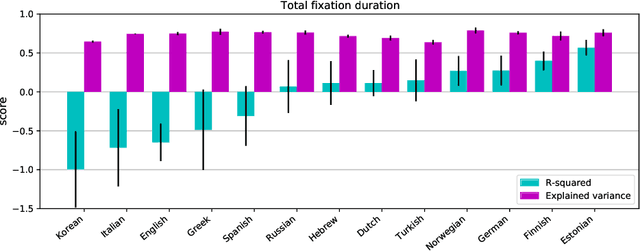
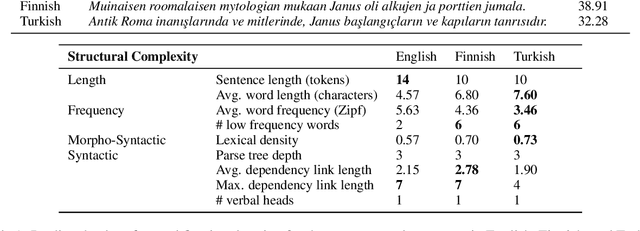
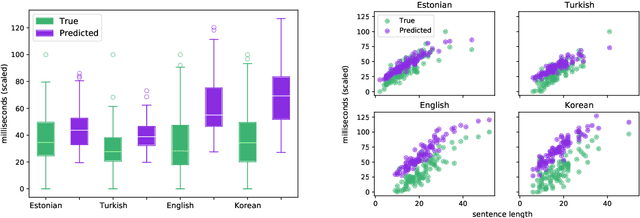
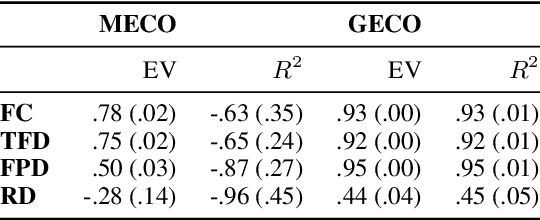
Abstract:When humans read a text, their eye movements are influenced by the structural complexity of the input sentences. This cognitive phenomenon holds across languages and recent studies indicate that multilingual language models utilize structural similarities between languages to facilitate cross-lingual transfer. We use sentence-level eye-tracking patterns as a cognitive indicator for structural complexity and show that the multilingual model XLM-RoBERTa can successfully predict varied patterns for 13 typologically diverse languages, despite being fine-tuned only on English data. We quantify the sensitivity of the model to structural complexity and distinguish a range of complexity characteristics. Our results indicate that the model develops a meaningful bias towards sentence length but also integrates cross-lingual differences. We conduct a control experiment with randomized word order and find that the model seems to additionally capture more complex structural information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge