Augustin Parjadis
Learning Lagrangian Multipliers for the Travelling Salesman Problem
Dec 22, 2023



Abstract:Lagrangian relaxation is a versatile mathematical technique employed to relax constraints in an optimization problem, enabling the generation of dual bounds to prove the optimality of feasible solutions and the design of efficient propagators in constraint programming (such as the weighted circuit constraint). However, the conventional process of deriving Lagrangian multipliers (e.g., using subgradient methods) is often computationally intensive, limiting its practicality for large-scale or time-sensitive problems. To address this challenge, we propose an innovative unsupervised learning approach that harnesses the capabilities of graph neural networks to exploit the problem structure, aiming to generate accurate Lagrangian multipliers efficiently. We apply this technique to the well-known Held-Karp Lagrangian relaxation for the travelling salesman problem. The core idea is to predict accurate Lagrangian multipliers and to employ them as a warm start for generating Held-Karp relaxation bounds. These bounds are subsequently utilized to enhance the filtering process carried out by branch-and-bound algorithms. In contrast to much of the existing literature, which primarily focuses on finding feasible solutions, our approach operates on the dual side, demonstrating that learning can also accelerate the proof of optimality. We conduct experiments across various distributions of the metric travelling salesman problem, considering instances with up to 200 cities. The results illustrate that our approach can improve the filtering level of the weighted circuit global constraint, reduce the optimality gap by a factor two for unsolved instances up to a timeout, and reduce the execution time for solved instances by 10%.
The Machine Learning for Combinatorial Optimization Competition (ML4CO): Results and Insights
Mar 17, 2022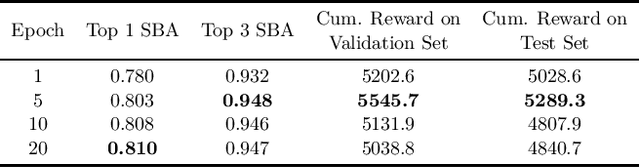

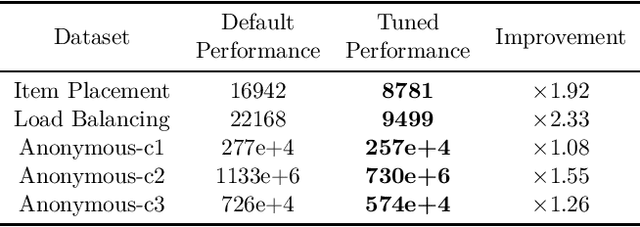
Abstract:Combinatorial optimization is a well-established area in operations research and computer science. Until recently, its methods have focused on solving problem instances in isolation, ignoring that they often stem from related data distributions in practice. However, recent years have seen a surge of interest in using machine learning as a new approach for solving combinatorial problems, either directly as solvers or by enhancing exact solvers. Based on this context, the ML4CO aims at improving state-of-the-art combinatorial optimization solvers by replacing key heuristic components. The competition featured three challenging tasks: finding the best feasible solution, producing the tightest optimality certificate, and giving an appropriate solver configuration. Three realistic datasets were considered: balanced item placement, workload apportionment, and maritime inventory routing. This last dataset was kept anonymous for the contestants.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge