Benjamin Schrauwen
Oncilla robot: a versatile open-source quadruped research robot with compliant pantograph legs
Jun 16, 2018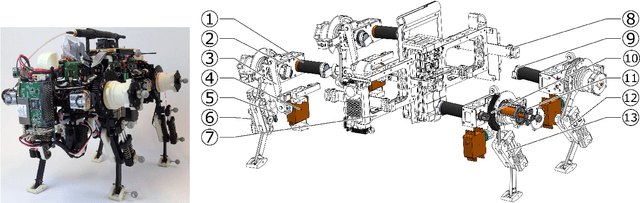
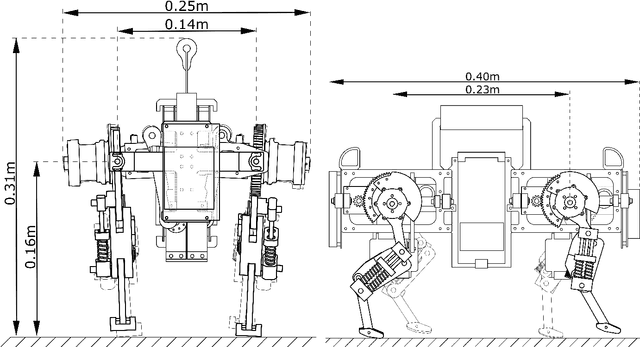
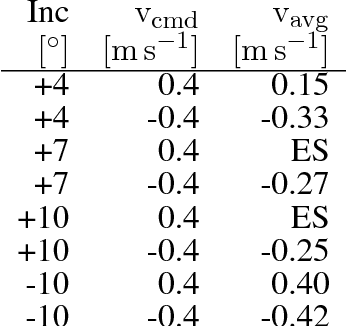
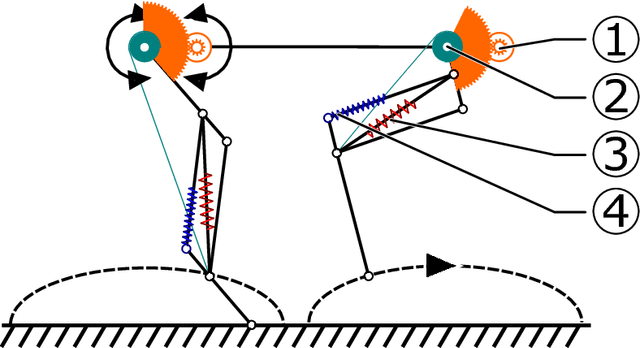
Abstract:We present Oncilla robot, a novel mobile, quadruped legged locomotion machine. This large-cat sized, 5.1 robot is one of a kind of a recent, bioinspired legged robot class designed with the capability of model-free locomotion control. Animal legged locomotion in rough terrain is clearly shaped by sensor feedback systems. Results with Oncilla robot show that agile and versatile locomotion is possible without sensory signals to some extend, and tracking becomes robust when feedback control is added (Ajaoolleian 2015). By incorporating mechanical and control blueprints inspired from animals, and by observing the resulting robot locomotion characteristics, we aim to understand the contribution of individual components. Legged robots have a wide mechanical and control design parameter space, and a unique potential as research tools to investigate principles of biomechanics and legged locomotion control. But the hardware and controller design can be a steep initial hurdle for academic research. To facilitate the easy start and development of legged robots, Oncilla-robot's blueprints are available through open-source. [...]
Memristor models for machine learning
Jul 14, 2014Abstract:In the quest for alternatives to traditional CMOS, it is being suggested that digital computing efficiency and power can be improved by matching the precision to the application. Many applications do not need the high precision that is being used today. In particular, large gains in area- and power efficiency could be achieved by dedicated analog realizations of approximate computing engines. In this work, we explore the use of memristor networks for analog approximate computation, based on a machine learning framework called reservoir computing. Most experimental investigations on the dynamics of memristors focus on their nonvolatile behavior. Hence, the volatility that is present in the developed technologies is usually unwanted and it is not included in simulation models. In contrast, in reservoir computing, volatility is not only desirable but necessary. Therefore, in this work, we propose two different ways to incorporate it into memristor simulation models. The first is an extension of Strukov's model and the second is an equivalent Wiener model approximation. We analyze and compare the dynamical properties of these models and discuss their implications for the memory and the nonlinear processing capacity of memristor networks. Our results indicate that device variability, increasingly causing problems in traditional computer design, is an asset in the context of reservoir computing. We conclude that, although both models could lead to useful memristor based reservoir computing systems, their computational performance will differ. Therefore, experimental modeling research is required for the development of accurate volatile memristor models.
Analog readout for optical reservoir computers
Sep 14, 2012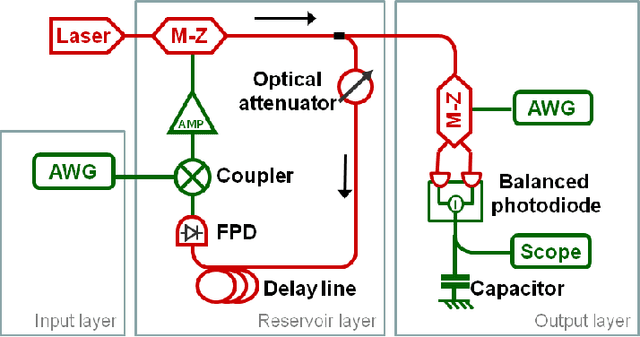
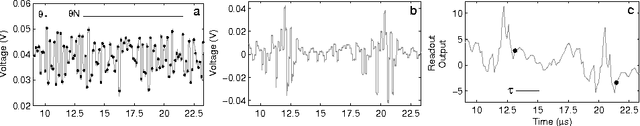
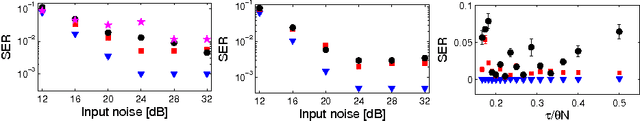
Abstract:Reservoir computing is a new, powerful and flexible machine learning technique that is easily implemented in hardware. Recently, by using a time-multiplexed architecture, hardware reservoir computers have reached performance comparable to digital implementations. Operating speeds allowing for real time information operation have been reached using optoelectronic systems. At present the main performance bottleneck is the readout layer which uses slow, digital postprocessing. We have designed an analog readout suitable for time-multiplexed optoelectronic reservoir computers, capable of working in real time. The readout has been built and tested experimentally on a standard benchmark task. Its performance is better than non-reservoir methods, with ample room for further improvement. The present work thereby overcomes one of the major limitations for the future development of hardware reservoir computers.
* to appear in NIPS 2012
Optoelectronic Reservoir Computing
Nov 30, 2011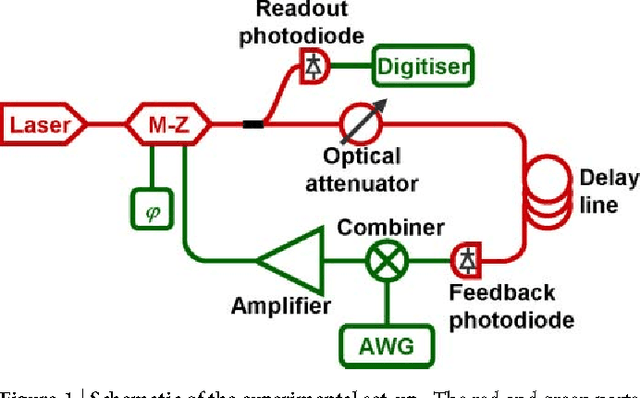
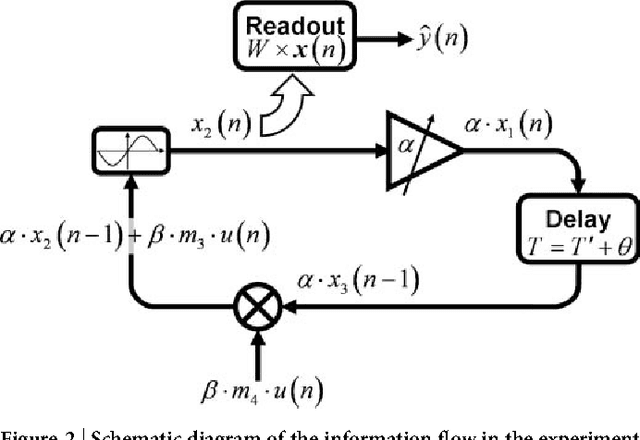
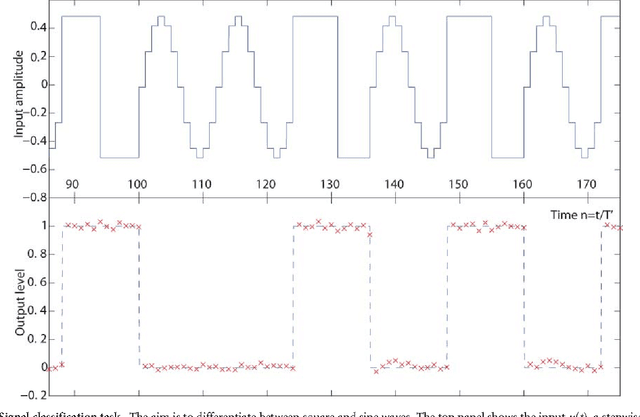
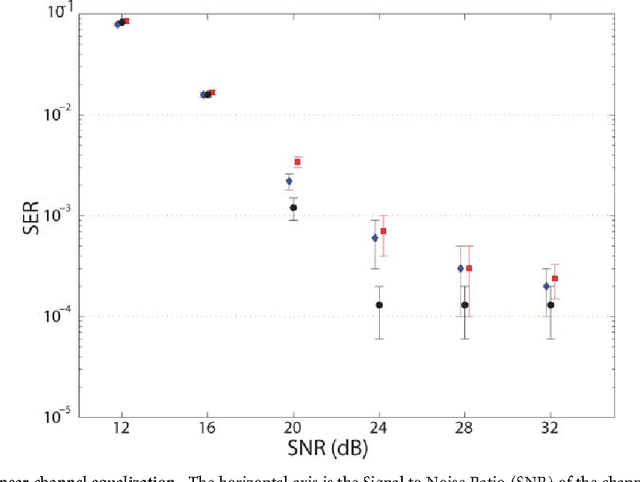
Abstract:Reservoir computing is a recently introduced, highly efficient bio-inspired approach for processing time dependent data. The basic scheme of reservoir computing consists of a non linear recurrent dynamical system coupled to a single input layer and a single output layer. Within these constraints many implementations are possible. Here we report an opto-electronic implementation of reservoir computing based on a recently proposed architecture consisting of a single non linear node and a delay line. Our implementation is sufficiently fast for real time information processing. We illustrate its performance on tasks of practical importance such as nonlinear channel equalization and speech recognition, and obtain results comparable to state of the art digital implementations.
* Contains main paper and two Supplementary Materials
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge