Atakan Dag
A Simulation Benchmark for Vision-based Autonomous Navigation
Apr 01, 2022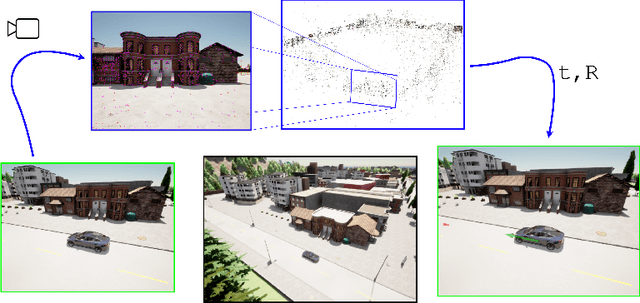
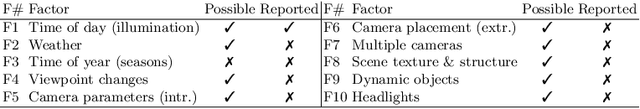
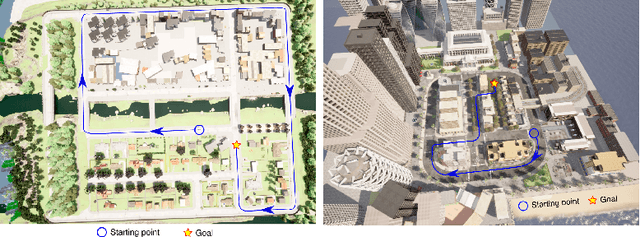
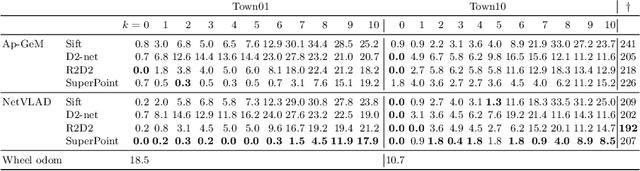
Abstract:This work introduces a simulator benchmark for vision-based autonomous navigation. The simulator offers control over real world variables such as the environment, time of day, weather and traffic. The benchmark includes a modular integration of different components of a full autonomous visual navigation stack. In the experimental part of the paper, state-of-the-art visual localization methods are evaluated as a part of the stack in realistic navigation tasks. To the authors' best knowledge, the proposed benchmark is the first to study modern visual localization methods as part of a full autonomous visual navigation stack.
Monolithic vs. hybrid controller for multi-objective Sim-to-Real learning
Aug 17, 2021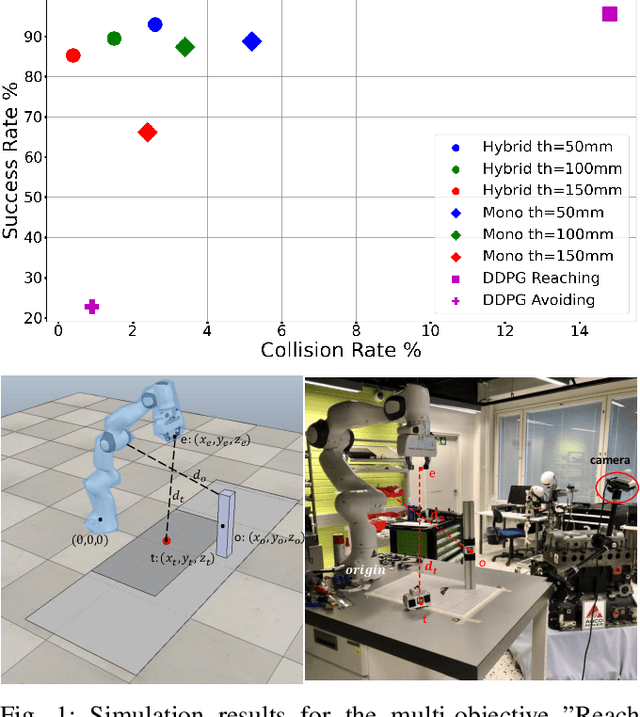
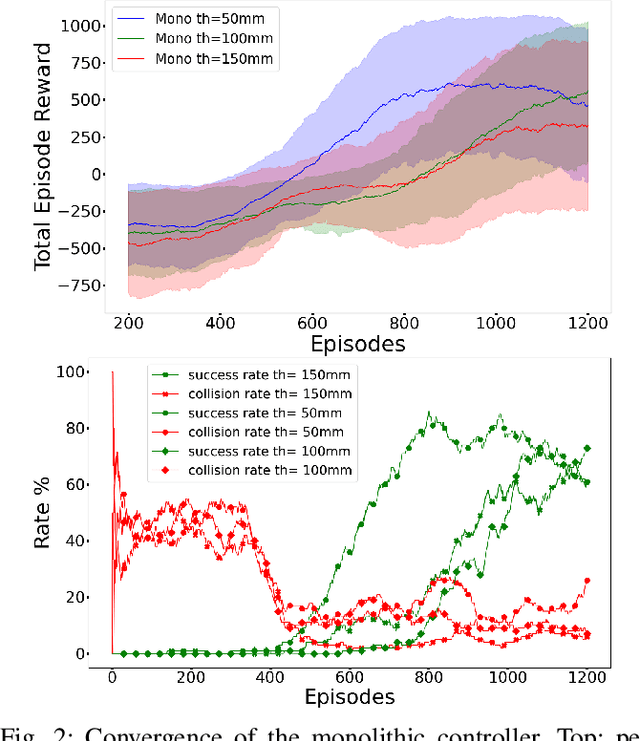
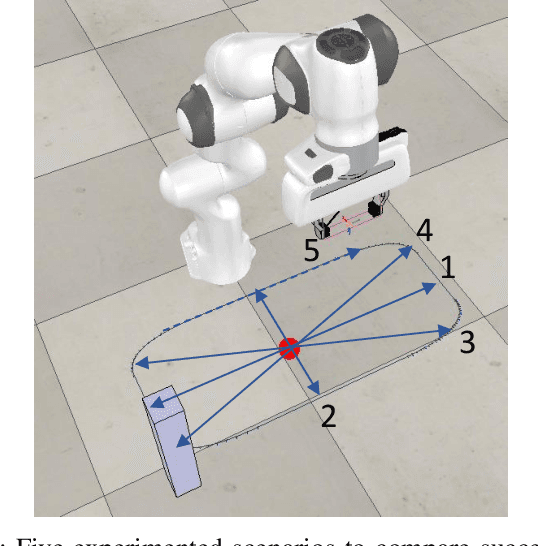

Abstract:Simulation to real (Sim-to-Real) is an attractive approach to construct controllers for robotic tasks that are easier to simulate than to analytically solve. Working Sim-to-Real solutions have been demonstrated for tasks with a clear single objective such as "reach the target". Real world applications, however, often consist of multiple simultaneous objectives such as "reach the target" but "avoid obstacles". A straightforward solution in the context of reinforcement learning (RL) is to combine multiple objectives into a multi-term reward function and train a single monolithic controller. Recently, a hybrid solution based on pre-trained single objective controllers and a switching rule between them was proposed. In this work, we compare these two approaches in the multi-objective setting of a robot manipulator to reach a target while avoiding an obstacle. Our findings show that the training of a hybrid controller is easier and obtains a better success-failure trade-off than a monolithic controller. The controllers trained in simulator were verified by a real set-up.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge