Selina Meyer
Query Smarter, Trust Better? Exploring Search Behaviours for Verifying News Accuracy
Apr 07, 2025



Abstract:While it is often assumed that searching for information to evaluate misinformation will help identify false claims, recent work suggests that search behaviours can instead reinforce belief in misleading news, particularly when users generate queries using vocabulary from the source articles. Our research explores how different query generation strategies affect news verification and whether the way people search influences the accuracy of their information evaluation. A mixed-methods approach was used, consisting of three parts: (1) an analysis of existing data to understand how search behaviour influences trust in fake news, (2) a simulation of query generation strategies using a Large Language Model (LLM) to assess the impact of different query formulations on search result quality, and (3) a user study to examine how 'Boost' interventions in interface design can guide users to adopt more effective query strategies. The results show that search behaviour significantly affects trust in news, with successful searches involving multiple queries and yielding higher-quality results. Queries inspired by different parts of a news article produced search results of varying quality, and weak initial queries improved when reformulated using full SERP information. Although 'Boost' interventions had limited impact, the study suggests that interface design encouraging users to thoroughly review search results can enhance query formulation. This study highlights the importance of query strategies in evaluating news and proposes that interface design can play a key role in promoting more effective search practices, serving as one component of a broader set of interventions to combat misinformation.
"You tell me": A Dataset of GPT-4-Based Behaviour Change Support Conversations
Jan 29, 2024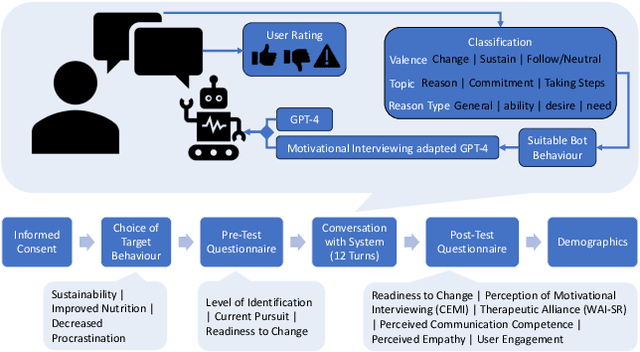

Abstract:Conversational agents are increasingly used to address emotional needs on top of information needs. One use case of increasing interest are counselling-style mental health and behaviour change interventions, with large language model (LLM)-based approaches becoming more popular. Research in this context so far has been largely system-focused, foregoing the aspect of user behaviour and the impact this can have on LLM-generated texts. To address this issue, we share a dataset containing text-based user interactions related to behaviour change with two GPT-4-based conversational agents collected in a preregistered user study. This dataset includes conversation data, user language analysis, perception measures, and user feedback for LLM-generated turns, and can offer valuable insights to inform the design of such systems based on real interactions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge