Atul Sahay
An Efficient Point of Gaze Estimator for Low-Resolution Imaging Systems Using Extracted Ocular Features Based Neural Architecture
Jun 09, 2021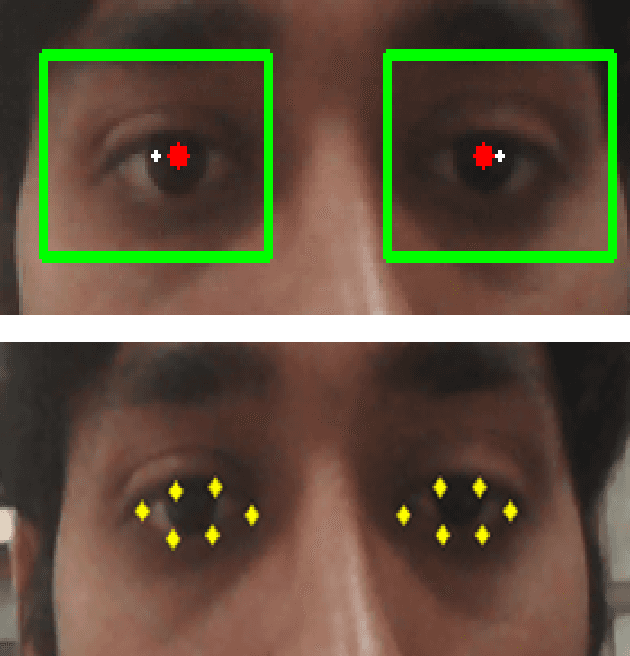
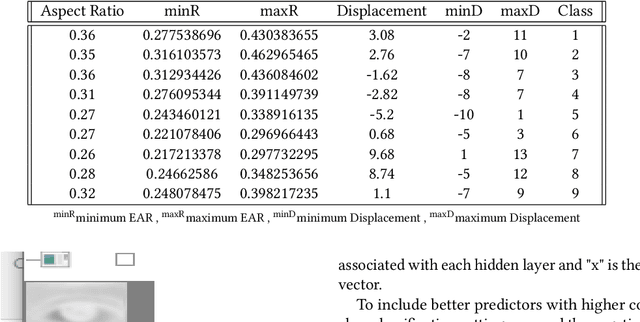
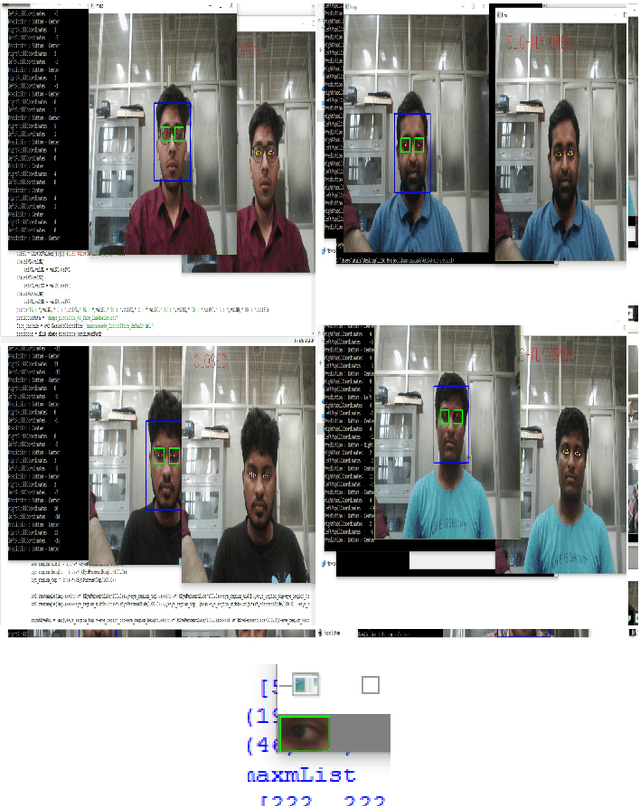
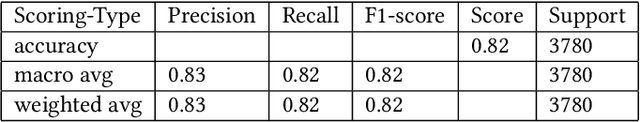
Abstract:A user's eyes provide means for Human Computer Interaction (HCI) research as an important modal. The time to time scientific explorations of the eye has already seen an upsurge of the benefits in HCI applications from gaze estimation to the measure of attentiveness of a user looking at a screen for a given time period. The eye tracking system as an assisting, interactive tool can be incorporated by physically disabled individuals, fitted best for those who have eyes as only a limited set of communication. The threefold objective of this paper is - 1. To introduce a neural network based architecture to predict users' gaze at 9 positions displayed in the 11.31{\deg} visual range on the screen, through a low resolution based system such as a webcam in real time by learning various aspects of eyes as an ocular feature set. 2.A collection of coarsely supervised feature set obtained in real time which is also validated through the user case study presented in the paper for 21 individuals ( 17 men and 4 women ) from whom a 35k set of instances was derived with an accuracy score of 82.36% and f1_score of 82.2% and 3.A detailed study over applicability and underlying challenges of such systems. The experimental results verify the feasibility and validity of the proposed eye gaze tracking model.
Rule Augmented Unsupervised Constituency Parsing
May 21, 2021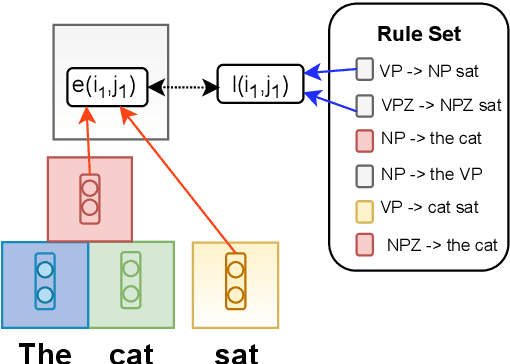



Abstract:Recently, unsupervised parsing of syntactic trees has gained considerable attention. A prototypical approach to such unsupervised parsing employs reinforcement learning and auto-encoders. However, no mechanism ensures that the learnt model leverages the well-understood language grammar. We propose an approach that utilizes very generic linguistic knowledge of the language present in the form of syntactic rules, thus inducing better syntactic structures. We introduce a novel formulation that takes advantage of the syntactic grammar rules and is independent of the base system. We achieve new state-of-the-art results on two benchmarks datasets, MNLI and WSJ. The source code of the paper is available at https://github.com/anshuln/Diora_with_rules.
Unsupervised Learning of Explainable Parse Trees for Improved Generalisation
Apr 11, 2021
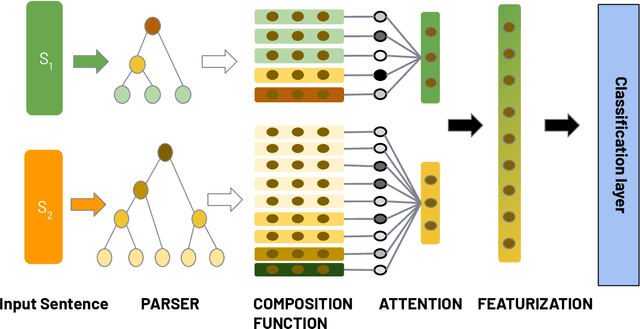
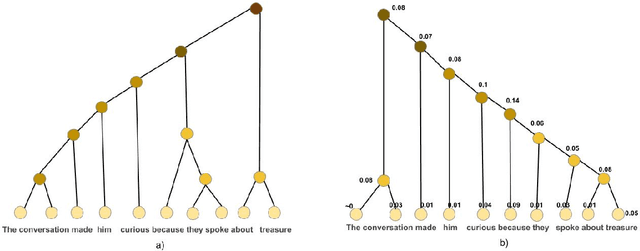
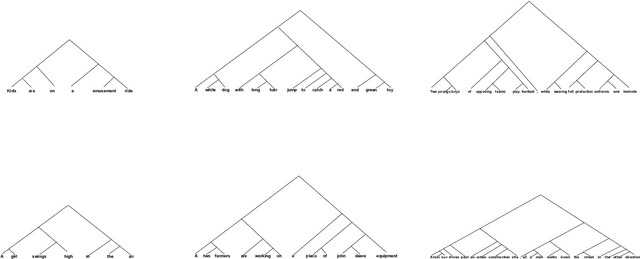
Abstract:Recursive neural networks (RvNN) have been shown useful for learning sentence representations and helped achieve competitive performance on several natural language inference tasks. However, recent RvNN-based models fail to learn simple grammar and meaningful semantics in their intermediate tree representation. In this work, we propose an attention mechanism over Tree-LSTMs to learn more meaningful and explainable parse tree structures. We also demonstrate the superior performance of our proposed model on natural language inference, semantic relatedness, and sentiment analysis tasks and compare them with other state-of-the-art RvNN based methods. Further, we present a detailed qualitative and quantitative analysis of the learned parse trees and show that the discovered linguistic structures are more explainable, semantically meaningful, and grammatically correct than recent approaches. The source code of the paper is available at https://github.com/atul04/Explainable-Latent-Structures-Using-Attention.
Selection-based Question Answering of an MOOC
Nov 15, 2019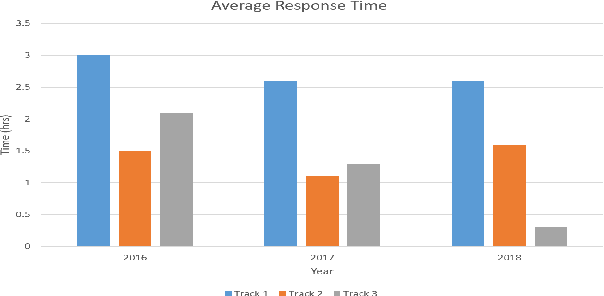
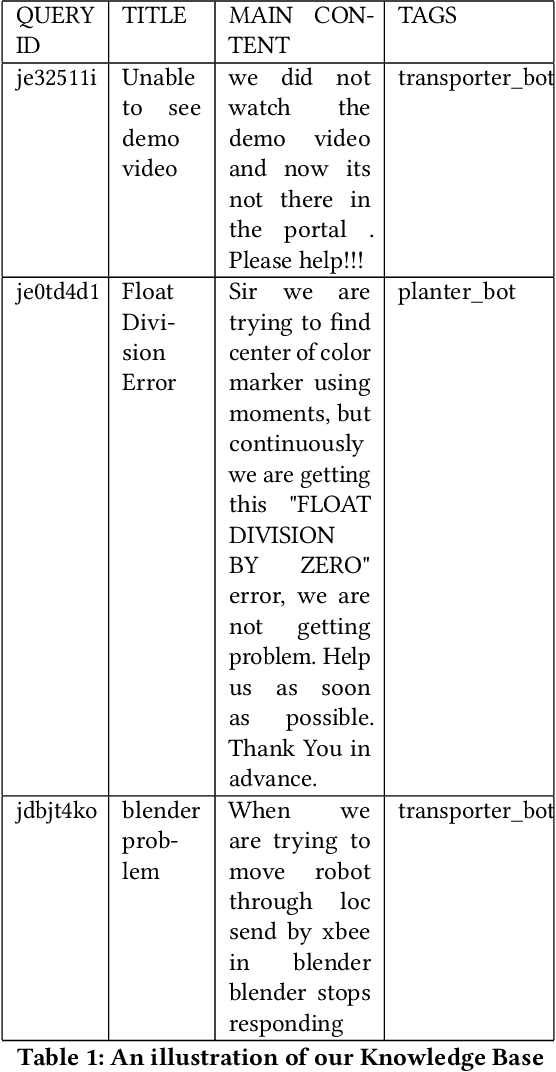
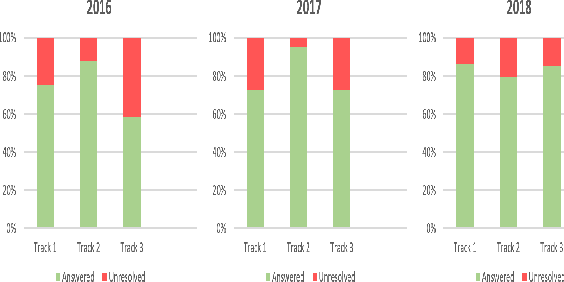
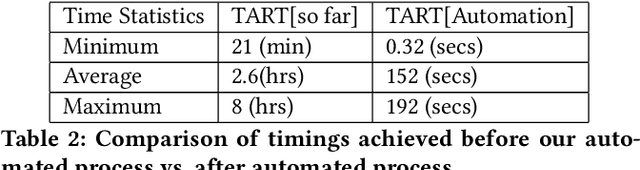
Abstract:e-Yantra Robotics Competition (eYRC) is a unique Robotics Competition hosted by IIT Bombay that is actually an Embedded Systems and Robotics MOOC. Registrations have been growing exponentially in each year from 4500 in 2012 to over 34000 in 2019. In this 5-month long competition students learn complex skills under severe time pressure and have access to a discussion forum to post doubts about the learning material. Responding to questions in real-time is a challenge for project staff. Here, we illustrate the advantage of Deep Learning for real-time question answering in the eYRC discussion forum. We illustrate the advantage of Transformer based contextual embedding mechanisms such as Bidirectional Encoder Representation From Transformer (BERT) over word embedding mechanisms such as Word2Vec. We propose a weighted similarity metric as a measure of matching and find it more reliable than Content-Content or Title-Title similarities alone. The automation of replying to questions has brought the turn around response time(TART) down from a minimum of 21 mins to a minimum of 0.3 secs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge