Carmine Tommaso Recchiuto
Enhancing Worker Safety in Harbors Using Quadruped Robots
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Infrastructure inspection is becoming increasingly relevant in the field of robotics due to its significant impact on ensuring workers' safety. The harbor environment presents various challenges in designing a robotic solution for inspection, given the complexity of daily operations. This work introduces an initial phase to identify critical areas within the port environment. Following this, a preliminary solution using a quadruped robot for inspecting these critical areas is analyzed.
Designing Empathetic Companions: Exploring Personality, Emotion, and Trust in Social Robots
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:How should a companion robot behave? In this research, we present a cognitive architecture based on a tailored personality model to investigate the impact of robotic personalities on the perception of companion robots. Drawing from existing literature, we identified empathy, trust, and enjoyability as key factors in building companionship with social robots. Based on these insights, we implemented a personality-dependent, emotion-aware generator, recognizing the crucial role of robot emotions in shaping these elements. We then conducted a user study involving 84 dyadic conversation sessions with the emotional robot Navel, which exhibited different personalities. Results were derived from a multimodal analysis, including questionnaires, open-ended responses, and behavioral observations. This approach allowed us to validate the developed emotion generator and explore the relationship between the personality traits of Agreeableness, Extraversion, Conscientiousness, and Empathy. Furthermore, we drew robust conclusions on how these traits influence relational trust, capability trust, enjoyability, and sociability.
EmoACT: a Framework to Embed Emotions into Artificial Agents Based on Affect Control Theory
Apr 16, 2025Abstract:As robots and artificial agents become increasingly integrated into daily life, enhancing their ability to interact with humans is essential. Emotions, which play a crucial role in human interactions, can improve the naturalness and transparency of human-robot interactions (HRI) when embodied in artificial agents. This study aims to employ Affect Control Theory (ACT), a psychological model of emotions deeply rooted in interaction, for the generation of synthetic emotions. A platform-agnostic framework inspired by ACT was developed and implemented in a humanoid robot to assess its impact on human perception. Results show that the frequency of emotional displays impacts how users perceive the robot. Moreover, appropriate emotional expressions seem to enhance the robot's perceived emotional and cognitive agency. The findings suggest that ACT can be successfully employed to embed synthetic emotions into robots, resulting in effective human-robot interactions, where the robot is perceived more as a social agent than merely a machine.
Moderating Group Conversation Dynamics with Social Robots
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:This research investigates the impact of social robot participation in group conversations and assesses the effectiveness of various addressing policies. The study involved 300 participants, divided into groups of four, interacting with a humanoid robot serving as the moderator. The robot utilized conversation data to determine the most appropriate speaker to address. The findings indicate that the robot's addressing policy significantly influenced conversation dynamics, resulting in more balanced attention to each participant and a reduction in subgroup formation.
Labeling Sentences with Symbolic and Deictic Gestures via Semantic Similarity
Jul 03, 2024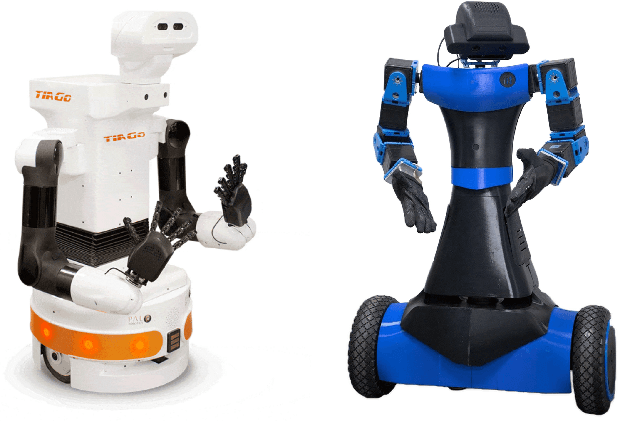
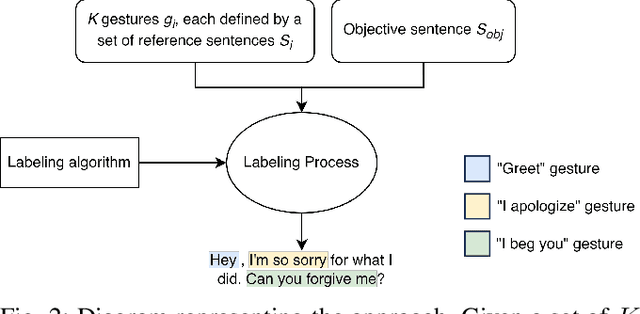
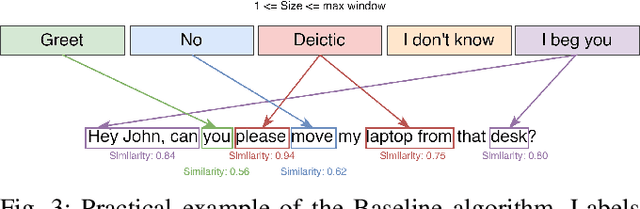
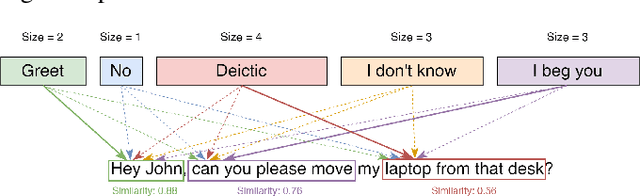
Abstract:Co-speech gesture generation on artificial agents has gained attention recently, mainly when it is based on data-driven models. However, end-to-end methods often fail to generate co-speech gestures related to semantics with specific forms, i.e., Symbolic and Deictic gestures. In this work, we identify which words in a sentence are contextually related to Symbolic and Deictic gestures. Firstly, we appropriately chose 12 gestures recognized by people from the Italian culture, which different humanoid robots can reproduce. Then, we implemented two rule-based algorithms to label sentences with Symbolic and Deictic gestures. The rules depend on the semantic similarity scores computed with the RoBerta model between sentences that heuristically represent gestures and sub-sentences inside an objective sentence that artificial agents have to pronounce. We also implemented a baseline algorithm that assigns gestures without computing similarity scores. Finally, to validate the results, we asked 30 persons to label a set of sentences with Deictic and Symbolic gestures through a Graphical User Interface (GUI), and we compared the labels with the ones produced by our algorithms. For this scope, we computed Average Precision (AP) and Intersection Over Union (IOU) scores, and we evaluated the Average Computational Time (ACT). Our results show that semantic similarity scores are useful for finding Symbolic and Deictic gestures in utterances.
Enhancing LLM-Based Human-Robot Interaction with Nuances for Diversity Awareness
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents a system for diversity-aware autonomous conversation leveraging the capabilities of large language models (LLMs). The system adapts to diverse populations and individuals, considering factors like background, personality, age, gender, and culture. The conversation flow is guided by the structure of the system's pre-established knowledge base, while LLMs are tasked with various functions, including generating diversity-aware sentences. Achieving diversity-awareness involves providing carefully crafted prompts to the models, incorporating comprehensive information about users, conversation history, contextual details, and specific guidelines. To assess the system's performance, we conducted both controlled and real-world experiments, measuring a wide range of performance indicators.
Entropy Based Multi-robot Active SLAM
Oct 09, 2023
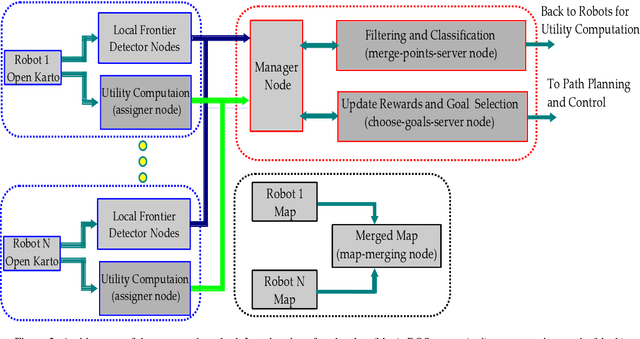
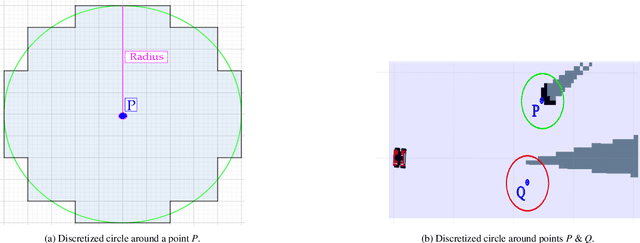
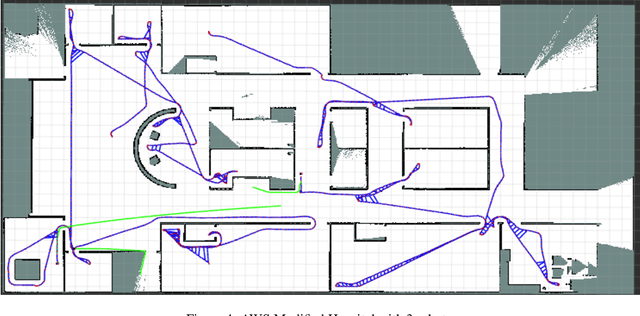
Abstract:In this article, we present an efficient multi-robot active SLAM framework that involves a frontier-sharing method for maximum exploration of an unknown environment. It encourages the robots to spread into the environment while weighting the goal frontiers with the pose graph SLAM uncertainly and path entropy. Our approach works on a limited number of frontier points and weights the goal frontiers with a utility function that encapsulates both the SLAM and map uncertainties, thus providing an efficient and not computationally expensive solution. Our approach has been tested on publicly available simulation environments and on real robots. An accumulative 31% more coverage than similar state-of-the-art approaches has been obtained, proving the capability of our approach for efficient environment exploration.
Collaborative Active SLAM: Synchronous and Asynchronous Coordination Among Agents
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:In the realm of autonomous robotics, a critical challenge lies in developing robust solutions for Active Collaborative SLAM, wherein multiple robots must collaboratively explore and map an unknown environment while intelligently coordinating their movements and sensor data acquisitions. To this aim, we present two approaches for coordinating a system consisting of multiple robots to perform Active Collaborative SLAM (AC-SLAM) for environmental exploration. Our two coordination approaches, synchronous and asynchronous implement a methodology to prioritize robot goal assignments by the central server. We also present a method to efficiently spread the robots for maximum exploration while keeping SLAM uncertainty low. Both coordination approaches were evaluated through simulation on publicly available datasets, obtaining promising results.
Sustainable Verbal and Non-verbal Human-Robot Interaction Through Cloud Services
Mar 04, 2022



Abstract:This article presents the design and the implementation of CAIR: a cloud system for knowledge-based autonomous interaction devised for Social Robots and other conversational agents. The system is particularly convenient for low-cost robots and devices. Developers are provided with a sustainable solution to manage verbal and non-verbal interaction through a network connection, with about 3,000 topics of conversation ready for "chit-chatting" and a library of pre-cooked plans that only needs to be grounded into the robot's physical capabilities. The system is structured as a set of REST API endpoints so that it can be easily expanded by adding new APIs to improve the capabilities of the clients connected to the cloud. Another key feature of the system is that it has been designed to make the development of its clients straightforward: in this way, multiple devices can be easily endowed with the capability of autonomously interacting with the user, understanding when to perform specific actions, and exploiting all the information provided by cloud services. The article outlines and discusses the results of the experiments performed to assess the system's performance in terms of response time, paving the way for its use both for research and market solutions. Links to repositories with clients for ROS and popular robots such as Pepper and NAO are given.
Thermal and Visual Tracking of Photovoltaic Plants for Autonomous UAV inspection
Feb 02, 2022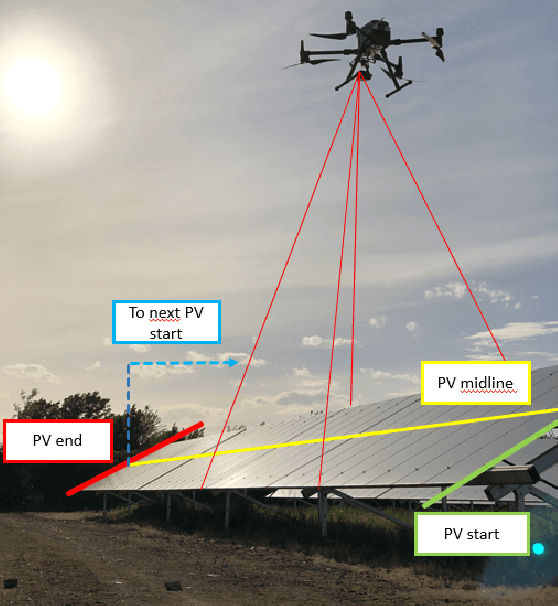
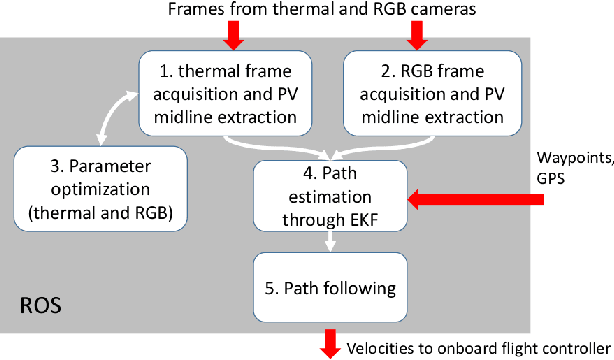
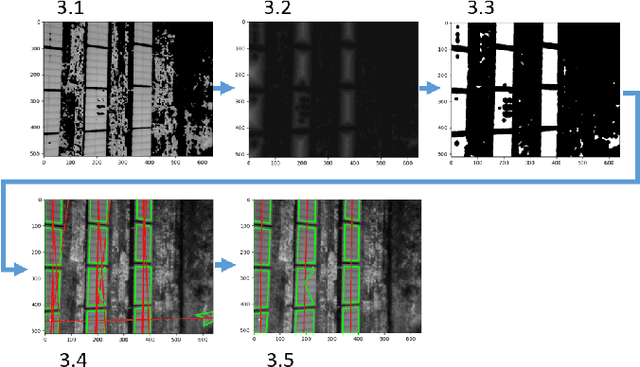

Abstract:Since the demand for renewable solar energy is continuously growing, the need for more frequent, precise, and quick autonomous aerial inspections using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV) may become fundamental to reduce costs. However, UAV-based inspection of Photovoltaic (PV) arrays is still an open problem. Companies in the field complain that GPS-based navigation is not adequate to accurately cover PV arrays to acquire images to be analyzed to determine the PV panels' status. Indeed, when instructing UAVs to move along a sequency of waypoints at a low altitude, two sources of errors may deteriorate performances: (i) the difference between the actual UAV position and the one estimated with the GPS, and (ii) the difference between the UAV position returned by the GPS and the position of waypoints extracted from georeferenced images acquired through Google Earth or similar tools. These errors make it impossible to reliably track rows of PV modules without human intervention reliably. The article proposes an approach for inspecting PV arrays with autonomous UAVs equipped with an RGB and a thermal camera, the latter being typically used to detect heat failures on the panels' surface: we introduce a portfolio of techniques to process data from both cameras for autonomous navigation. %, including an optimization procedure for improving panel detection and an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF) to filter data from RGB and thermal cameras. Experimental tests performed in simulation and an actual PV plant are reported, confirming the validity of the approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge