Branislava Jankovic
Real-Time Aerial Fire Detection on Resource-Constrained Devices Using Knowledge Distillation
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:Wildfire catastrophes cause significant environmental degradation, human losses, and financial damage. To mitigate these severe impacts, early fire detection and warning systems are crucial. Current systems rely primarily on fixed CCTV cameras with a limited field of view, restricting their effectiveness in large outdoor environments. The fusion of intelligent fire detection with remote sensing improves coverage and mobility, enabling monitoring in remote and challenging areas. Existing approaches predominantly utilize convolutional neural networks and vision transformer models. While these architectures provide high accuracy in fire detection, their computational complexity limits real-time performance on edge devices such as UAVs. In our work, we present a lightweight fire detection model based on MobileViT-S, compressed through the distillation of knowledge from a stronger teacher model. The ablation study highlights the impact of a teacher model and the chosen distillation technique on the model's performance improvement. We generate activation map visualizations using Grad-CAM to confirm the model's ability to focus on relevant fire regions. The high accuracy and efficiency of the proposed model make it well-suited for deployment on satellites, UAVs, and IoT devices for effective fire detection. Experiments on common fire benchmarks demonstrate that our model suppresses the state-of-the-art model by 0.44%, 2.00% while maintaining a compact model size. Our model delivers the highest processing speed among existing works, achieving real-time performance on resource-constrained devices.
UAV-Assisted Real-Time Disaster Detection Using Optimized Transformer Model
Jan 21, 2025



Abstract:Disaster recovery and management present significant challenges, particularly in unstable environments and hard-to-reach terrains. These difficulties can be overcome by employing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) equipped with onboard embedded platforms and camera sensors. In this work, we address the critical need for accurate and timely disaster detection by enabling onboard aerial imagery processing and avoiding connectivity, privacy, and latency issues despite the challenges posed by limited onboard hardware resources. We propose a UAV-assisted edge framework for real-time disaster management, leveraging our proposed model optimized for real-time aerial image classification. The optimization of the model employs post-training quantization techniques. For real-world disaster scenarios, we introduce a novel dataset, DisasterEye, featuring UAV-captured disaster scenes as well as ground-level images taken by individuals on-site. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our model, achieving high accuracy with reduced inference latency and memory usage on resource-constrained devices. The framework's scalability and adaptability make it a robust solution for real-time disaster detection on resource-limited UAV platforms.
All Languages Matter: Evaluating LMMs on Culturally Diverse 100 Languages
Nov 25, 2024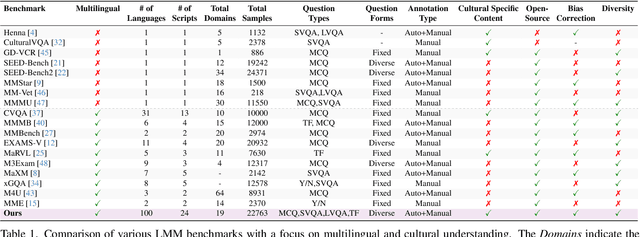
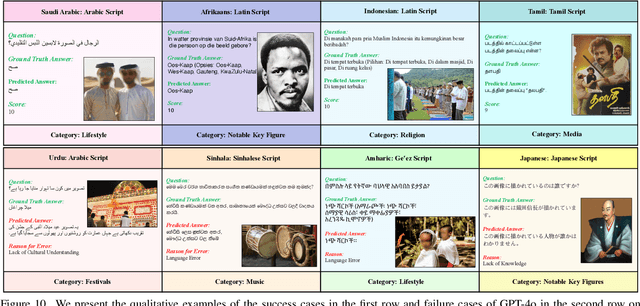
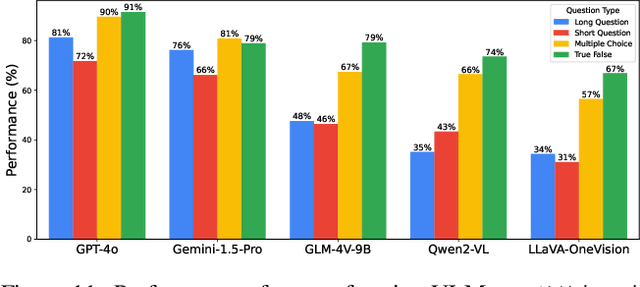
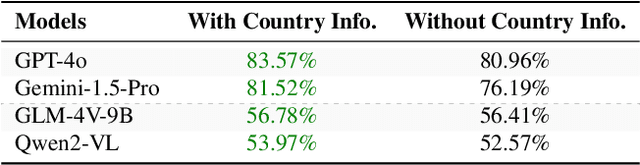
Abstract:Existing Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) generally focus on only a few regions and languages. As LMMs continue to improve, it is increasingly important to ensure they understand cultural contexts, respect local sensitivities, and support low-resource languages, all while effectively integrating corresponding visual cues. In pursuit of culturally diverse global multimodal models, our proposed All Languages Matter Benchmark (ALM-bench) represents the largest and most comprehensive effort to date for evaluating LMMs across 100 languages. ALM-bench challenges existing models by testing their ability to understand and reason about culturally diverse images paired with text in various languages, including many low-resource languages traditionally underrepresented in LMM research. The benchmark offers a robust and nuanced evaluation framework featuring various question formats, including true/false, multiple choice, and open-ended questions, which are further divided into short and long-answer categories. ALM-bench design ensures a comprehensive assessment of a model's ability to handle varied levels of difficulty in visual and linguistic reasoning. To capture the rich tapestry of global cultures, ALM-bench carefully curates content from 13 distinct cultural aspects, ranging from traditions and rituals to famous personalities and celebrations. Through this, ALM-bench not only provides a rigorous testing ground for state-of-the-art open and closed-source LMMs but also highlights the importance of cultural and linguistic inclusivity, encouraging the development of models that can serve diverse global populations effectively. Our benchmark is publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge