Atsushi Keyaki
LLM-jp: A Cross-organizational Project for the Research and Development of Fully Open Japanese LLMs
Jul 04, 2024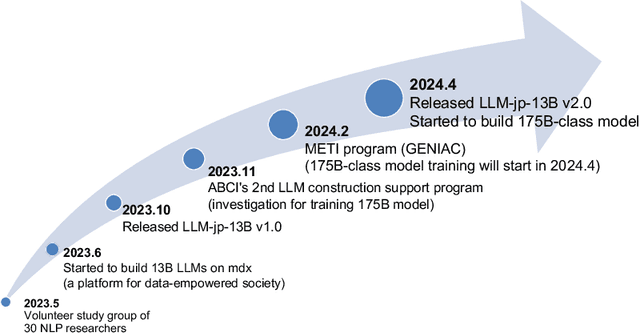
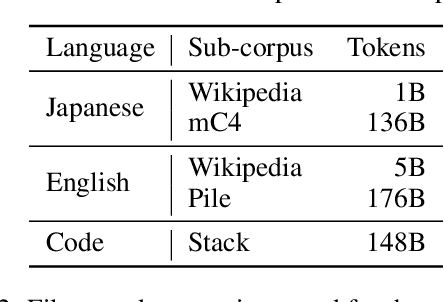

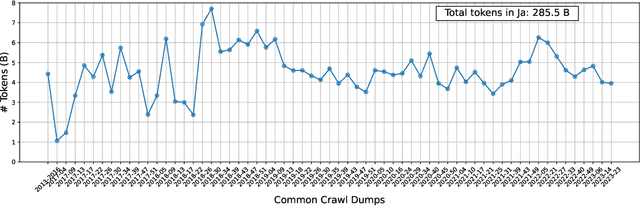
Abstract:This paper introduces LLM-jp, a cross-organizational project for the research and development of Japanese large language models (LLMs). LLM-jp aims to develop open-source and strong Japanese LLMs, and as of this writing, more than 1,500 participants from academia and industry are working together for this purpose. This paper presents the background of the establishment of LLM-jp, summaries of its activities, and technical reports on the LLMs developed by LLM-jp. For the latest activities, visit https://llm-jp.nii.ac.jp/en/.
Coarse-Tuning for Ad-hoc Document Retrieval Using Pre-trained Language Models
Mar 27, 2024Abstract:Fine-tuning in information retrieval systems using pre-trained language models (PLM-based IR) requires learning query representations and query-document relations, in addition to downstream task-specific learning. This study introduces coarse-tuning as an intermediate learning stage that bridges pre-training and fine-tuning. By learning query representations and query-document relations in coarse-tuning, we aim to reduce the load of fine-tuning and improve the learning effect of downstream IR tasks. We propose Query-Document Pair Prediction (QDPP) for coarse-tuning, which predicts the appropriateness of query-document pairs. Evaluation experiments show that the proposed method significantly improves MRR and/or nDCG@5 in four ad-hoc document retrieval datasets. Furthermore, the results of the query prediction task suggested that coarse-tuning facilitated learning of query representation and query-document relations.
Joint Optimization of Tokenization and Downstream Model
May 26, 2021



Abstract:Since traditional tokenizers are isolated from a downstream task and model, they cannot output an appropriate tokenization depending on the task and model, although recent studies imply that the appropriate tokenization improves the performance. In this paper, we propose a novel method to find an appropriate tokenization to a given downstream model by jointly optimizing a tokenizer and the model. The proposed method has no restriction except for using loss values computed by the downstream model to train the tokenizer, and thus, we can apply the proposed method to any NLP task. Moreover, the proposed method can be used to explore the appropriate tokenization for an already trained model as post-processing. Therefore, the proposed method is applicable to various situations. We evaluated whether our method contributes to improving performance on text classification in three languages and machine translation in eight language pairs. Experimental results show that our proposed method improves the performance by determining appropriate tokenizations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge