Benjamin Midtvedt
Roadmap on Deep Learning for Microscopy
Mar 07, 2023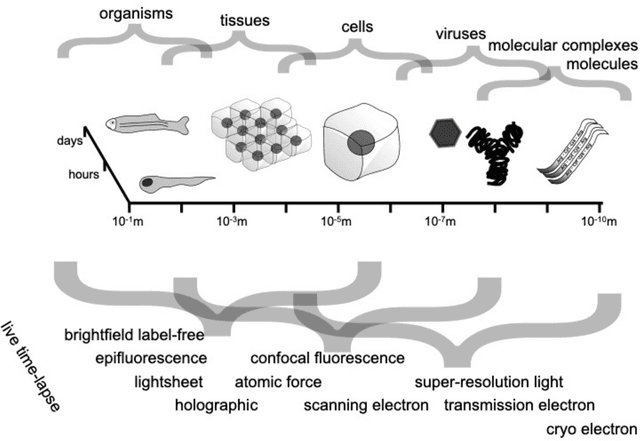
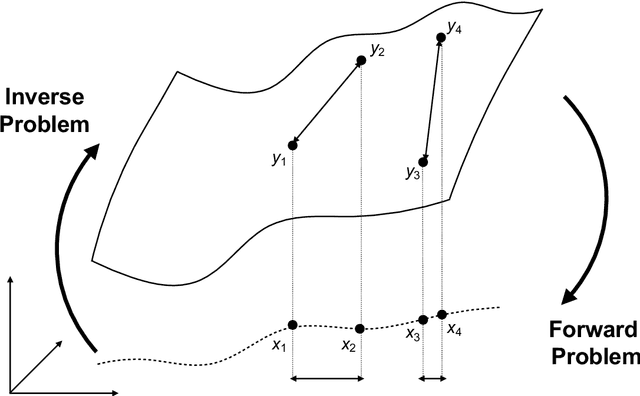
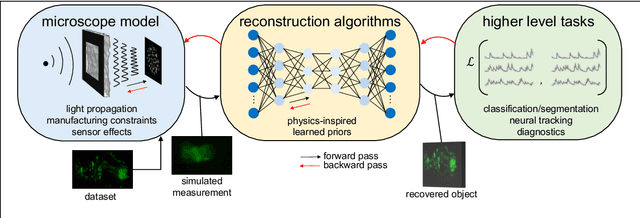
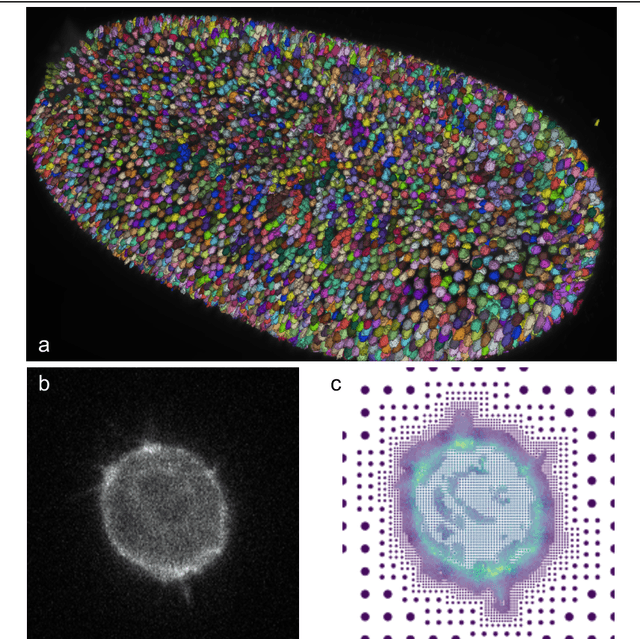
Abstract:Through digital imaging, microscopy has evolved from primarily being a means for visual observation of life at the micro- and nano-scale, to a quantitative tool with ever-increasing resolution and throughput. Artificial intelligence, deep neural networks, and machine learning are all niche terms describing computational methods that have gained a pivotal role in microscopy-based research over the past decade. This Roadmap is written collectively by prominent researchers and encompasses selected aspects of how machine learning is applied to microscopy image data, with the aim of gaining scientific knowledge by improved image quality, automated detection, segmentation, classification and tracking of objects, and efficient merging of information from multiple imaging modalities. We aim to give the reader an overview of the key developments and an understanding of possibilities and limitations of machine learning for microscopy. It will be of interest to a wide cross-disciplinary audience in the physical sciences and life sciences.
Single-shot self-supervised particle tracking
Feb 28, 2022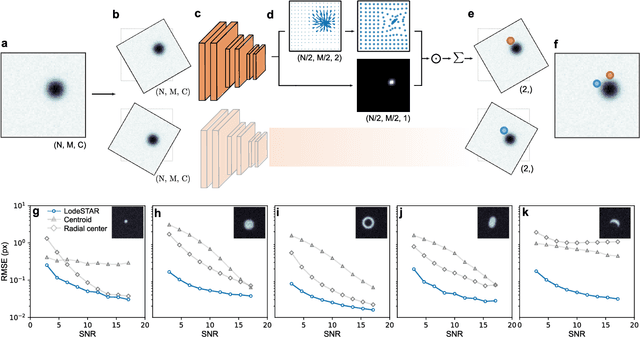
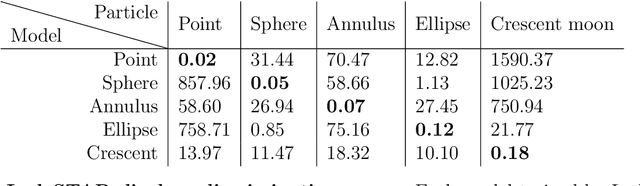
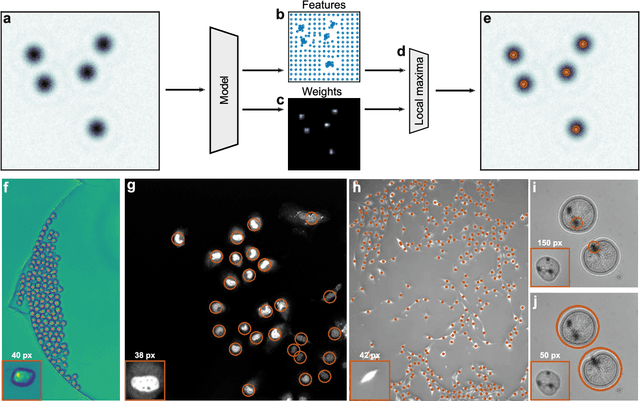
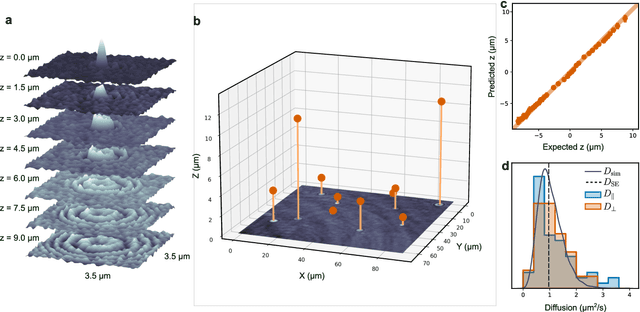
Abstract:Particle tracking is a fundamental task in digital microscopy. Recently, machine-learning approaches have made great strides in overcoming the limitations of more classical approaches. The training of state-of-the-art machine-learning methods almost universally relies on either vast amounts of labeled experimental data or the ability to numerically simulate realistic datasets. However, the data produced by experiments are often challenging to label and cannot be easily reproduced numerically. Here, we propose a novel deep-learning method, named LodeSTAR (Low-shot deep Symmetric Tracking And Regression), that learns to tracks objects with sub-pixel accuracy from a single unlabeled experimental image. This is made possible by exploiting the inherent roto-translational symmetries of the data. We demonstrate that LodeSTAR outperforms traditional methods in terms of accuracy. Furthermore, we analyze challenging experimental data containing densely packed cells or noisy backgrounds. We also exploit additional symmetries to extend the measurable particle properties to the particle's vertical position by propagating the signal in Fourier space and its polarizability by scaling the signal strength. Thanks to the ability to train deep-learning models with a single unlabeled image, LodeSTAR can accelerate the development of high-quality microscopic analysis pipelines for engineering, biology, and medicine.
Microplankton life histories revealed by holographic microscopy and deep learning
Feb 18, 2022



Abstract:The marine microbial food web plays a central role in the global carbon cycle. Our mechanistic understanding of the ocean, however, is biased towards its larger constituents, while rates and biomass fluxes in the microbial food web are mainly inferred from indirect measurements and ensemble averages. Yet, resolution at the level of the individual microplankton is required to advance our understanding of the oceanic food web. Here, we demonstrate that, by combining holographic microscopy with deep learning, we can follow microplanktons throughout their lifespan, continuously measuring their three dimensional position and dry mass. The deep learning algorithms circumvent the computationally intensive processing of holographic data and allow rapid measurements over extended time periods. This permits us to reliably estimate growth rates, both in terms of dry mass increase and cell divisions, as well as to measure trophic interactions between species such as predation events. The individual resolution provides information about selectivity, individual feeding rates and handling times for individual microplanktons. This method is particularly useful to explore the flux of carbon through micro-zooplankton, the most important and least known group of primary consumers in the global oceans. We exemplify this by detailed descriptions of micro-zooplankton feeding events, cell divisions, and long term monitoring of single cells from division to division.
Geometric deep learning reveals the spatiotemporal fingerprint of microscopic motion
Feb 13, 2022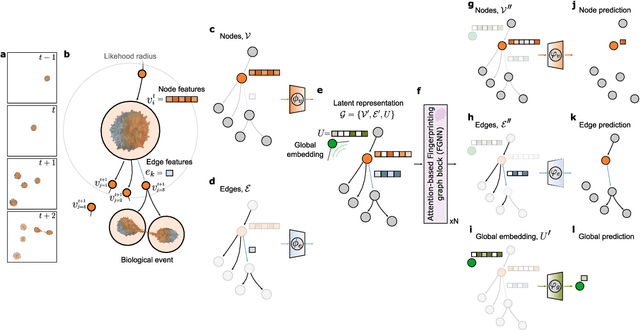
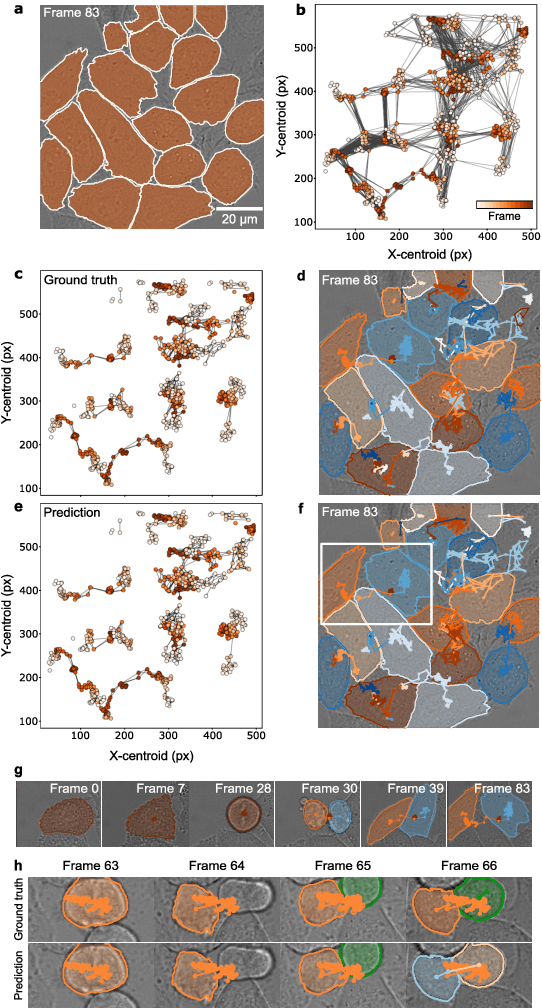
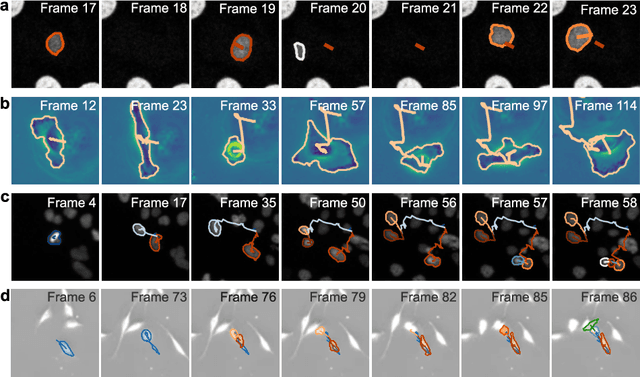
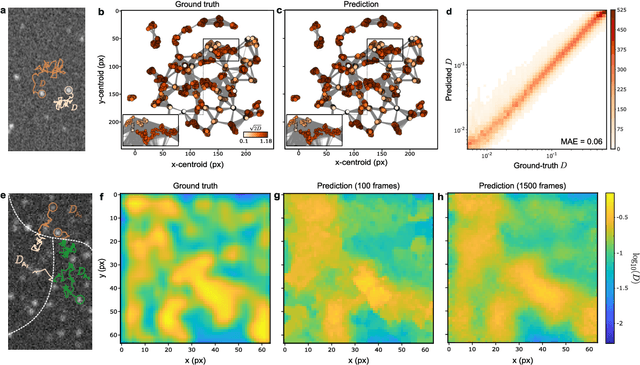
Abstract:The characterization of dynamical processes in living systems provides important clues for their mechanistic interpretation and link to biological functions. Thanks to recent advances in microscopy techniques, it is now possible to routinely record the motion of cells, organelles, and individual molecules at multiple spatiotemporal scales in physiological conditions. However, the automated analysis of dynamics occurring in crowded and complex environments still lags behind the acquisition of microscopic image sequences. Here, we present a framework based on geometric deep learning that achieves the accurate estimation of dynamical properties in various biologically-relevant scenarios. This deep-learning approach relies on a graph neural network enhanced by attention-based components. By processing object features with geometric priors, the network is capable of performing multiple tasks, from linking coordinates into trajectories to inferring local and global dynamic properties. We demonstrate the flexibility and reliability of this approach by applying it to real and simulated data corresponding to a broad range of biological experiments.
Extracting quantitative biological information from brightfield cell images using deep learning
Dec 23, 2020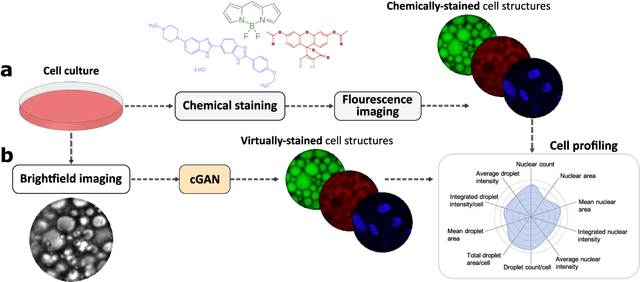
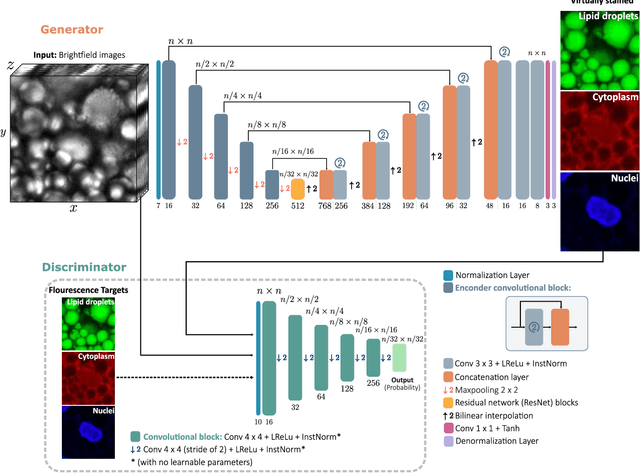
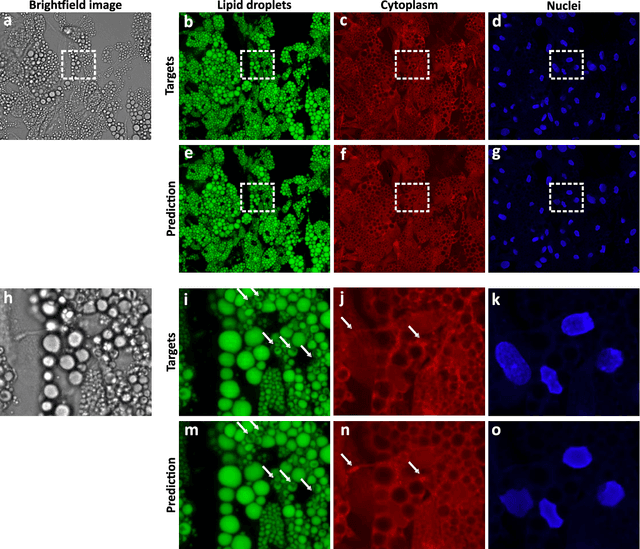
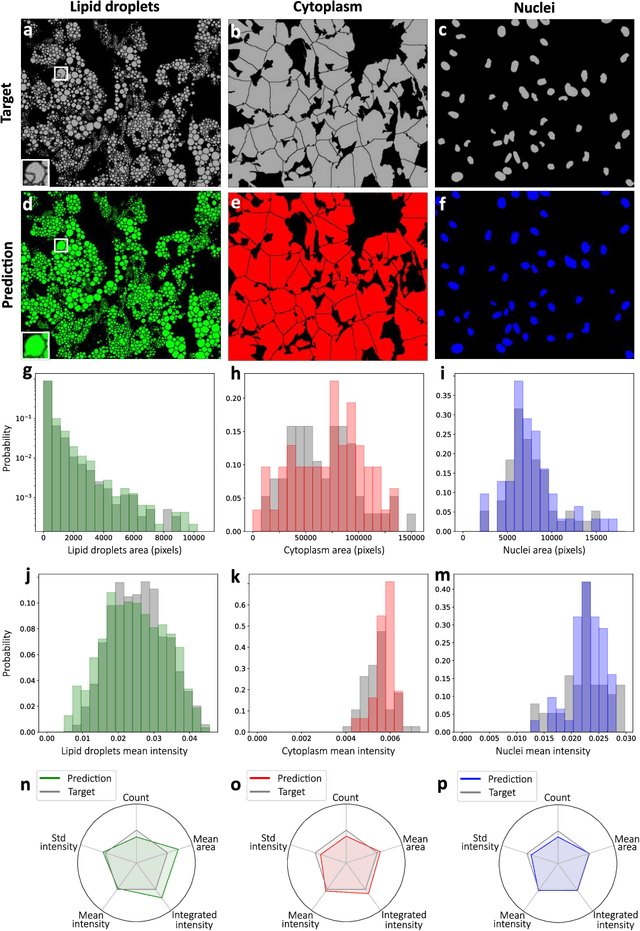
Abstract:Quantitative analysis of cell structures is essential for biomedical and pharmaceutical research. The standard imaging approach relies on fluorescence microscopy, where cell structures of interest are labeled by chemical staining techniques. However, these techniques are often invasive and sometimes even toxic to the cells, in addition to being time-consuming, labor-intensive, and expensive. Here, we introduce an alternative deep-learning-powered approach based on the analysis of brightfield images by a conditional generative adversarial neural network (cGAN). We show that this approach can extract information from the brightfield images to generate virtually-stained images, which can be used in subsequent downstream quantitative analyses of cell structures. Specifically, we train a cGAN to virtually stain lipid droplets, cytoplasm, and nuclei using brightfield images of human stem-cell-derived fat cells (adipocytes), which are of particular interest for nanomedicine and vaccine development. Subsequently, we use these virtually-stained images to extract quantitative measures about these cell structures. Generating virtually-stained fluorescence images is less invasive, less expensive, and more reproducible than standard chemical staining; furthermore, it frees up the fluorescence microscopy channels for other analytical probes, thus increasing the amount of information that can be extracted from each cell.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge