Charles Xie
Starling: An I/O-Efficient Disk-Resident Graph Index Framework for High-Dimensional Vector Similarity Search on Data Segment
Jan 16, 2024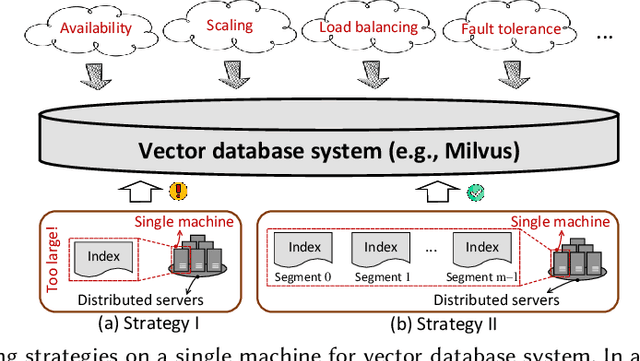

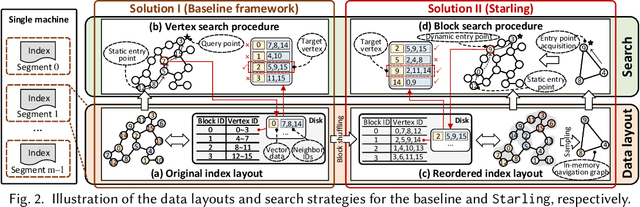

Abstract:High-dimensional vector similarity search (HVSS) is gaining prominence as a powerful tool for various data science and AI applications. As vector data scales up, in-memory indexes pose a significant challenge due to the substantial increase in main memory requirements. A potential solution involves leveraging disk-based implementation, which stores and searches vector data on high-performance devices like NVMe SSDs. However, implementing HVSS for data segments proves to be intricate in vector databases where a single machine comprises multiple segments for system scalability. In this context, each segment operates with limited memory and disk space, necessitating a delicate balance between accuracy, efficiency, and space cost. Existing disk-based methods fall short as they do not holistically address all these requirements simultaneously. In this paper, we present Starling, an I/O-efficient disk-resident graph index framework that optimizes data layout and search strategy within the segment. It has two primary components: (1) a data layout incorporating an in-memory navigation graph and a reordered disk-based graph with enhanced locality, reducing the search path length and minimizing disk bandwidth wastage; and (2) a block search strategy designed to minimize costly disk I/O operations during vector query execution. Through extensive experiments, we validate the effectiveness, efficiency, and scalability of Starling. On a data segment with 2GB memory and 10GB disk capacity, Starling can accommodate up to 33 million vectors in 128 dimensions, offering HVSS with over 0.9 average precision and top-10 recall rate, and latency under 1 millisecond. The results showcase Starling's superior performance, exhibiting 43.9$\times$ higher throughput with 98% lower query latency compared to state-of-the-art methods while maintaining the same level of accuracy.
Using Machine Learning to Predict Engineering Technology Students' Success with Computer Aided Design
Aug 12, 2021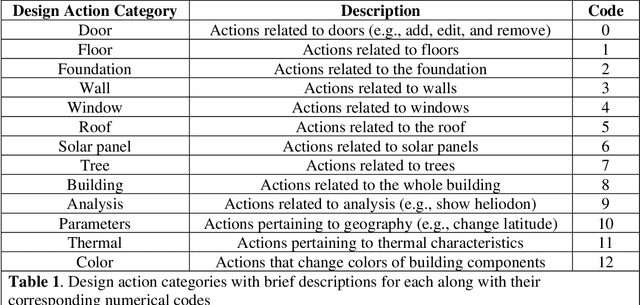
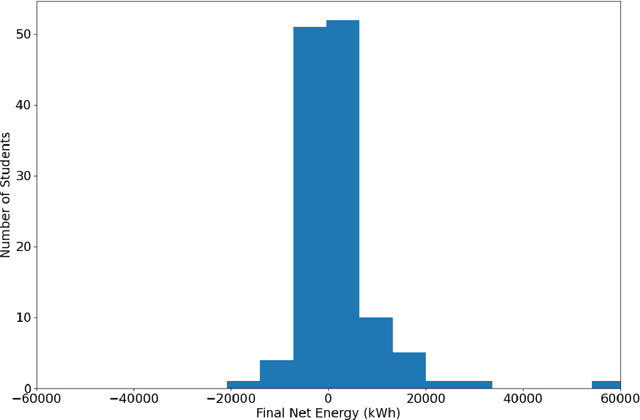
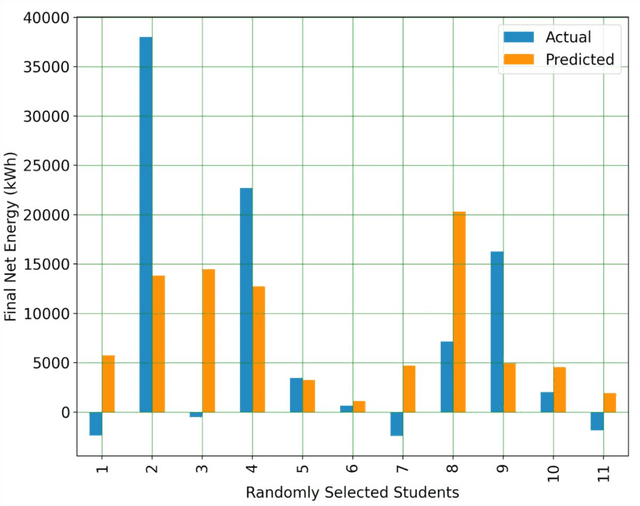
Abstract:Computer-aided design (CAD) programs are essential to engineering as they allow for better designs through low-cost iterations. While CAD programs are typically taught to undergraduate students as a job skill, such software can also help students learn engineering concepts. A current limitation of CAD programs (even those that are specifically designed for educational purposes) is that they are not capable of providing automated real-time help to students. To encourage CAD programs to build in assistance to students, we used data generated from students using a free, open source CAD software called Aladdin to demonstrate how student data combined with machine learning techniques can predict how well a particular student will perform in a design task. We challenged students to design a house that consumed zero net energy as part of an introductory engineering technology undergraduate course. Using data from 128 students, along with the scikit-learn Python machine learning library, we tested our models using both total counts of design actions and sequences of design actions as inputs. We found that our models using early design sequence actions are particularly valuable for prediction. Our logistic regression model achieved a >60% chance of predicting if a student would succeed in designing a zero net energy house. Our results suggest that it would be feasible for Aladdin to provide useful feedback to students when they are approximately halfway through their design. Further improvements to these models could lead to earlier predictions and thus provide students feedback sooner to enhance their learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge