Bocheng Zeng
Benchmarking neural surrogates on realistic spatiotemporal multiphysics flows
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Predicting multiphysics dynamics is computationally expensive and challenging due to the severe coupling of multi-scale, heterogeneous physical processes. While neural surrogates promise a paradigm shift, the field currently suffers from an "illusion of mastery", as repeatedly emphasized in top-tier commentaries: existing evaluations overly rely on simplified, low-dimensional proxies, which fail to expose the models' inherent fragility in realistic regimes. To bridge this critical gap, we present REALM (REalistic AI Learning for Multiphysics), a rigorous benchmarking framework designed to test neural surrogates on challenging, application-driven reactive flows. REALM features 11 high-fidelity datasets spanning from canonical multiphysics problems to complex propulsion and fire safety scenarios, alongside a standardized end-to-end training and evaluation protocol that incorporates multiphysics-aware preprocessing and a robust rollout strategy. Using this framework, we systematically benchmark over a dozen representative surrogate model families, including spectral operators, convolutional models, Transformers, pointwise operators, and graph/mesh networks, and identify three robust trends: (i) a scaling barrier governed jointly by dimensionality, stiffness, and mesh irregularity, leading to rapidly growing rollout errors; (ii) performance primarily controlled by architectural inductive biases rather than parameter count; and (iii) a persistent gap between nominal accuracy metrics and physically trustworthy behavior, where models with high correlations still miss key transient structures and integral quantities. Taken together, REALM exposes the limits of current neural surrogates on realistic multiphysics flows and offers a rigorous testbed to drive the development of next-generation physics-aware architectures.
PhyMPGN: Physics-encoded Message Passing Graph Network for spatiotemporal PDE systems
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Solving partial differential equations (PDEs) serves as a cornerstone for modeling complex dynamical systems. Recent progresses have demonstrated grand benefits of data-driven neural-based models for predicting spatiotemporal dynamics (e.g., tremendous speedup gain compared with classical numerical methods). However, most existing neural models rely on rich training data, have limited extrapolation and generalization abilities, and suffer to produce precise or reliable physical prediction under intricate conditions (e.g., irregular mesh or geometry, complex boundary conditions, diverse PDE parameters, etc.). To this end, we propose a new graph learning approach, namely, Physics-encoded Message Passing Graph Network (PhyMPGN), to model spatiotemporal PDE systems on irregular meshes given small training datasets. Specifically, we incorporate a GNN into a numerical integrator to approximate the temporal marching of spatiotemporal dynamics for a given PDE system. Considering that many physical phenomena are governed by diffusion processes, we further design a learnable Laplace block, which encodes the discrete Laplace-Beltrami operator, to aid and guide the GNN learning in a physically feasible solution space. A boundary condition padding strategy is also designed to improve the model convergence and accuracy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PhyMPGN is capable of accurately predicting various types of spatiotemporal dynamics on coarse unstructured meshes, consistently achieves the state-of-the-art results, and outperforms other baselines with considerable gains.
AI-accelerated Discovery of Altermagnetic Materials
Nov 13, 2023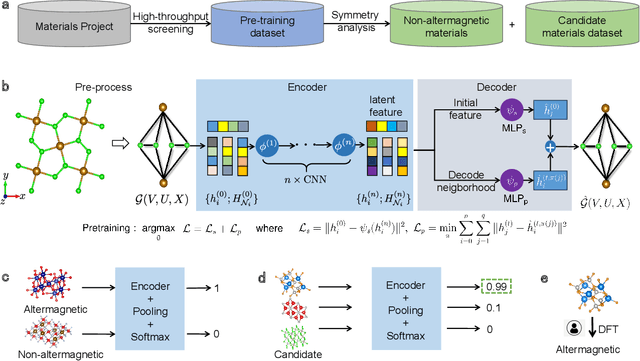
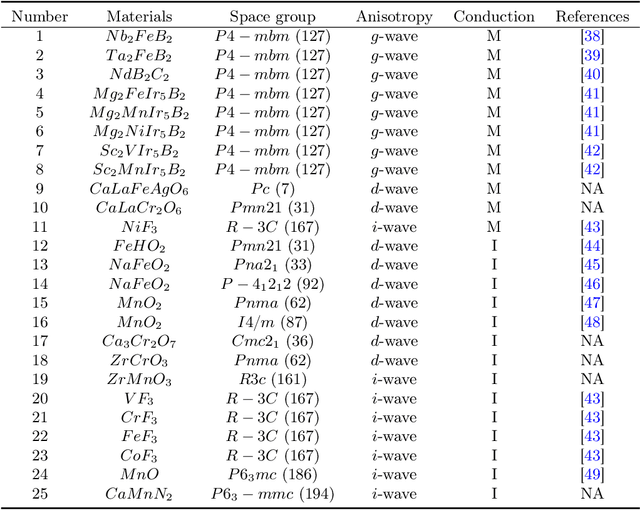
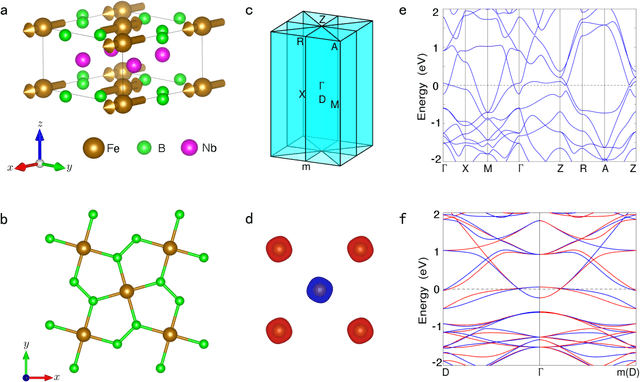
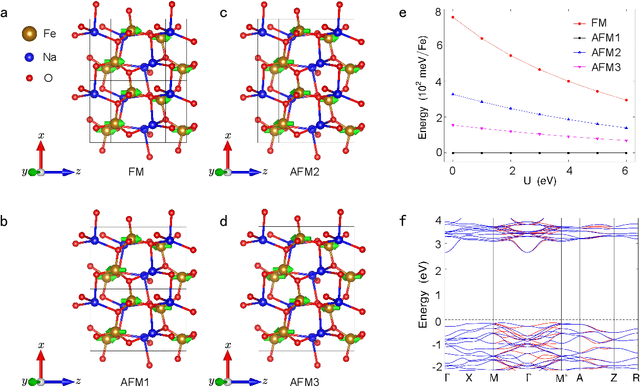
Abstract:Altermagnetism, a new magnetic phase, has been theoretically proposed and experimentally verified to be distinct from ferromagnetism and antiferromagnetism. Although altermagnets have been found to possess many exotic physical properties, the very limited availability of known altermagnetic materials (e.g., 14 confirmed materials) hinders the study of such properties. Hence, discovering more types of altermagnetic materials is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of altermagnetism and thus facilitating new applications in the next-generation information technologies, e.g., storage devices and high-sensitivity sensors. Here, we report 25 new altermagnetic materials that cover metals, semiconductors, and insulators, discovered by an AI search engine unifying symmetry analysis, graph neural network pre-training, optimal transport theory, and first-principles electronic structure calculation. The wide range of electronic structural characteristics reveals that various novel physical properties manifest in these newly discovered altermagnetic materials, e.g., anomalous Hall effect, anomalous Kerr effect, and topological property. Noteworthy, we discovered 8 i-wave altermagnetic materials for the first time. Overall, the AI search engine performs much better than human experts and suggests a set of new altermagnetic materials with unique properties, outlining its potential for accelerated discovery of the materials with targeting properties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge