Bernd Ludwig
FORWISS and Institute of Computer Science, University of Erlangen
Query Smarter, Trust Better? Exploring Search Behaviours for Verifying News Accuracy
Apr 07, 2025



Abstract:While it is often assumed that searching for information to evaluate misinformation will help identify false claims, recent work suggests that search behaviours can instead reinforce belief in misleading news, particularly when users generate queries using vocabulary from the source articles. Our research explores how different query generation strategies affect news verification and whether the way people search influences the accuracy of their information evaluation. A mixed-methods approach was used, consisting of three parts: (1) an analysis of existing data to understand how search behaviour influences trust in fake news, (2) a simulation of query generation strategies using a Large Language Model (LLM) to assess the impact of different query formulations on search result quality, and (3) a user study to examine how 'Boost' interventions in interface design can guide users to adopt more effective query strategies. The results show that search behaviour significantly affects trust in news, with successful searches involving multiple queries and yielding higher-quality results. Queries inspired by different parts of a news article produced search results of varying quality, and weak initial queries improved when reformulated using full SERP information. Although 'Boost' interventions had limited impact, the study suggests that interface design encouraging users to thoroughly review search results can enhance query formulation. This study highlights the importance of query strategies in evaluating news and proposes that interface design can play a key role in promoting more effective search practices, serving as one component of a broader set of interventions to combat misinformation.
MonoTODia: Translating Monologue Requests to Task-Oriented Dialogues
Feb 24, 2025



Abstract:Data scarcity is one of the main problems when it comes to real-world applications of transformer-based models. This is especially evident for task-oriented dialogue (TOD) systems, which require specialized datasets, that are usually not readily available. This can hinder companies from adding TOD systems to their services. This study therefore investigates a novel approach to sourcing annotated dialogues from existing German monologue material. Focusing on a real-world example, we investigate whether these monologues can be transformed into dialogue formats suitable for training TOD systems. We show the approach with the concrete example of a company specializing in travel bookings via e-mail. We fine-tune state-of-the-art Large Language Models for the task of rewriting e-mails as dialogues and annotating them. To ensure the quality and validity of the generated data, we employ crowd workers to evaluate the dialogues across multiple criteria and to provide gold-standard annotations for the test dataset. We further evaluate the usefulness of the dialogues for training TOD systems. Our evaluation shows that the dialogues and annotations are of high quality and can serve as a valuable starting point for training TOD systems. Finally, we make the annotated dataset publicly available to foster future research.
CoPrUS: Consistency Preserving Utterance Synthesis towards more realistic benchmark dialogues
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Large-scale Wizard-Of-Oz dialogue datasets have enabled the training of deep learning-based dialogue systems. While they are successful as benchmark datasets, they lack certain types of utterances, which would make them more realistic. In this work, we investigate the creation of synthetic communication errors in an automatic pipeline. Based on linguistic theory, we propose and follow a simple error taxonomy. We focus on three types of miscommunications that could happen in real-world dialogues but are underrepresented in the benchmark dataset: misunderstandings, non-understandings and vaguely related questions. Our two-step approach uses a state-of-the-art Large Language Model (LLM) to first create the error and secondly the repairing utterance. We perform Language Model-based evaluation to ensure the quality of the generated utterances. We apply the method to the MultiWOZ dataset and evaluate it both qualitatively and empirically as well as with human judges. Our results indicate that current LLMs can aid in adding post-hoc miscommunications to benchmark datasets as a form of data augmentation. We publish the resulting dataset, in which nearly 1900 dialogues have been modified, as CoPrUS-MultiWOZ to facilitate future work on dialogue systems.
The influence of persona and conversational task on social interactions with a LLM-controlled embodied conversational agent
Nov 08, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in conversational tasks. Embodying an LLM as a virtual human allows users to engage in face-to-face social interactions in Virtual Reality. However, the influence of person- and task-related factors in social interactions with LLM-controlled agents remains unclear. In this study, forty-six participants interacted with a virtual agent whose persona was manipulated as extravert or introvert in three different conversational tasks (small talk, knowledge test, convincing). Social-evaluation, emotional experience, and realism were assessed using ratings. Interactive engagement was measured by quantifying participants' words and conversational turns. Finally, we measured participants' willingness to ask the agent for help during the knowledge test. Our findings show that the extraverted agent was more positively evaluated, elicited a more pleasant experience and greater engagement, and was assessed as more realistic compared to the introverted agent. Whereas persona did not affect the tendency to ask for help, participants were generally more confident in the answer when they had help of the LLM. Variation of personality traits of LLM-controlled embodied virtual agents, therefore, affects social-emotional processing and behavior in virtual interactions. Embodied virtual agents allow the presentation of naturalistic social encounters in a virtual environment.
"What can I cook with these ingredients?" -- Understanding cooking-related information needs in conversational search
Dec 10, 2021
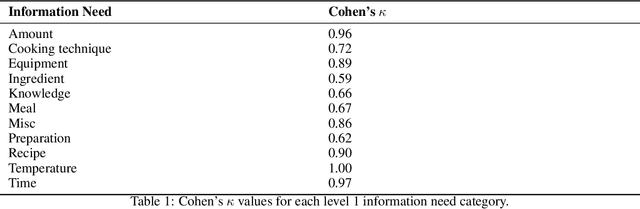


Abstract:As conversational search becomes more pervasive, it becomes increasingly important to understand the user's underlying information needs when they converse with such systems in diverse domains. We conduct an in-situ study to understand information needs arising in a home cooking context as well as how they are verbally communicated to an assistant. A human experimenter plays this role in our study. Based on the transcriptions of utterances, we derive a detailed hierarchical taxonomy of diverse information needs occurring in this context, which require different levels of assistance to be solved. The taxonomy shows that needs can be communicated through different linguistic means and require different amounts of context to be understood. In a second contribution we perform classification experiments to determine the feasibility of predicting the type of information need a user has during a dialogue using the turn provided. For this multi-label classification problem, we achieve average F1 measures of 40% using BERT-based models. We demonstrate with examples, which types of need are difficult to predict and show why, concluding that models need to include more context information in order to improve both information need classification and assistance to make such systems usable.
User Preferences and the Shortest Path
Jul 23, 2021

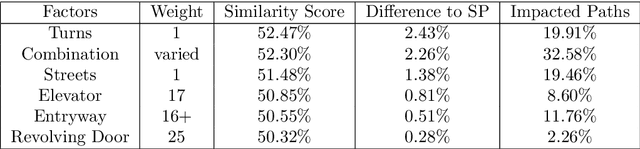
Abstract:Indoor navigation systems leverage shortest path algorithms to calculate routes. In order to define the "shortest path", a cost function has to be specified based on theories and heuristics in the application domain. For the domain of indoor routing, we survey theories and criteria identified in the literature as essential for human path planning. We drive quantitative definitions and integrate them into a cost function that weights each of the criteria separately. We then apply an exhaustive grid search to find weights that lead to an ideal cost function. "Ideal" here is defined as guiding the algorithm to plan routes that are most similar to those chosen by humans. To explore which criteria should be taken into account in an improved pathfinding algorithm, eleven different factors whose favorable impact on route selection has been established in past research were considered. Each factor was included separately in the Dijkstra algorithm and the similarity of thus calculated routes to the actual routes chosen by students at the University of Regensburg was determined. This allows for a quantitative assessment of the factors' impact and further constitutes a way to directly compare them. A reduction of the number of turns, streets, revolving doors, entryways, elevators as well as the combination of the aforementioned factors was found to have a positive effect and generate paths that were favored over the shortest path. Turns and the combination of criteria turned out to be most impactful.
Modelling Users, Intentions, and Structure in Spoken Dialog
Sep 17, 1998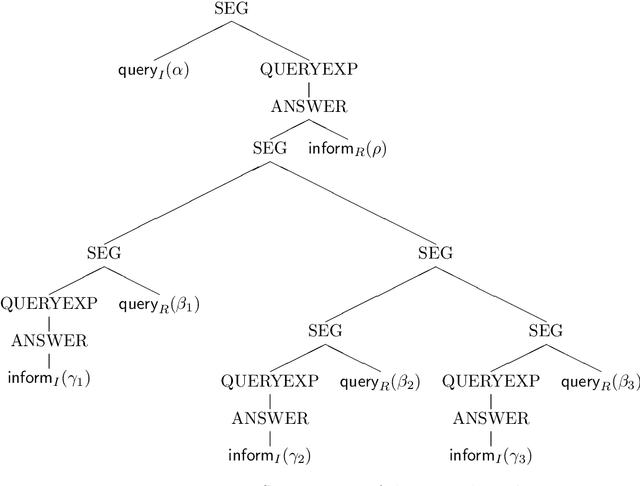
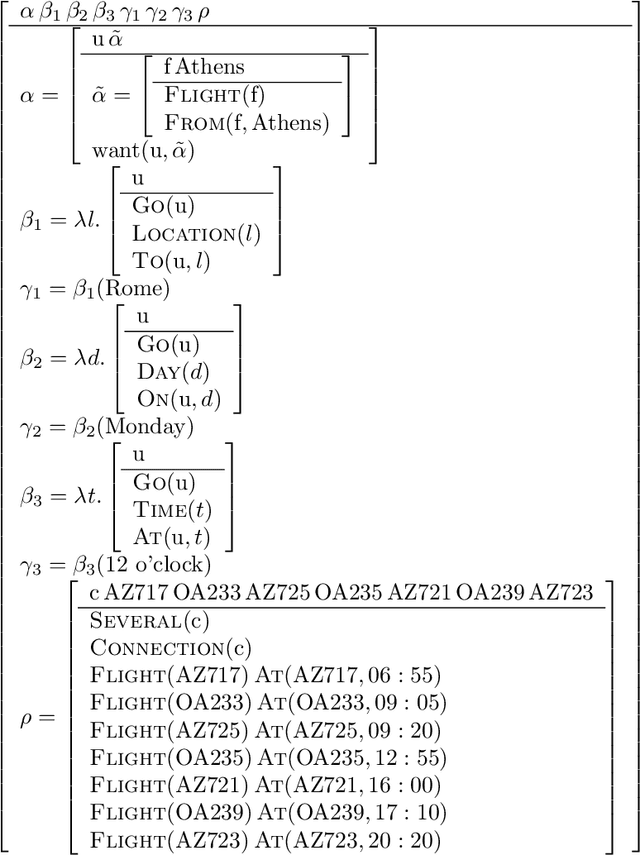
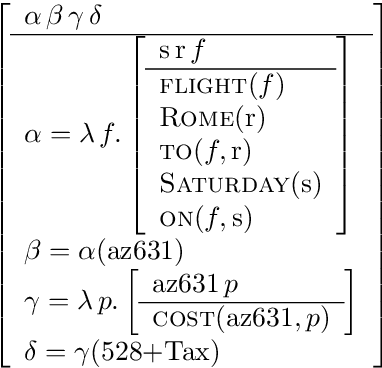
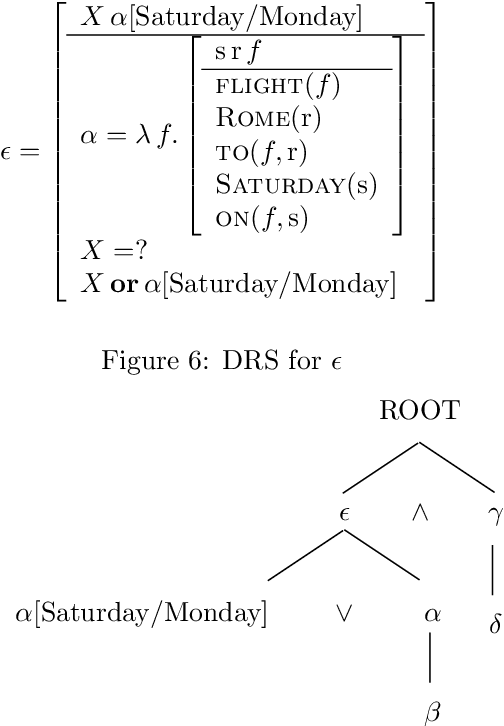
Abstract:We outline how utterances in dialogs can be interpreted using a partial first order logic. We exploit the capability of this logic to talk about the truth status of formulae to define a notion of coherence between utterances and explain how this coherence relation can serve for the construction of AND/OR trees that represent the segmentation of the dialog. In a BDI model we formalize basic assumptions about dialog and cooperative behaviour of participants. These assumptions provide a basis for inferring speech acts from coherence relations between utterances and attitudes of dialog participants. Speech acts prove to be useful for determining dialog segments defined on the notion of completing expectations of dialog participants. Finally, we sketch how explicit segmentation signalled by cue phrases and performatives is covered by our dialog model.
Combining Expression and Content in Domains for Dialog Managers
Aug 13, 1998Abstract:We present work in progress on abstracting dialog managers from their domain in order to implement a dialog manager development tool which takes (among other data) a domain description as input and delivers a new dialog manager for the described domain as output. Thereby we will focus on two topics; firstly, the construction of domain descriptions with description logics and secondly, the interpretation of utterances in a given domain.
* 5 pages, uses conference.sty
Part-of-Speech-Tagging using morphological information
Jun 04, 1996Abstract:This paper presents the results of an experiment to decide the question of authenticity of the supposedly spurious Rhesus - a attic tragedy sometimes credited to Euripides. The experiment involves use of statistics in order to test whether significant deviations in the distribution of word categories between Rhesus and the other works of Euripides can or cannot be found. To count frequencies of word categories in the corpus, a part-of-speech-tagger for Greek has been implemented. Some special techniques for reducing the problem of sparse data are used resulting in an accuracy of ca. 96.6%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge